|
Rudolf Slánský
Rudolf Slánský (31 July 1901 – 3 December 1952) was a leading Czech Communist politician. Holding the post of the party's General Secretary after World War II, he was one of the leading creators and organizers of Communist rule in Czechoslovakia. After the split between Josip Broz Tito and Joseph Stalin, the latter instigated a wave of "purges" of the respective Communist Party leaderships, to prevent more splits between the Soviet Union and its Central European "satellite" countries. In Czechoslovakia, Slánský was one of 14 leaders arrested in 1951, tortured into confessing their "crimes", and put on show trial ''en masse'' in November 1952, charged with high treason. After eight days, 11 of the 14 were convicted and sentenced to death. Slánský was executed five days later. Early life Born at Nezvěstice, now in Plzeň-City District. Slánský's family was Jewish and conservative. He attended secondary school in Plzeň at the Commercial Academy. After the end of Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nezvěstice
Nezvěstice is a municipality and village in Plzeň-City District in the Plzeň Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 1,500 inhabitants. Nezvěstice lies approximately south-east of Plzeň and south-west of Prague Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P .... Administrative division Nezvěstice consists of two municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Nezvěstice (1,137) *Olešná (281) Demographics References External links * Villages in Plzeň-City District {{Plzeň-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Jews
The history of the Jews in the Czech lands, historically the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, including the modern Czech Republic (i.e. Bohemia, Moravia, and the southeast or Czech Silesia), goes back at least 1100 years. There is evidence that Jews have lived in Moravia and Bohemia since as early as the 10th century. Jewish communities flourished here specifically in the 13th, 16th, 17th centuries, and again in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Local Jews were mostly murdered in the Holocaust, or exiled at various points. As of 2021, there were only about 3000 Jews officially registered in the Czech Republic, albeit the actual number is probably as much as ten times higher. Jewish Prague Jews are believed to have settled in Prague as early as the 10th century. The 16th century was a "golden age" for Jewry in Prague. the city was called the "Mother of Israel" Samuel Usque, The Foundation for the Advancement of Sephardic Studies and Culture, p. 1 or "Jerusalem upon Vltava" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slánský Trial
The Slánský trial (officially English: "Trial of the Leadership of the Anti-State Conspiracy Centre Headed by Rudolf Slánský") was a 1952 antisemiticBlumenthal, Helaine. (2009). Communism on Trial: The Slansky Affair and Anti-Semitism in Post-WWII Europe. UC Berkeley: Berkeley Program in Soviet and Post-Soviet Studies.Read online show trial against fourteen members of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia (KSČ), including many high-ranking officials. Several charges, including high treason, were announced against the group on the grounds of allegedly conspiring against the Czechoslovak Republic. General Secretary of the KSČ Rudolf Slánský was the alleged leader of the conspirators. All fourteen defendants were found guilty of crimes that they did not commit. Eleven of them were sentenced to death and executed; the remaining three received life sentences. Background After World War II, Czechoslovakia initially enjoyed limited democracy. This changed with the Februa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignác Bilík
Ignác, also sometimes spelled Ignac in English, is the Czech, Slovak and Hungarian version of the name Ignatius. Ignac is also a surname, among the most common surnames in the Međimurje County of Croatia. Notable people with this name include: * Ignác Alpár (1855–1928), Hungarian architect * Jozef Ignác Bajza (1755–1836), Slovak writer, satirist and Catholic priest * Ignác Batthyány (1741–1798), Hungarian Roman Catholic Bishop of Transylvania * Jan Josef Ignác Brentner (1689–1742), Czech composer of baroque era * Ignác Frank (1788–1850), Hungarian jurist and private law scholar *Ignác Goldziher Ignác (Yitzhaq Yehuda) Goldziher (22 June 1850 – 13 November 1921), often credited as Ignaz Goldziher, was a Hungary, Hungarian scholar of Islam. Alongside Joseph Schacht and G.H.A. Juynboll, he is considered one of the pioneers of modern aca ... (1850–1921), Hungarian orientalist * Ignác Gyulay (1763–1831), Hungarian military officer * Ignác Irhás (born 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
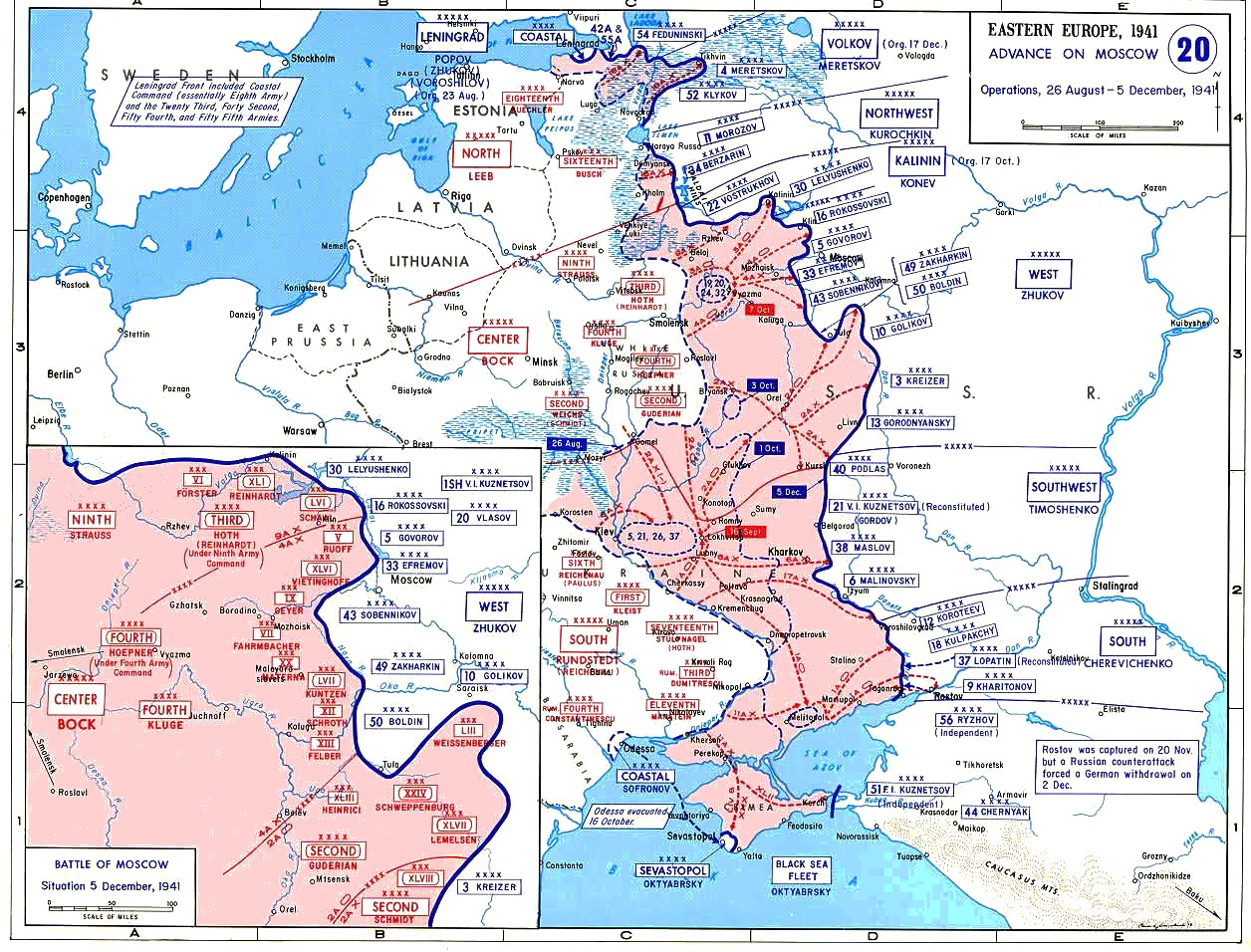
Battle Of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II, between October 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated Hitler's attack on Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Soviet Union. Moscow was one of the primary military and political objectives for Axis forces in their invasion of the Soviet Union. The German Strategic Offensive, named Operation Typhoon, called for two pincer offensives, one to the north of Moscow against the Kalinin Front by the 3rd and 4th Panzer Armies, simultaneously severing the Moscow–Leningrad railway, and another to the south of Moscow Oblast against the Western Front south of Tula, by the 2nd Panzer Army, while the 4th Army advanced directly towards Moscow from the west. Initially, the Soviet forces conducted a strategic defence of Moscow Oblast by constructing three defensive belts, deploying newly r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Moscow
Radio Moscow (), also known as Radio Moscow World Service, was the official international broadcasting station of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics until 1993, when it was reorganized into Voice of Russia, which was subsequently reorganized and renamed into Radio Sputnik in 2014. At its peak, Radio Moscow broadcast in over 70 languages using transmitters in the Soviet Union, Eastern Europe, and Cuba. Radio Moscow's interval signal was " Wide Is My Motherland" (). '' Moscow Nights'' was the station's signature tune since its relaunch as the Radio Moscow World Service in 1978. History Early years Radio Moscow's first foreign language broadcast was in German on 29 October 1929; English and French services soon followed. Previously, Radio Moscow broadcast in 1922 with a transmitter station RV-1 in the Moscow region, and a second broadcasting centre came on air at Leningrad in 1925. By 1939, Radio Moscow was broadcasting (on mediumwave and shortwave) in English, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 19.1 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in Moscow metropolitan area, its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's List of largest cities, largest cities, being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow became the capital of the Grand Principality of Moscow, which led the unification of the Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and ) is a German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the border districts of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia since the Middle Ages. The word "Sudetenland" did not come into being until the early part of the 20th century and did not come to prominence until almost two decades into the century, after World War I, when Austria-Hungary disintegrated and the Sudeten Germans found themselves living in the new country of Czechoslovakia. The ''Sudeten crisis'' of 1938 was provoked by the Pan-Germanist demands of Nazi Germany that the Sudetenland be annexed to Germany, which happened after the later Munich Agreement. Part of the borderland was invaded and annexed by Poland. Afterwards, the formerly unrecognized Sudetenland became an administrative division of Germany. When Czechoslovakia was reconstituted after World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich Conference
The Munich Agreement was reached in Munich on 30 September 1938, by Nazi Germany, the United Kingdom, the French Third Republic, French Republic, and the Kingdom of Italy. The agreement provided for the Occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–1945), German annexation of part of Czechoslovakia called the Sudetenland, where 3 million people, mainly Sudeten Germans, ethnic Germans, lived. The pact is known in some areas as the Munich Betrayal (; ), because of a previous 1924 alliance agreement and a 1925 military pact between France and the Czechoslovak Republic. Germany had started a Sudetendeutsches Freikorps#Undeclared German–Czechoslovak War, low-intensity undeclared war on Czechoslovakia on 17 September 1938. In reaction, Britain and France on 20 September formally requested Czechoslovakia cede the Sudetenland territory to Germany. This was followed by Polish and Hungarian territorial demands brought on 21 and 22 September, respectively. Meanwhile, German forces conquered part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klement Gottwald
Klement Gottwald (; 23 November 1896 – 14 March 1953) was a Czech communist politician, who was the leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia from 1929 until his death in 1953 – titled as general secretary until 1945 and as chairman from 1945 to 1953. He was the first leader of Communist Czechoslovakia from 1948 to 1953. Following the collapse of democratic Czechoslovakia after the Munich Agreement, the right-wing leadership of the Czechoslovak Second Republic banned the Communist Party, forcing Gottwald to emigrate to the Soviet Union in November 1938. In 1943, Gottwald agreed with representatives of the Czechoslovak-government-in-exile located in London, along with President Edvard Beneš, to unify domestic and foreign anti-fascist resistance and form the National Front. He was the 14th prime minister of Czechoslovakia from July 1946 until June 1948, the first Communist to hold the post. In June 1948, he was elected as Czechoslovakia's first Communist president, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |