|
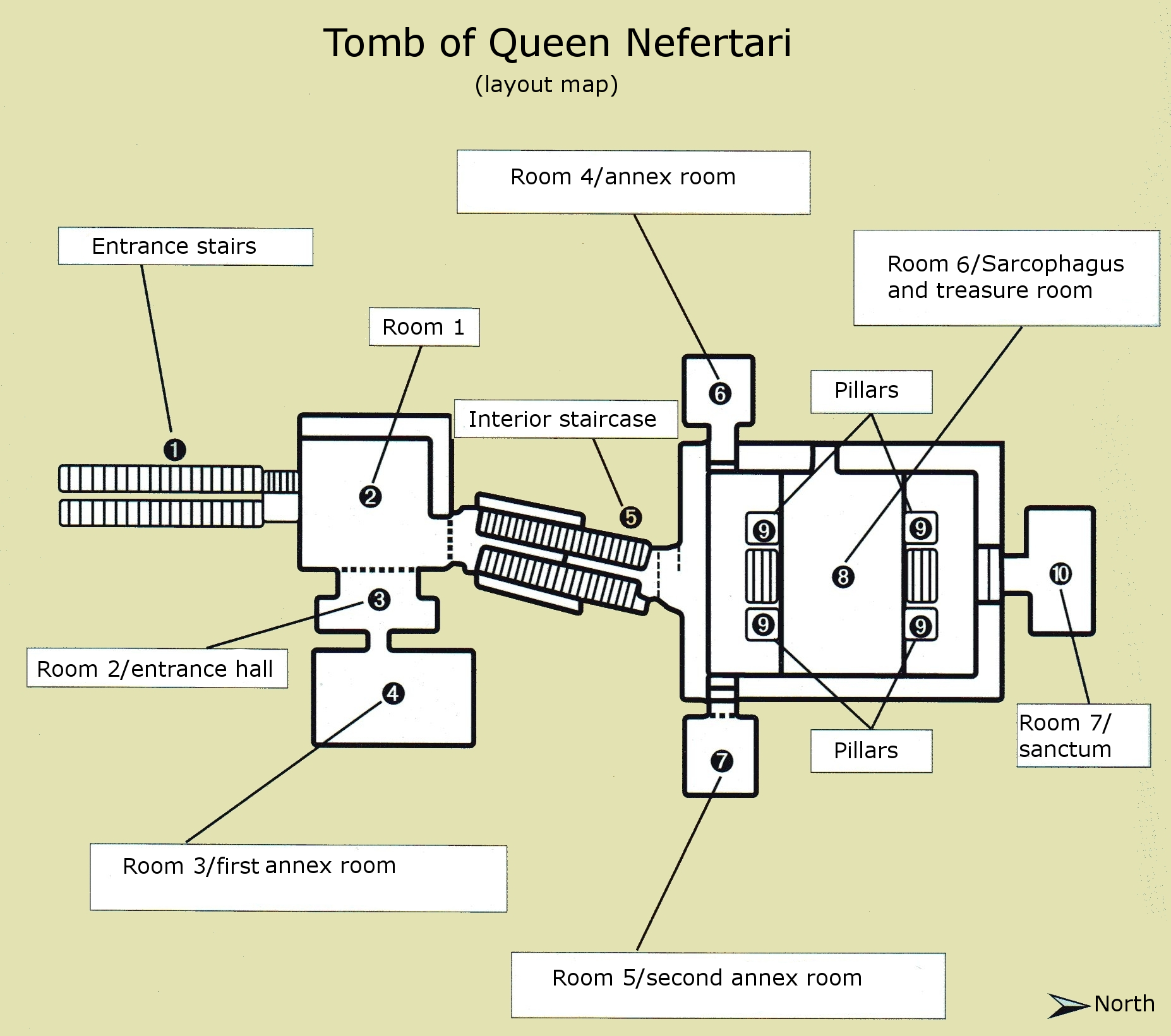
QV66
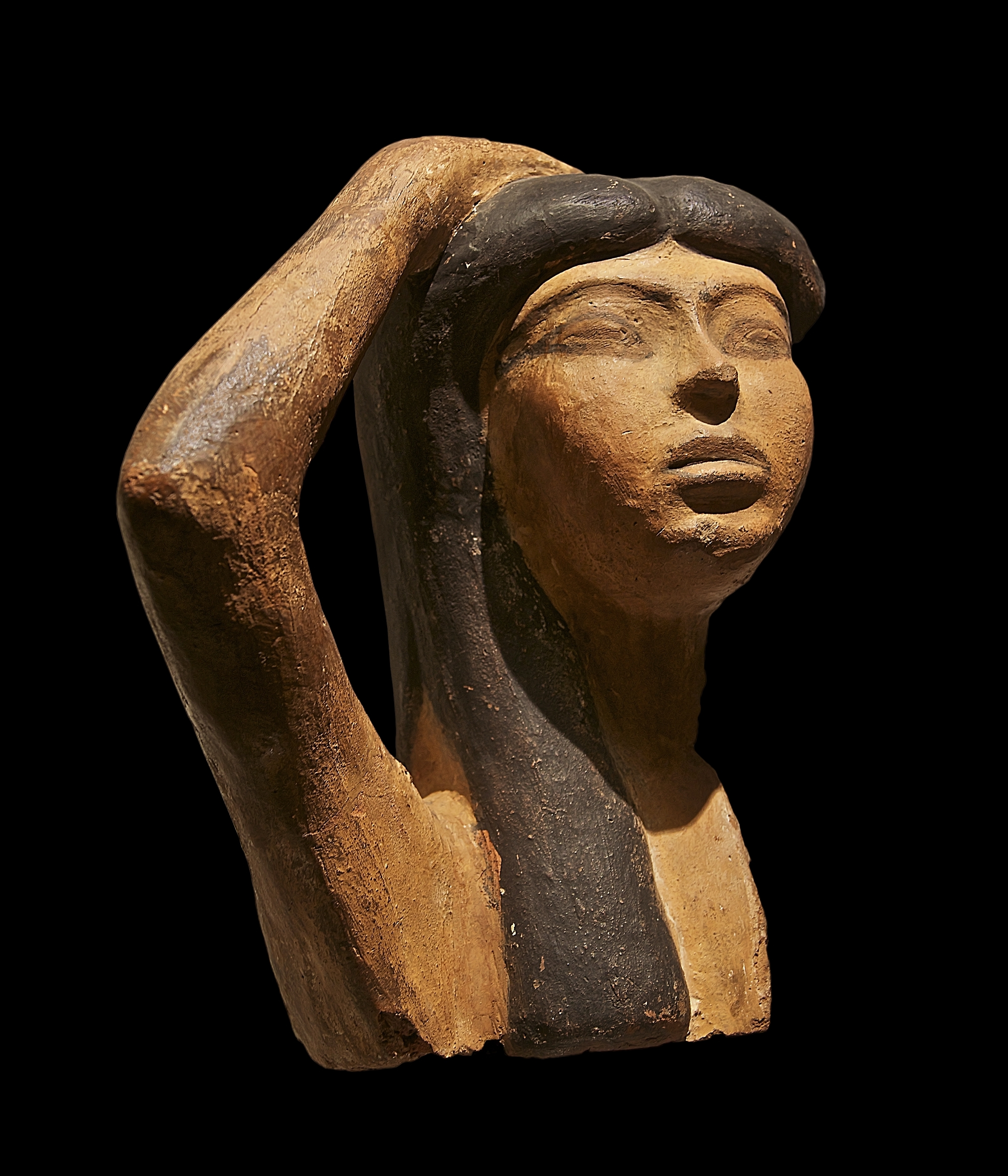
QV66 is the tomb of Nefertari, the Great Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses II, in Egypt's Valley of the Queens. It was discovered by Ernesto Schiaparelli (the director of the Museo Egizio, Egyptian Museum in Turin) in 1904. Nefertari, which means "beautiful companion", was Ramesses II's favorite wife; he went out of his way to make this obvious, referring to her as "the one for whom the sun shines" in his writings, built the Temple of Hathor at Abu Simbel to idolize her as a deity, and commissioned portraiture wall paintings. In the Valley of the Queens, Nefertari's tomb once held the mummified body and representative symbolisms of her, consistent with most Egyptian tombs of the period. Now, everything had been looted except for two thirds of the 5,200 square feet of wall paintings. For what still remains, these wall paintings characterized Nefertari's character. Her face received particular attention to emphasize her beauty, especially the shape of her eyes, the blush of her cheeks, and her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nefertari
Nefertari, also known as Nefertari Meritmut, was an Egyptian queen and the first of the Great Royal Wife, Great Royal Wives (or principal wives) of Ramesses II, Ramesses the Great. She is one of the best known Egyptian queens, among such women as Cleopatra VII, Cleopatra, Nefertiti, and Hatshepsut, and one of the most prominent not known or thought to have queen regnant, reigned in her own right. She was highly educated and able to both read and write hieroglyphs, a very rare skill at the time. She used these skills in her diplomatic work, corresponding with other prominent royals of the time. Her lavishly decorated tomb, QV66, is one of the largest and most spectacular in the Valley of the Queens. Ramesses also constructed a temple for her at Abu Simbel next to his colossal monument there. Translation of name There are different interpretations of the meaning of the name Nefertari. Nefertari means 'beautiful companion' and Meritmut means 'Beloved of the goddess Mut'. Some sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Nefertari (52785472724)
QV66 is the tomb of Nefertari, the Great Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses II, in Egypt's Valley of the Queens. It was discovered by Ernesto Schiaparelli (the director of the Egyptian Museum in Turin) in 1904. Nefertari, which means "beautiful companion", was Ramesses II's favorite wife; he went out of his way to make this obvious, referring to her as "the one for whom the sun shines" in his writings, built the Temple of Hathor at Abu Simbel to idolize her as a deity, and commissioned portraiture wall paintings. In the Valley of the Queens, Nefertari's tomb once held the mummified body and representative symbolisms of her, consistent with most Egyptian tombs of the period. Now, everything had been looted except for two thirds of the 5,200 square feet of wall paintings. For what still remains, these wall paintings characterized Nefertari's character. Her face received particular attention to emphasize her beauty, especially the shape of her eyes, the blush of her cheeks, and her eyebrows. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khepri
Khepri (Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''ḫprj,'' also transliterated Khepera, Kheper, Khepra, Chepri) is a scarab-faced Egyptian pantheon, god in ancient Egyptian religion who represents the rising or morning sun. By extension, he can also represent creation and the renewal of life.van Ryneveld, Maria M. ''The Presence and Significance of Khepri in Egyptian Religion and Art'', University of Pretoria (South Africa), Ann Arbor, 1992''. . Etymology The name "Khepri" appeared in the Pyramid Texts, Pyramid texts and usually included the scarab hieroglyph as a determinative or ideogram as a potential means to make any allusions to the god clear. Khepri is also mentioned in the Amduat, as the god is intrinsically linked to cycle of the sun and Ra's nightly journey through the Duat, the Egyptian underworld. Khepri (''ḫprj'') is derived from the Egyptian language verb ''ḫpr,'' meaning to "develop" or "create".Wilkinson, Richard H. (2003). ''The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isis
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her slain brother and husband, the divine king Osiris, and produces and protects his heir, Horus. She was believed to help the dead enter the afterlife as she had helped Osiris, and she was considered the divine mother of the pharaoh, who was likened to Horus. Her maternal aid was invoked in healing spells to benefit ordinary people. Originally, she played a limited role in royal rituals and temple rites, although she was more prominent in funerary practices and magical texts. She was usually portrayed in art as a human woman wearing a throne-like hieroglyph on her head. During the New Kingdom (), as she took on traits that originally belonged to Hathor, the preeminent goddess of earlier times, Isis was portrayed wearing Hathor's headdress: a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses II
Ramesses II (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses) (; , , ; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty, he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom, which itself was the most powerful period of ancient Egypt. He is also widely considered one of ancient Egypt's most successful warrior pharaohs, conducting no fewer than 15 military campaigns, all resulting in victories, excluding the Battle of Kadesh, generally considered a stalemate. In Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek sources, he is called Ozymandias, derived from the first part of his Egyptian-language regnal name: . Ramesses was also referred to as the "Great Ancestor" by successor pharaohs and the Egyptian people. For the early part of his reign, he focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathor
Hathor (, , , Meroitic language, Meroitic: ') was a major ancient Egyptian deities, goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god Ra, both of whom were connected with kingship, and thus she was the mother goddess, symbolic mother of their earthly representatives, the pharaohs. She was one of several goddesses who acted as the Eye of Ra, Ra's feminine counterpart, and in this form, she had a vengeful Aspect (religion), aspect that protected him from his enemies. Her beneficent side represented music, dance, joy, love, sexuality, and maternal care, and she acted as the consort of several male deities and the mother of their sons. These two aspects of the goddess exemplified the women in ancient Egypt, Egyptian conception of femininity. Hathor crossed boundaries between worlds, helping deceased ancient Egyptian conception of the soul, souls in the transition to the ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernesto Schiaparelli
Ernesto Schiaparelli (; 12 July 1856 – 14 February 1928) was an Italian Egyptologist. Biography Schiaparelli was born on 12 July 1856, in Biella. He found Queen Nefertari's tomb in Deir el-Medina in the Valley of the Queens (1904) and excavated the TT8 tomb of the royal architect Kha (1906), found intact and displayed ''in toto'' in Turin. He was appointed director of the Egyptian Museum in Florence, where he professionally reorganized the collection in new quarters in 1880, then at the peak of his career was made director of the Museo Egizio di Torino, which became with him and his many seasons of excavating, the second biggest Egyptian museum in the world. He was the author of famous scholarly works and a Senator of the Kingdom of Italy. At the same time, he was deeply involved, from his first stay with Franciscan missionaries at Luxor in 1884, with relieving the poverty he saw among the missionaries of Upper Egypt, for whom he founded the Association to Succour Italia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Hathor
Hathor (, , , Meroitic language, Meroitic: ') was a major ancient Egyptian deities, goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god Ra, both of whom were connected with kingship, and thus she was the mother goddess, symbolic mother of their earthly representatives, the pharaohs. She was one of several goddesses who acted as the Eye of Ra, Ra's feminine counterpart, and in this form, she had a vengeful Aspect (religion), aspect that protected him from his enemies. Her beneficent side represented music, dance, joy, love, sexuality, and maternal care, and she acted as the consort of several male deities and the mother of their sons. These two aspects of the goddess exemplified the women in ancient Egypt, Egyptian conception of femininity. Hathor crossed boundaries between worlds, helping deceased ancient Egyptian conception of the soul, souls in the transition to the ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serket
Serket /ˈsɜːrˌkɛt/ (Ancient Egyptian: ''srqt'') is the goddess of protection against the venomous stings and bites of scorpions in Egyptian mythology. She was primarily worshiped in Lower Egypt during the Predynastic Period (c. 6000 – c. 3150 BCE). Serket is often depicted as a woman whose head is surmounted by a scorpion with its tail is ready to sting, an ankh in one hand, and a ''was-''sceptre in her other. Her name, also rendered as Serqet, Selkis, or Selket, is a shortened version of 'Serket hetyt' which means "she who causes the throat to breathe." Old Kingdom Name and Roles She is associated with healing, magic, and protection. Another interpretation of her name is, 'she who gives breath.' As many of the venomous creatures of Egypt could prove fatal, Serket was considered a protector of the dead, particularly being associated with venoms and fluids that cause stiffening. It has been suggested that Serket's identification with a scorpion may be a misinterpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neith
Neith (, a borrowing of the Demotic (Egyptian), Demotic form , also spelled Nit, Net, or Neit) was an ancient Egyptian deity, possibly of Ancient Libya, Libyan origin. She was connected with warfare, as indicated by her emblem of two crossed bows, and with motherhood, as shown by texts that call her the mother of particular deities, such as the sun god Ra and the crocodile god Sobek. As a mother goddess, she was sometimes said to be the Ancient Egyptian creation myths, creator of the world. She also had a presence in Ancient Egyptian funerary practices, funerary religion, and this aspect of her character grew over time: she became one of the four goddesses who protected the coffin and Canopic jar, internal organs of the deceased. Neith is one of the earliest Egyptian deities to appear in the archaeological record; the earliest signs of her worship date to the Naqada II period ( 3600–3350 BC). Her main cult center was the city of Sais in Lower Egypt, near the western edge of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nekhbet
Nekhbet (; also spelt Nekhebet) is an early predynastic local goddess in Egyptian mythology, who was the patron of the city of Nekheb (her name meaning ''of Nekheb''). Ultimately, she became the patron of Upper Egypt and one of the two patron deities (alongside Wadjet) for all of Ancient Egypt when it was unified.Wilkinson, Richard H. (2003). ''The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt''. Thames & Hudson. pp. 213–214. Mythology One of Egypt's earliest temples was the shrine of Nekhbet at Nekheb (also referred to as El Kab). It was the companion city to Nekhen, the religious and political capital of Upper Egypt, at the end of the Predynastic period (c. 3200–3100 BC) and probably, also during the Early Dynastic Period (c. 3100–2686 BC). The original settlement on the Nekhen site dates from Naqada I or the late Badarian cultures. At its height, from about 3400 BC, Nekhen had at least 5,000 and possibly as many as 10,000 inhabitants. Nekhbet was the tutelary de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma'at
Maat or Maʽat (Egyptian: ''mꜣꜥt'' /ˈmuʀʕat/, Coptic: ⲙⲉⲓ) comprised the ancient Egyptian concepts of truth, balance, order, harmony, law, morality, and justice. Maat was also the goddess who personified these concepts, and regulated the stars, seasons, and the actions of mortals and the deities who had brought order from chaos at the moment of creation. Her ideological opposite was Isfet (Egyptian '' jzft''), meaning injustice, chaos, violence or to do evil. Pronunciation Cuneiform texts indicate that the word ''m3ˤt'' was pronounced /múʔʕa/ during the New Kingdom of Egypt, having lost the feminine ending ''t''. Vowel assimilation of ''u'' to ''e'' later produced the Coptic word "truth, justice". History The earliest surviving records indicating that Maat is the norm for nature and society, in this world and the next, were recorded during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, the earliest substantial surviving examples being found in the Pyramid Texts of Unas ( and 23 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |