|
Pangwali
Pangwali ( Takri: ) is a Western Pahari language of Himachal Pradesh, India. It is spoken in the Pangi Tehsil of Chamba district, and is threatened to go extinct. Pangwali is natively written in the Takri script, but Devanagari is used as well. Classification The linguist George Abraham Grierson recorded Pangwali as a dialect of Chambeali in his Linguistic Survey of India. It is now regarded as a language in its own right as a part of the Chamealic group of Western Pahari, affiliated with Chambeali, Bilaspuri, Bhadarwahi, among others. Pangwali has about 64% inherent intelligibility with Mandeali, 52% with Kangri, 44% with Chambeali, and 50% with Bhadarwahi. Its lexical similarity is 55% with Hindi, 77% with Kullu Pahari, and 45% with Bhadarwahi. Phonology Pangwali exhibits a fossilized system of vowel harmony as other languages of the area (such as Kashmiri) do. The original conditioning vowels that caused harmony have often been lost, so the system is no long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangi, Himachal Pradesh
Pangi is a tehsil of Chamba, Himachal Pradesh, India. The Pangi Valley is a beautiful and poorly developed tribal area, as well as one of the most remote areas in Himachal Pradesh state. The Pangi Valley is divided into the Saichu, Hudan Bhatori, Anch Chaloli and Sural Bhatori valleys, which are inhabited at elevations of to above sea level. The Valley is bordered by Padder, Jammu and Kashmir in North, Lahaul and Spiti in West and Chamba in Southeast. The Sach Pass at the elevation of 4,414m is the only route connecting Pangi with District headquarter Chamba. History People are said to have arrived in the valley thousands of years ago. There are only folk tales and stories indicating human presence in the valley. It is said that the King of Chamba exiled criminals to the other side of the Sach Pass, where they eventually established civilization. It is also said that during Mughal attacks, Rajput warriors sent their families into the Himalayan high valleys to protect them, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Indo-Aryan Languages
The Northern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Pahāṛi languages, are a proposed group of Indo-Aryan languages spoken in the lower ranges of the Himalayas, from Nepal in the east, through the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Punjab(not to be confused with the various other languages with that name) was coined by G. A. Grierson. Classification The Pahari languages fall into three groups. Eastern Pahari *Nepali is spoken by an estimated 11,100,000 people in Nepal, 265,000 people in Bhutan, and 2,500,000 people in India. It is an official language in Nepal and India. * Jumli is spoken by an estimated 40,000 people in the Karnali zone of Nepal. * Doteli spoken by an estimated 1 million people in far west Nepal. It is considered by many to be a dialect of Nepali, according to some scholars (e.g., Rahul Sankrityayan), a dialect of Kumaoni, but the Nepalese Language Commission considers it a separate language. Central Pahari * Kumaoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
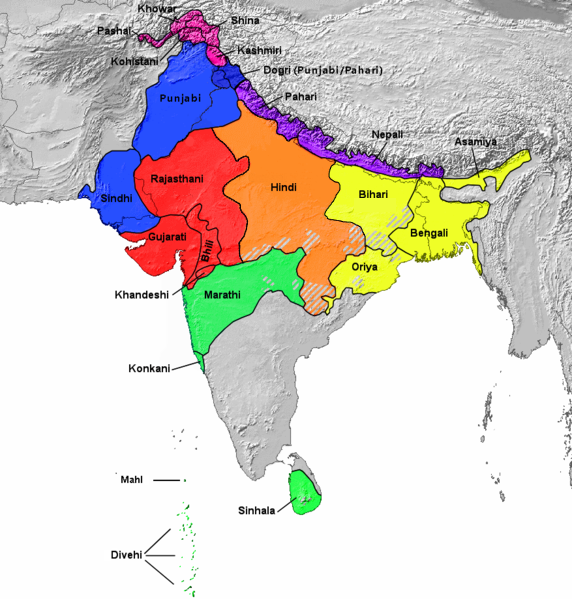
Western Pahari
The Western Pahari languages are a group of Northern Indo-Aryan languages that are spoken in the state of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir and parts of Uttarakhand and Punjab Languages The following lists the languages classified as belonging to Western Pahari, with the provisional grouping used in Glottolog 4.1: : Jaunsari :Nuclear Himachali: :: Hinduri :: Pahari Kinnauri :: Kullu Pahari ::Mahasu Pahari :: Sirmauri : Mandeali :Kangric-Chamealic-Bhattiyali: ::Chamealic: :::Bhadarwahi ::: Churahi ::: Bhattiyali ::: Bilaspuri ::: Chambeali ::: Gaddi :::Pangwali ::Kangri-Dogri: :::Dogri ::: Kangri These languages are a dialect chain, and neighbouring varieties may be mutually intelligible. Some Western Pahari languages have occasionally been regarded as dialects of either Dogri, Hindustani or Punjabi. Some Western Pahari languages, notably Dogri and Kangri, are tonal, like their close relative Punjabi but unlike most other Indic languages. Dogri has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Maldives. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of First language, first-speakers are Hindustani language, Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Pahari Language
The Western Pahari languages are a group of Northern Indo-Aryan languages that are spoken in the state of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir and parts of Uttarakhand and Punjab Languages The following lists the languages classified as belonging to Western Pahari, with the provisional grouping used in Glottolog 4.1: : Jaunsari :Nuclear Himachali: :: Hinduri :: Pahari Kinnauri :: Kullu Pahari ::Mahasu Pahari :: Sirmauri :Mandeali :Kangric-Chamealic-Bhattiyali: ::Chamealic: :::Bhadarwahi ::: Churahi ::: Bhattiyali :::Bilaspuri :::Chambeali ::: Gaddi :::Pangwali ::Kangri-Dogri: :::Dogri :::Kangri These languages are a dialect chain, and neighbouring varieties may be mutually intelligible. Some Western Pahari languages have occasionally been regarded as dialects of either Dogri, Hindustani or Punjabi. Some Western Pahari languages, notably Dogri and Kangri, are tonal, like their close relative Punjabi but unlike most other Indic languages. Dogri has been an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamba District
Chamba is the northwestern district of Himachal Pradesh, in India, with its headquarters in Chamba town. The towns of Dalhousie, Khajjhiar and Churah Valley are popular hill stations and vacation spots for the people from the plains of northern India. Economy In 2006 the Ministry of Panchayati Raj named Chamba one of the country's 250 most backward districts (out of a total of 640). It is one of the two districts in Himachal Pradesh currently receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF). Demographics According to the 2011 census Chamba district has a population of 519,080, roughly equal to the nation of Cape Verde. This gives it a ranking of 544th in India (out of a total of 640). The district has a population density of . Its population growth rate over the decade 2001–2011 was 12.58%. Chamba has a sex ratio of 989 females for every 1000 males, and a literacy rate of 73.19%. The Gaddis, the largest Scheduled Tribe in Himachal Pradesh, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks and extensive river systems. Himachal Pradesh is the northernmost state of India and shares borders with the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the north, and the states of Punjab to the west, Haryana to the southwest, Uttarakhand to the southeast and a very narrow border with Uttar Pradesh to the south. The state also shares an international border to the east with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. Himachal Pradesh is also known as , meaning 'Land of Gods' and which means 'Land of the Brave'. The predominantly mountainous region comprising the present-day Himachal Pradesh has been inhabited since pre-historic times, having witnessed multiple waves of human migrations from other areas. Through its history, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangwala
The Pangwala is a tribal community predominant in the Pangi valley of Chamba district in Himachal Pradesh. Social status , the Pangwalas were classified as a Scheduled Tribe under the Indian government's reservation program of positive discrimination. Language The native language of Pangwalas is Pangwali Pangwali ( Takri: ) is a Western Pahari language of Himachal Pradesh, India. It is spoken in the Pangi Tehsil of Chamba district, and is threatened to go extinct. Pangwali is natively written in the Takri script, but Devanagari is used as well. .... References Scheduled Tribes of Himachal Pradesh {{india-ethno-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatal Consonant
Palatals are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate (the middle part of the roof of the mouth). Consonants with the tip of the tongue curled back against the palate are called retroflex. Characteristics The most common type of palatal consonant is the extremely common approximant , which ranks as among the ten most common sounds in the world's languages. The nasal is also common, occurring in around 35 percent of the world's languages, in most of which its equivalent obstruent is not the stop , but the affricate . Only a few languages in northern Eurasia, the Americas and central Africa contrast palatal stops with postalveolar affricates—as in Hungarian, Czech, Latvian, Macedonian, Slovak, Turkish and Albanian. Consonants with other primary articulations may be palatalized, that is, accompanied by the raising of the tongue surface towards the hard palate. For example, English (spelled ''sh'') has such a palatal compone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Consonant
Alveolar (; UK also ) consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli (the sockets) of the upper teeth. Alveolar consonants may be articulated with the tip of the tongue (the apical consonants), as in English, or with the flat of the tongue just above the tip (the "blade" of the tongue; called laminal consonants), as in French and Spanish. The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) does not have separate symbols for the alveolar consonants. Rather, the same symbol is used for all coronal places of articulation that are not palatalized like English palato-alveolar ''sh'', or retroflex. To disambiguate, the ''bridge'' (, ''etc.'') may be used for a dental consonant, or the under-bar (, ''etc.'') may be used for the postalveolars. differs from dental in that the former is a sibilant and the latter is not. differs from postalveolar in being unpalatalized. The bare letters , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postalveolar Consonant
Postalveolar or post-alveolar consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the ''back'' of the alveolar ridge. Articulation is farther back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but not as far back as the hard palate, the place of articulation for palatal consonants. Examples of postalveolar consonants are the English palato-alveolar consonants , as in the words "ship", "'chill", "vision", and "jump", respectively. There are many types of postalveolar sounds—especially among the sibilants. The three primary types are '' palato-alveolar'' (such as , weakly palatalized), ''alveolo-palatal'' (such as , strongly palatalized), and '' retroflex'' (such as , unpalatalized). The palato-alveolar and alveolo-palatal subtypes are commonly counted as "palatals" in phonology since they rarely contrast with true palatal consonants. Postalveolar sibilants For most sounds involving the tongue, the place of articulation can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroflex Consonant
A retroflex ( /ˈɹɛtʃɹoːflɛks/), apico-domal ( /əpɪkoːˈdɔmɪnəl/), or cacuminal () consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants—especially in Indology. The Latin-derived word ''retroflex'' means "bent back"; some retroflex consonants are pronounced with the tongue fully curled back so that articulation involves the underside of the tongue tip ( subapical). These sounds are sometimes described as "true" retroflex consonants. However, retroflexes are commonly taken to include other consonants having a similar place of articulation without such extreme curling of the tongue; these may be articulated with the tongue tip ( apical) or the tongue blade (laminal). Types Retroflex consonants, like other coronal consonants, come in several varieties, depending on the shape of the tongue. The tongue may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |