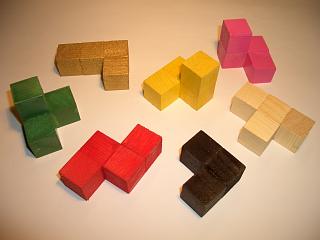|
Puzzle
A puzzle is a game, problem, or toy that tests a person's ingenuity or knowledge. In a puzzle, the solver is expected to put pieces together ( or take them apart) in a logical way, in order to find the solution of the puzzle. There are different genres of puzzles, such as crossword puzzles, word-search puzzles, number puzzles, relational puzzles, and logic puzzles. The academic study of puzzles is called enigmatology. Puzzles are often created to be a form of entertainment but they can also arise from serious mathematical or logical problems. In such cases, their solution may be a significant contribution to mathematical research. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' dates the word ''puzzle'' (as a verb) to the 16th century. Its earliest use documented in the ''OED'' was in a book titled ''The Voyage of Robert Dudley...to the West Indies, 1594–95, narrated by Capt. Wyatt, by himself, and by Abram Kendall, master'' (published circa 1595). The word later came to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosswords
A crossword (or crossword puzzle) is a word game consisting of a grid of black and white squares, into which solvers enter words or phrases ("entries") crossing each other horizontally ("across") and vertically ("down") according to a set of clues. Each white square is typically filled with one letter, while the black squares are used to separate entries. The first white square in each entry is typically numbered to correspond to its clue. Crosswords commonly appear in newspapers and magazines. The earliest crosswords that resemble their modern form were popularized by the ''New York World'' in the 1910s. Many variants of crosswords are popular around the world, including cryptic crosswords and many language-specific variants. Crossword construction in modern times usually involves the use of software. Constructors choose a theme (except for themeless puzzles), place the theme answers in a grid which is usually symmetric, fill in the rest of the grid, and then write clues. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Puzzle
A mechanical puzzle is a puzzle presented as a set of mechanically interlinked pieces in which the solution is to manipulate the whole object or parts of it. While puzzles of this type have been in use by humanity as early as the 3rd century BC, one of the most well-known mechanical puzzles of modern day is the Rubik's Cube, invented by the Hungarian architect Ernő Rubik in 1974. The puzzles are typically designed for a single player, where the goal is for the player to discover the principle of the object, rather than accidentally coming up with the right solution through trial and error. With this in mind, they are often used as an intelligence test or in problem solving training. History The oldest known mechanical puzzle comes from Greece and appeared in the 3rd century BC. The game consists of a square divided into 14 parts, and the aim was to create different shapes from these pieces. This is not easy to do. (see Ostomachion loculus Archimedius) In Iran "puzzle-locks" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enigmatology
A puzzle is a game, problem, or toy that tests a person's ingenuity or knowledge. In a puzzle, the solver is expected to put pieces together ( or take them apart) in a logical way, in order to find the solution of the puzzle. There are different genres of puzzles, such as crossword puzzles, word-search puzzles, number puzzles, relational puzzles, and logic puzzles. The academic study of puzzles is called enigmatology. Puzzles are often created to be a form of entertainment but they can also arise from serious mathematical or logical problems. In such cases, their solution may be a significant contribution to mathematical research. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' dates the word ''puzzle'' (as a verb) to the 16th century. Its earliest use documented in the ''OED'' was in a book titled ''The Voyage of Robert Dudley...to the West Indies, 1594–95, narrated by Capt. Wyatt, by himself, and by Abram Kendall, master'' (published circa 1595). The word later came to be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disentanglement Puzzle
Disentanglement puzzles (also called entanglement puzzles, tanglement puzzles, tavern puzzles or topological puzzles) are a type or group of mechanical puzzle that involves disentangling one piece or set of pieces from another piece or set of pieces. Several subtypes are included under this category, the names of which are sometimes used synonymously for the group: wire puzzles; nail puzzles; ring-and-string puzzles; ''et al''. Although the initial object is disentanglement, the reverse problem of reassembling the puzzle can be as hard as—or even harder than—disentanglement. There are several different kinds of disentanglement puzzles, though a single puzzle may incorporate several of these features. Wire-and-string puzzles image:Staircasepuzzle-disentanglement-2branchesandmerge-buildyourown.jpg, upright=1.2, A complex ''Baguenaudier'' puzzle. The goal is to free the string. Wire-and-string puzzles usually consist of: * one piece of string, ribbon or similar, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Utilities Problem
The three utilities problem, also known as water, gas and electricity, is a mathematical puzzle that asks for non-crossing connections to be drawn between three houses and three utility companies on a Plane (geometry), plane. When posing it in the early 20th century, Henry Dudeney wrote that it was already an old problem. It is an List of impossible puzzles, impossible puzzle: it is not possible to connect all nine lines without any of them crossing. Versions of the problem on nonplanar surfaces such as a torus or Möbius strip, or that allow connections to pass through other houses or utilities, can be solved. This puzzle can be formalized as a problem in topological graph theory by asking whether the complete bipartite graph K_, with vertices representing the houses and utilities and edges representing their connections, has a graph embedding in the plane. The impossibility of the puzzle corresponds to the fact that K_ is not a planar graph. Multiple proofs of this impossibili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Puzzle
Mathematical puzzles make up an integral part of recreational mathematics. They have specific rules, but they do not usually involve competition between two or more players. Instead, to solve such a puzzle, the solver must find a solution that satisfies the given conditions. Mathematical puzzles require mathematics to solve them. Logic puzzles are a common type of mathematical puzzle. Conway's Game of Life and fractals, as two examples, may also be considered mathematical puzzles even though the solver interacts with them only at the beginning by providing a set of initial conditions. After these conditions are set, the rules of the puzzle determine all subsequent changes and moves. Many of the puzzles are well known because they were discussed by Martin Gardner in his "Mathematical Games" column in Scientific American. Mathematical puzzles are sometimes used to motivate students in teaching elementary school Mathematical problem, math problem solving techniques.Kulkarni, DEnjoying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soma Cube
The Soma cube is a mechanical puzzle#Assembly, solid dissection puzzle invented by Danish polymath Piet Hein (scientist), Piet Hein in 1933 during a lecture on quantum mechanics conducted by Werner Heisenberg. Seven different Polycube, pieces made out of unit cubes must be assembled into a 3×3×3 cube. The pieces can also be used to make a variety of other Three-dimensional space, 3D shapes. The pieces of the Soma cube consist of all possible combinations of at most four unit cubes, joined at their faces, such that at least one inside corner is formed. There are no combinations of one or two cubes that satisfy this condition, but one combination of three cubes and six combinations of four cubes that do. Thus, 3 + (6 × 4) is 27, which is exactly the number of cells in a 3×3×3 cube. Of these seven combinations, two are mirror images of each other (see Chirality (mathematics), Chirality). The Soma cube was popularized by Martin Gardner in the September 1958 Mathematical Games ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
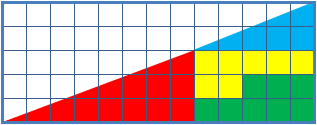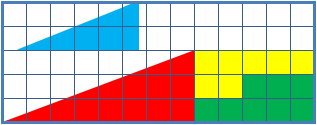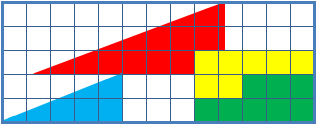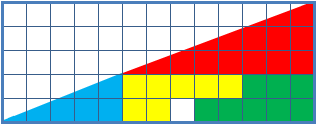
Missing Square Puzzle
The missing square puzzle is an optical illusion used in mathematics classes to help students reason about geometrical figures; or rather to teach them not to reason using figures, but to use only textual descriptions and the axioms of geometry. It depicts two arrangements made of similar shapes in slightly different configurations. Each apparently forms a 13×5 right-angled triangle, but one has a 1×1 hole in it. Solution The key to the puzzle is the fact that neither of the 13×5 "triangles" is truly a triangle, nor would either truly be 13x5 if it were, because what appears to be the hypotenuse is bent. In other words, the "hypotenuse" does not maintain a consistent slope, even though it may appear that way to the human eye. A true 13×5 triangle cannot be created from the given component parts. The four figures (the yellow, red, blue and green shapes) total 32 units of area. The apparent triangles formed from the figures are 13 units wide and 5 units tall, so it appears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Thinking Puzzle
Situation puzzles, often referred to as minute mysteries, lateral thinking puzzles or "yes/no" puzzles, are puzzles in which participants are to construct a story that the host has in mind, basing on a puzzling situation that is given at the start. Usually, situation puzzles are played in a group, with one person hosting the puzzle and the others asking questions which can only be answered with a "yes" or "no" answer. Depending upon the settings and level of difficulty, other answers, hints or simple explanations of why the answer is yes or no, may be considered acceptable. The puzzle is solved when one of the players is able to recite the narrative the host had in mind, in particular explaining whatever aspect of the initial scenario was puzzling. These puzzles are inexact and many puzzle statements have more than one possible fitting answer. The goal however is to find out the story as the host has it in mind, not just any plausible answer. Critical thinking and reading, logi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eight Queens Puzzle
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other; thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal. There are 92 solutions. The problem was first posed in the mid-19th century. In the modern era, it is often used as an example problem for various computer programming techniques. The eight queens puzzle is a special case of the more general ''n'' queens problem of placing ''n'' non-attacking queens on an ''n''×''n'' chessboard. Solutions exist for all natural numbers ''n'' with the exception of ''n'' = 2 and ''n'' = 3. Although the exact number of solutions is only known for ''n'' ≤ 27, the asymptotic growth rate of the number of solutions is approximately (0.143 ''n'')''n''. History Chess composer Max Bezzel published the eight queens puzzle in 1848. Franz Nauck published the first solutions in 1850. W. W. Rouse Ball (1960) "The Eight Queens Problem" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Problem
A chess problem, also called a chess composition, is a puzzle created by the composer using chess pieces on a chessboard, which presents the solver with a particular task. For instance, a position may be given with the instruction that White is to move first, and checkmate Black in two moves against any possible defence. A chess problem fundamentally differs from play in that the latter involves a struggle between Black and White, whereas the former involves a competition between the composer and the solver. Most positions which occur in a chess problem are unrealistic in the sense that they are very unlikely to occur in over-the-board play. There is a substantial amount of specialized jargon used in connection with chess problems. Definition The term chess problem is not sharply defined: there is no clear demarcation between chess compositions on the one hand and puzzle or tactical exercises on the other. In practice, however, the distinction is very clear. There are common c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
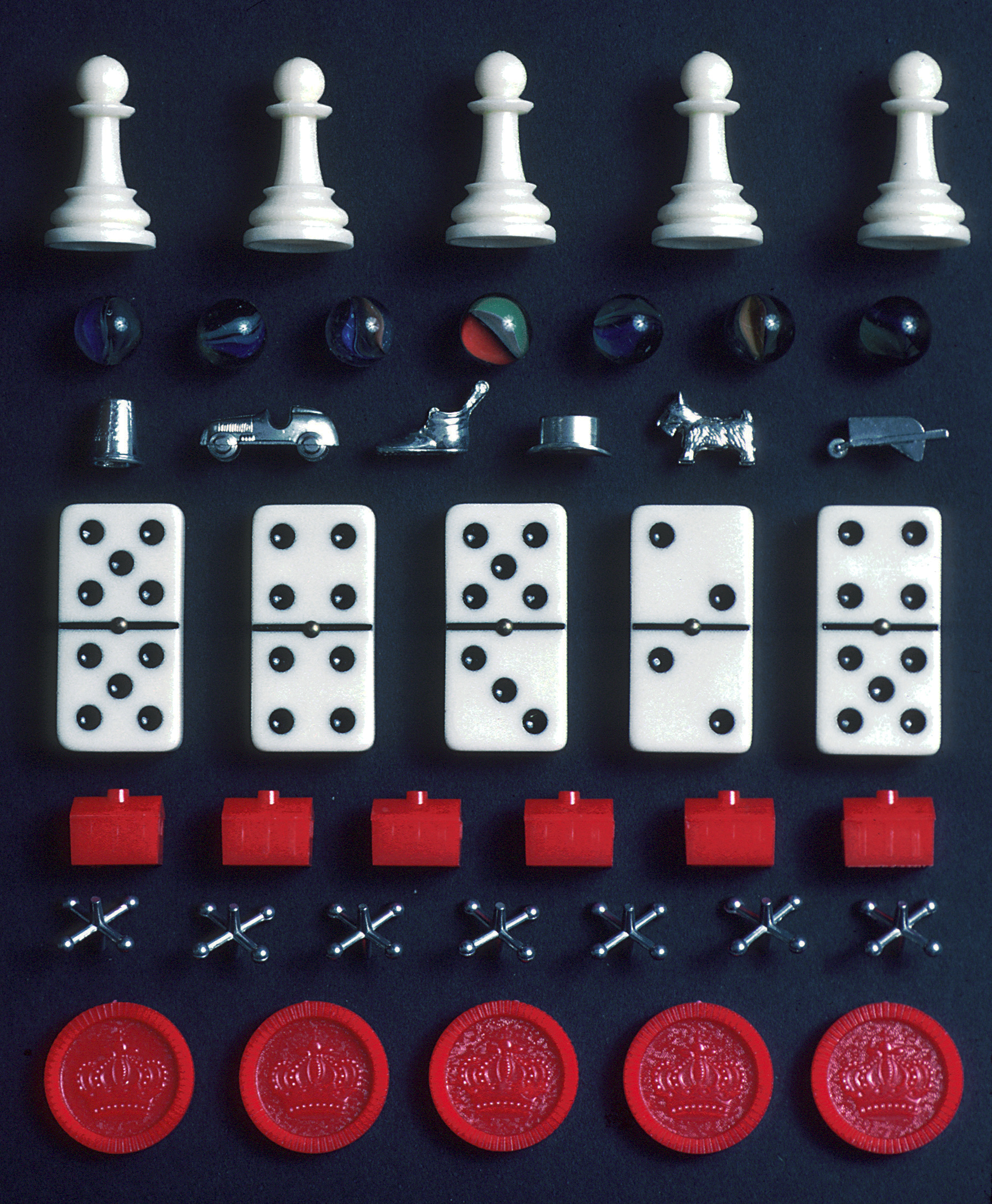
Game
A game is a structured type of play usually undertaken for entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator sports or video games) or art (such as games involving an artistic layout such as mahjong, solitaire, or some video games). Games have a wide range of occasions, reflecting both the generality of its concept and the variety of its play. Games are sometimes played purely for enjoyment, sometimes for achievement or reward as well. They can be played alone, in teams, or online; by amateurs or by professionals. The players may have an audience of non-players, such as when people are entertained by watching a chess championship. On the other hand, players in a game may constitute their own audience as they take their turn to play. Often, part of the entertainment for children playing a game is deciding who is part of their audience and who participates as a player. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |