|
Piperazine
Piperazine () is an organic compound with the formula . In term of its structure, it can be described as cyclohexane with the 1- and 4-CH2 groups replaced by NH. Piperazine exists as deliquescent solid with a saline taste. Piperazine is freely soluble in water and ethylene glycol, but poorly soluble in diethyl ether. Piperazine is commonly available industrially is as the hexahydrate, , which melts at 44 °C and boils at 125–130 °C.''The Merck index, 10th Ed.'' (1983), p. 1076, Rahway:Merck & Co. Substituted derivatives of piperazine are a broad class of chemical compounds. Many piperazines have useful pharmacological properties, prominent examples include viagra, ciprofloxacin, and ziprasidone. Origin and naming Piperazines were originally named because of their chemical similarity with piperidine, part of the structure of piperine in the black pepper plant (''Piper nigrum''). The -az- infix added to "piperazine" refers to the extra nitrogen atom, compared to piperidine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoethylpiperazine
Aminoethylpiperazine (AEP) is a derivative of piperazine. This ethyleneamine contains three nitrogen atoms; one primary, one secondary and one tertiary. It is a corrosive organic liquid and can cause second or third degree burns. Aminoethylpiperazine can also cause pulmonary edema as a result of inhalation. It is REACH and TSCA registered. Production Ethylene dichloride is reacted with ammonia as a main method of production. This process produces various ethylene amines which can then be purified by distillation. These include ethylenediamine, diethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine, tetraethylenepentamine, other higher homologues and aminoethyl piperazine. AEP is also manufactured by reacting ethylenediamine or ethanolamine/ammonia mixtures over a catalyst. Epoxy resin curing agent A key use of AEP is as an epoxy curing agent. When used as an epoxy resin curing agent, it is usually used in conjunction with other amines as an accelerator as it only has 3 amine hydrogens for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
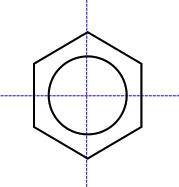
Pyrazine
Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2. It is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Pyrazine is less basic than pyridine, pyridazine and pyrimidine. It is a ''"deliquescent crystal or wax-like solid with a pungent, sweet, corn-like, nutty odour"''. Pyrazine and a variety of alkylpyrazines are flavor and aroma compounds found in baked and roasted goods. Tetramethylpyrazine (also known as ligustrazine) is reported to scavenge superoxide anions and decrease nitric oxide production in human granulocytes. Synthesis Many methods exist for the organic synthesis of pyrazine and its derivatives. Some of these are among the oldest synthesis reactions still in use. In the Staedel–Rugheimer pyrazine synthesis (1876), 2-chloroacetophenone is reacted with ammonia to the amino ketone, then condensed and then oxidized to a pyrazine. A variation is the Gutknecht pyrazine synthesis (1879) also based on this selfcondensation, but di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor described as objectionable, typical of amines. The name comes from the genus name '' Piper'', which is the Latin word for pepper. Although piperidine is a common organic compound, it is best known as a representative structure element within many pharmaceuticals and alkaloids, such as natural-occurring solenopsins. Production Piperidine was first reported in 1850 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson and again, independently, in 1852 by the French chemist Auguste Cahours, who named it. Both of them obtained piperidine by reacting piperine with nitric acid. Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of pyridine, usually over a molybdenum disulfide catalyst: : C5H5N + 3 H2 → C5H10NH Pyridine can also be reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziprasidone
Ziprasidone, sold under the brand name Geodon among others, is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It may be used by mouth and by injection into a muscle (IM). The intramuscular form may be used for acute agitation in people with schizophrenia. Common side effects include tremors, tics, dizziness, dry mouth, restlessness, nausea, and mild sedation. Although it can also cause weight gain, the risk is much lower than for other atypical antipsychotics. How it works is not entirely clear but is believed to involve effects on serotonin and dopamine in the brain. Ziprasidone was approved for medical use in the United States in 2001. The pills are made up of the hydrochloride salt, ziprasidone hydrochloride. The intramuscular form is the mesylate, ziprasidone mesylate trihydrate, and is provided as a lyophilized powder. In 2020, it was the 282nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin infections, typhoid fever, and urinary tract infections, among others. For some infections it is used in addition to other antibiotics. It can be taken by mouth, as eye drops, as ear drops, or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Severe side effects include tendon rupture, hallucinations, and nerve damage. In people with myasthenia gravis, there is worsening muscle weakness. Rates of side effects appear to be higher than some groups of antibiotics such as cephalosporins but lower than others such as clindamycin. Studies in other animals raise concerns regarding use in pregnancy. No problems were identified, however, in the children of a small number of women who took the medication. It appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viagra
Sildenafil, sold under the brand name Viagra among others, is a medication used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is also sometimes used off-label for the treatment of certain symptoms in secondary Raynaud's phenomenon. It is unclear if it is effective for treating sexual dysfunction in females. It can be taken orally (swallowed by mouth), intravenously (injection into a vein), or through the sublingual route (dissolved under the tongue). Onset when taken orally is typically within twenty minutes and lasts for about two hours. Common side effects include headaches, heartburn, and flushed skin. Caution is advised in those with cardiovascular disease. Rare but serious side effects include vision problems, hearing loss, and prolonged erection (priapism) that can lead to damage to the penis. Sildenafil should not be taken by people on nitric oxide donors such as nitroglycerin, as this may result in a serious drop in blood pressure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society and professional association in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 49,000 in the world. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing and Shanghai, People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethylenetriamine
Diethylenetriamine (abbreviated and also known as 2,2’-Iminodi(ethylamine)) is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2NH2)2. This colourless hygroscopic liquid is soluble in water and polar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons. Diethylenetriamine is structural analogue of diethylene glycol. Its chemical properties resemble those for ethylene diamine, and it has similar uses. It is a weak base and its aqueous solution is alkaline. DETA is a byproduct of the production of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride. Reactions and uses Diethylenetriamine is a common curing agent for epoxy resins in epoxy adhesives and other thermosets. It is N-alkylated upon reaction with epoxide groups forming crosslinks. In coordination chemistry, it serves as a tridentate ligand forming complexes such as Co(dien)(NO2)3. Like some related amines, it is used in oil industry for the extraction of acid gas. Like ethylenediamine, DETA can also be used to sensitize nitromethane, mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanolamine
Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is a naturally occurring organic chemical compound with the formula or . The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorless, viscous liquid with an odor reminiscent of ammonia. Ethanolamine is commonly called monoethanolamine or MEA in order to be distinguished from diethanolamine (DEA) and triethanolamine (TEOA). The ethanolamines comprise a group of amino alcohols. A class of antihistamines is identified as ethanolamines, which includes carbinoxamine, clemastine, dimenhydrinate, chlorphenoxamine, diphenhydramine and doxylamine. History Ethanolamines, or in particular, their salts, were discovered by Charles Adolphe Wurtz in 1860 by heating 2-chloroethanol with ammonia solution while studying derivatives of ethylene oxide he discovered a year earlier. He wasn't able to separate the salts or isolate any free bases. In 1897 Ludwig Knorr deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosymmetric
In crystallography, a centrosymmetric point group contains an inversion center as one of its symmetry elements. In such a point group, for every point (x, y, z) in the unit cell there is an indistinguishable point (-x, -y, -z). Such point groups are also said to have ''inversion'' symmetry. Point reflection is a similar term used in geometry. Crystals with an inversion center cannot display certain properties, such as the piezoelectric effect and the frequency doubling effect (second-harmonic generation). In addition, in such crystals, one-photon absorption (OPA) and two-photon absorption (TPA) processes are mutually exclusive, i.e., they do not occur simultaneously, and provide complementary information. The following space groups have inversion symmetry: the triclinic space group 2, the monoclinic 10-15, the orthorhombic 47-74, the tetragonal 83-88 and 123-142, the trigonal 147, 148 and 162-167, the hexagonal 175, 176 and 191-194, the cubic 200-206 and 221-230. Point g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |