|
Ocean Optics
Ocean optics is the study of how light interacts with water and the materials in water. Although research often focuses on the sea, the field broadly includes rivers, lakes, inland waters, coastal waters, and large ocean basins. How light acts in water is critical to how ecosystems function underwater. Knowledge of ocean optics is needed in Water remote sensing, aquatic remote sensing research in order to understand what information can be extracted from the Color of water, color of the water as it appears from satellite sensors in space. The color of the water as seen by satellites is known as ocean color. While ocean color is a key theme of ocean optics, optics is a broader term that also includes the development of underwater sensors using optical methods to study much more than just color, including ocean chemistry, particle size, imaging of microscopic plants and animals, and more. Key terminology Optically deep Where waters are “optically deep,” the bottom does not refle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PARTICLE OF DETRITUS PHOTOGRAPHED AT THE ATLANTIC MARINE FISHERIES LABORATORY AT SANDY HOOK, NEW JERSEY
In the Outline of physical science, physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small wikt:local, localized physical body, object which can be described by several physical property, physical or chemical property, chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass. They vary greatly in size or quantity, from subatomic particles like the electron, to microscopic scale, microscopic particles like atoms and molecules, to macroscopic scale, macroscopic particles like powder (substance), powders and other granular materials. Particles can also be used to create scientific models of even larger objects depending on their density, such as humans moving in a crowd or celestial bodies in motion (physics), motion. The term ''particle'' is rather general in meaning, and is refined as needed by various scientific fields. Anything that is composed of particles may be referred to as being particulate. However, the noun ''particulates, particulate'' is most frequently u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geophysics, geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. exploration geophysics, hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology). It also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or airborne-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on wave propagation, propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
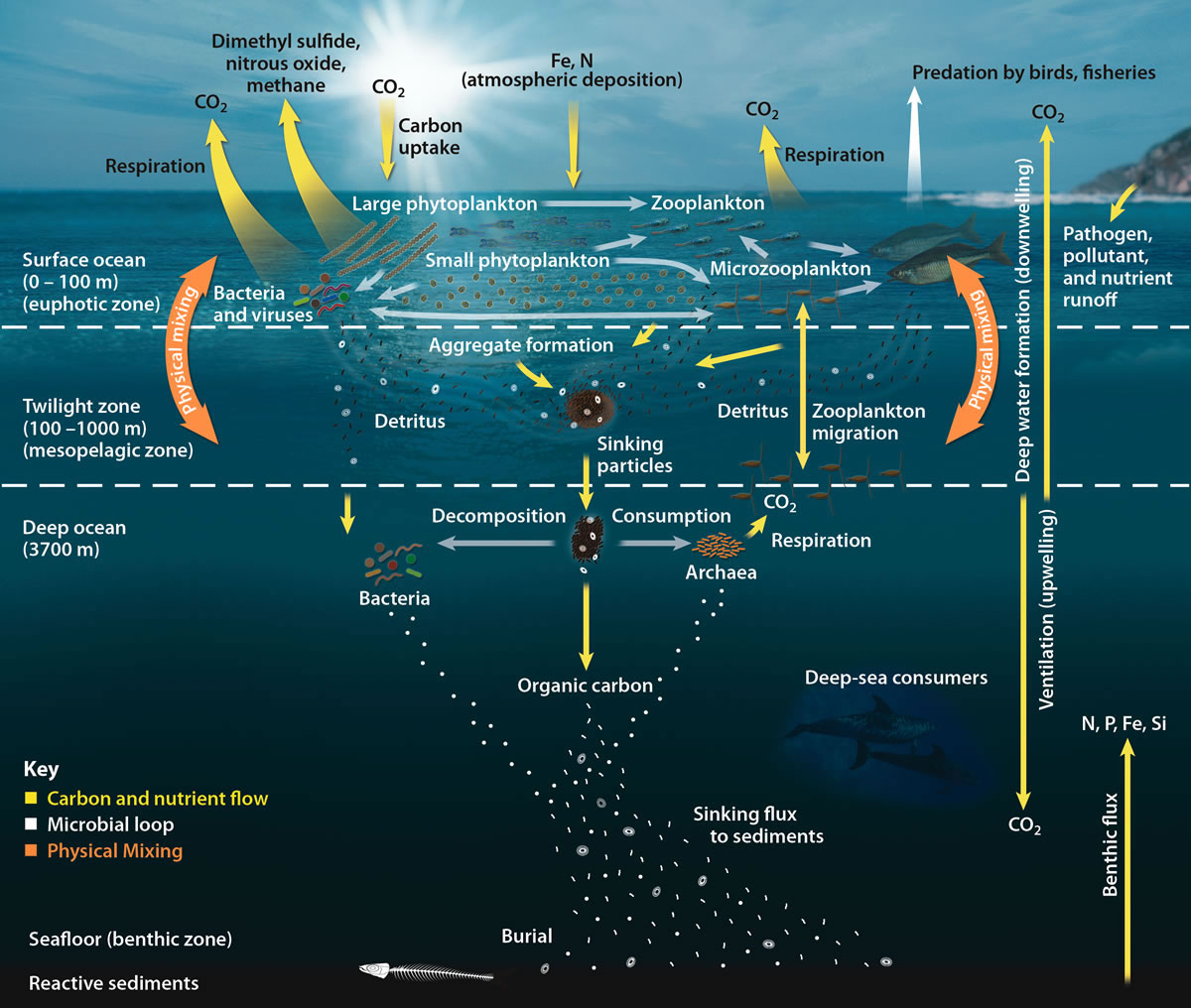
Biological Pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH Haug. 2006. The biological pump in the past. In: Treatise on Geochemistry; vol. 6, (ed.). Pergamon Press, pp. 491-528 In other words, it is a biologically mediated process which results in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calcul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Biogeochemical Cycles
Marine biogeochemical cycles are biogeochemical cycles that occur within Marine habitat, marine environments, that is, in the saline water, saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal Estuary, estuaries. These biogeochemical cycles are the pathways chemical substances and chemical element, elements move through within the marine environment. In addition, substances and elements can be imported into or exported from the marine environment. These imports and exports can occur as exchanges with the atmosphere above, the ocean floor below, or as runoff from the land. There are biogeochemistry, biogeochemical cycles for the elements calcium cycle, calcium, carbon cycle, carbon, hydrogen cycle, hydrogen, mercury cycle, mercury, nitrogen cycle, nitrogen, oxygen cycle, oxygen, phosphorus cycle, phosphorus, selenium cycle, selenium, and sulfur cycle, sulfur; molecular cycles for water cycle, water and silica cycle, silica; macroscopic cycles such as the rock cycle; as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups. Coral belongs to the class Anthozoa in the animal phylum Cnidaria, which includes sea anemones and jellyfish. Unlike sea anemones, corals secrete hard carbonate exoskeletons that support and protect the coral. Most reefs grow best in warm, shallow, clear, sunny and agitated water. Coral reefs first appeared 485 million years ago, at the dawn of the Early Ordovician, displacing the microbial and sponge reefs of the Cambrian. Sometimes called ''rainforests of the sea'', shallow coral reefs form some of Earth's most diverse ecosystems. They occupy less than 0.1% of the world's ocean area, about half the area of France, yet they provide a home for at least 25% of all marine species, including fish, mollusks, worms, crustaceans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seagrass Meadow
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems and long green, grass-like leaves. They produce seeds and pollen and have roots and rhizomes which anchor them in seafloor sand. Seagrasses form dense underwater meadows which are among the most productive ecosystems in the world. They provide habitats and food for a diversity of marine life comparable to that of coral reefs. This includes invertebrates like shrimp and crabs, cod and flatfish, marine mammals and birds. They provide refuges for endangered species such as seahorses, turtles, and dugongs. They function as nursery habitats for shrimps, scallops and many commercial fish species. Seagrass meadows provide coastal storm protection by the way their leaves absorb energy from waves as they hit the coast. They keep coastal waters health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton (cyanobacteria and microalgae), which are the plant-like component of the plankton community (the " phyto-" prefix comes from , although taxonomically ''not'' plants). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding), often generating biological energy and macromolecules through chlorophyllic carbon fixation using sunlightin other words, zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food, while phytoplankton can. As a result, zooplankton must acquire nutrients by feeding on other organisms such as phytoplankton, which are generally smaller t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as trees and other plants do on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are known as '' primary producers'' or autotrophs, and form the base of the food chain. In terrestrial ecoregions, these are mainly plants, while in aquatic ecoregions algae predominate in this role. Ecologists distinguish primary production as either ''net'' or ''gross'', the former accounting for losses to processes such as cellular respiration, the latter not. Overview Primary production is the production of chemical energy, in organic compounds by living organisms. The main source of such energy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement Error
Observational error (or measurement error) is the difference between a measured value of a quantity and its unknown true value.Dodge, Y. (2003) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', OUP. Such errors are inherent in the measurement process; for example lengths measured with a ruler calibrated in whole centimeters will have a measurement error of several millimeters. The error or uncertainty of a measurement can be estimated, and is specified with the measurement as, for example, 32.3 ± 0.5 cm. Scientific observations are marred by two distinct types of errors, systematic errors on the one hand, and random, on the other hand. The effects of random errors can be mitigated by the repeated measurements. Constant or systematic errors on the contrary must be carefully avoided, because they arise from one or more causes which constantly act in the same way, and have the effect of always altering the result of the experiment in the same direction. They therefore alter the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |