|
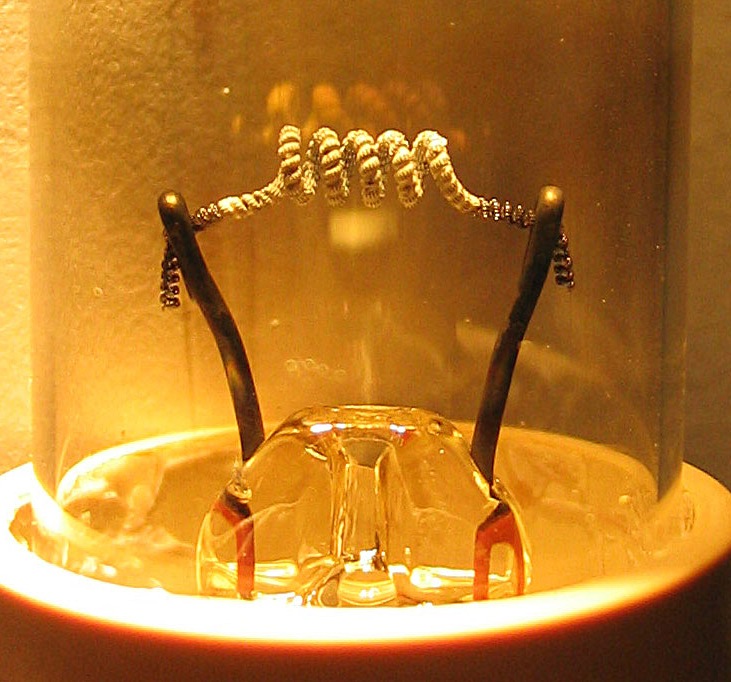
Nuvistor
The nuvistor is a type of vacuum tube announced by RCA in 1959. Nuvistors were made to compete with the then-new bipolar junction transistors, and were much smaller than conventional tubes of the day, almost approaching the compactness of early discrete transistor casings. Due to their small size, there was no space to include a vacuum fitting to evacuate the tube; instead, nuvistors were assembled and processed in a vacuum chamber with simple robotic devices. The tube is made entirely of metal with a ceramic base. Triodes and a few tetrodes were made; Nuvistor tetrodes were taller than their triode counterparts. Nuvistors are among the highest performing small signal receiving tubes. They feature excellent VHF and UHF performance plus low noise figures, and were widely used throughout the 1960s in television sets (beginning with RCA's "New Vista" line of color sets in 1961 with the CTC-11 chassis), radio and high-fidelity equipment primarily in RF sections, and oscilloscope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defection Of Viktor Belenko
On September 6, 1976, Lieutenant Viktor Belenko of the Soviet Air Defense Forces defected by flying his Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25P "Foxbat" aircraft from near Vladivostok in the Far East of the Soviet Union to Hakodate Airport in Hokkaido Prefecture of Japan. Belenko's defection caused tension between Japan and the Soviet Union, especially after Japanese and American specialists disassembled and examined the aircraft. The examination revealed to the US that while impressive in speed, the MiG-25 was not the superfighter that they had feared it to be. It was later returned to the Soviets while it was still disassembled with some parts missing. Belenko was granted political asylum in and later citizenship of the US, where he became a military consultant, public speaker, and businessman. Belenko later visited Moscow in 1995, after the end of the Soviet Union. Background During the Cold War, there were many defections by pilots and aircrews. In addition to pilots defecting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiG-25
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-25; NATO reporting name: Foxbat) is a supersonic interceptor and reconnaissance aircraft that is among the fastest military aircraft to enter service. Designed by the Soviet Union's Mikoyan-Gurevich bureau, it is an aircraft built primarily using stainless steel. It was to be the last plane designed by Mikhail Gurevich, before his retirement. The first prototype flew in 1964 and the aircraft entered service in 1970. It has an operational top speed of Mach 2.83. Although its thrust was sufficient to reach Mach 3.2+, its speed was limited to prevent engines from overheating at higher air speeds and possibly damaging them beyond repair."Intelligence: Big-Mouth Belenko" ''Time'', 11 Oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire
Overhead power cabling. The conductor consists of seven strands of steel (centre, high tensile strength), surrounded by four outer layers of aluminium (high conductivity). Sample diameter 40 mm A wire is a flexible strand of metal. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Wire gauges come in various standard sizes, as expressed in terms of a gauge number. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads, often in the form of wire rope. In electricity and telecommunications signals, a "wire" can refer to an electrical cable, which can contain a "solid core" of a single wire or separate strands in stranded or braided forms. Usually cylindrical in geometry, wire can also be made in square, hexagonal, flattened rectangular, or other cross-sections, either for decorative purposes, or for technical purposes such as high-efficiency voice coils in loudspeakers. Edge-wound coil springs, such as the Slinky toy, are made of special flattened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternate name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements barring carbon (which sublimes at normal pressure), melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is , comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons. From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in which positive charges move. Electrons have a negative electrical charge, so the movement of electrons is opposite to that of the conventional current flow. Consequently, the mnemonic ''cathode current departs'' also means that electrons flow ''into'' the device's cathode from the external circuit. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a + (plus) is the cathode. The electrode through which conventional current flows the other way, into the device, is termed an anode. Charge flow Conventional current flows from cathode to anode outside the cell or device (with electrons moving in the opposite direction), regardless of the cell or device type and operating mode. Cathode polarity with respect to the anode can be posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)