|
Non-convergent Discourse
A non-convergent discourse (NCD) is a discourse in which the participants do not converge in their language, which results in the use of different languages. Alternative names for this phenomenon are asymmetric and bilingual discourse. The term was introduced by the sociologist Reitze Jonkman. He distinguishes two motivations for people to engage in an NCD: *Insufficient active knowledge of the other participants' language, combined with a good passive knowledge. It usually takes longer for a person learning a foreign language to speak it fluently than to understand it when it is being spoken. This type of NCD is common in areas of the world where closely-related languages or dialects are spoken, but which are not individually widespread to be commonly taught to outsiders. Such examples include the North Germanic languages of Scandinavia; Dutch and Afrikaans; Romance languages such as Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, and regional languages of Spain and Italy; various Slavic language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discourse
Discourse is a generalization of the notion of a conversation to any form of communication. Discourse is a major topic in social theory, with work spanning fields such as sociology, anthropology, continental philosophy, and discourse analysis. Following work by Michel Foucault, these fields view discourse as a system of thought, knowledge, or communication that constructs our world experience. Since control of discourse amounts to control of how the world is perceived, social theory often studies discourse as a window into Power (social and political), power. Within theoretical linguistics, discourse is understood more narrowly as linguistic information exchange and was one of the major motivations for the framework of dynamic semantics. In these expressions, denotations are equated with their ability to update a discourse context. Social theory In the humanities and social sciences, discourse describes a formal way of thinking that can be expressed through language. Discourse i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociolinguistics
Sociolinguistics is the descriptive, scientific study of how language is shaped by, and used differently within, any given society. The field largely looks at how a language changes between distinct social groups, as well as how it varies under the influence of assorted cultural norms, expectations, and contexts. Sociolinguistics combines the older field of dialectology with the social sciences in order to identify regional dialects, sociolects, ethnolects, and other sub-varieties and styles within a language, as well as the distinctions and variations inside each of these. A major branch of linguistics since the second half of the 20th century, sociolinguistics is closely related to and can partly overlap with pragmatics, linguistic anthropology, and sociology of language, the latter focusing on the effect of language back on society. Sociolinguistics' historical interrelation with anthropology can be observed in studies of how language varieties differ between groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Situational Code-switching
Situational code-switching is the tendency in a speech community to use different languages or language varieties in different social situations, or to switch linguistic structures in order to change an established social setting. Some languages are viewed as more suited for a particular social group, setting, or topic more so than others. Social factors like class, religion, gender, and age influence the pattern of language that is used and switched between. Development There are three different types of code switching which include: situational, metaphorical, and unmarked discourse code- switching. Situational and metaphorical code-switching were first described by John J. Gumperz and Jan-Petter Bloom. In the paper, "Social meaning in linguistic structures,"Gumper and Bloom are the first to suggest the division between situational and metaphorical code-switching. Gumperz and Dell Hymes describe this difference between situational and metaphorical code-switching. :An import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between different but related language varieties in which speakers of the different varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. Mutual intelligibility is sometimes used to distinguish languages from dialects, although sociolinguistic factors are often also used. Intelligibility between varieties can be asymmetric; that is, speakers of one variety may be able to better understand another than vice versa. An example of this is the case between Afrikaans and Dutch. It is generally easier for Dutch speakers to understand Afrikaans than for Afrikaans speakers to understand Dutch. In a dialect continuum, neighbouring varieties are mutually intelligible, but differences mount with distance, so that more widely separated varieties may not be mutually intelligible. Intelligibility can be partial, as is the case with Azerbaijani and Turkish, or significant, as is the case with Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diglossia
In linguistics, diglossia ( , ) is where two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled "L" or "low" variety), a second, highly codified lect (labeled "H" or "high") is used in certain situations such as literature, formal education, or other specific settings, but not used normally for ordinary conversation. The H variety may have no native speakers within the community. In cases of three dialects, the term triglossia is used. When referring to two writing systems coexisting for a single language, the term digraphia is used. The high variety may be an older stage of the same language (as in medieval Europe, where Latin (H) remained in formal use even as colloquial speech (L) diverged), an unrelated language, or a distinct yet closely related present-day dialect (as in northern India and Pakistan, where Hindustani (L) is used alongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Giles
Howard Giles (born December 22, 1946) is a British-American social psychologist and a Distinguished Research Professor of Communication at the Department of Communication, University of California, Santa Barbara. He was the chair of the department from 1991 to 1998, and has been president of both the International Communication Association and the International Association for the Study of Language and Social Psychology. He is the founding co-editor of the ''Journal of Language and Social Psychology'' and the '' Journal of Asian Pacific Communication'', and was the editor of '' Human Communication Research'' from 1992 to 1995. He has received the Spearman Award and the President's Award from the British Psychological Society, and has also received the Mark L. Knapp Award from the National Communication Association. He is known for developing communication accommodation theory, and has diverse research interests in the areas of applied intergroup communication research and theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
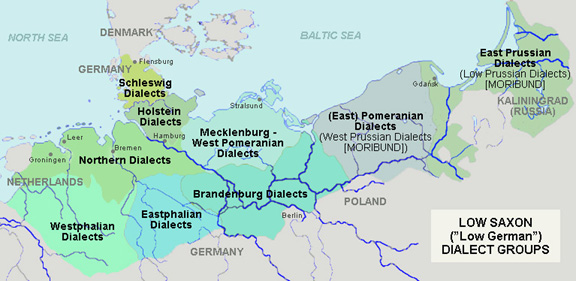
Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian languages, Frisian and English language, English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch language, Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath line, Benrath and Uerdingen line, Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German languages, High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard German, Standard High German, which is based on High German langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
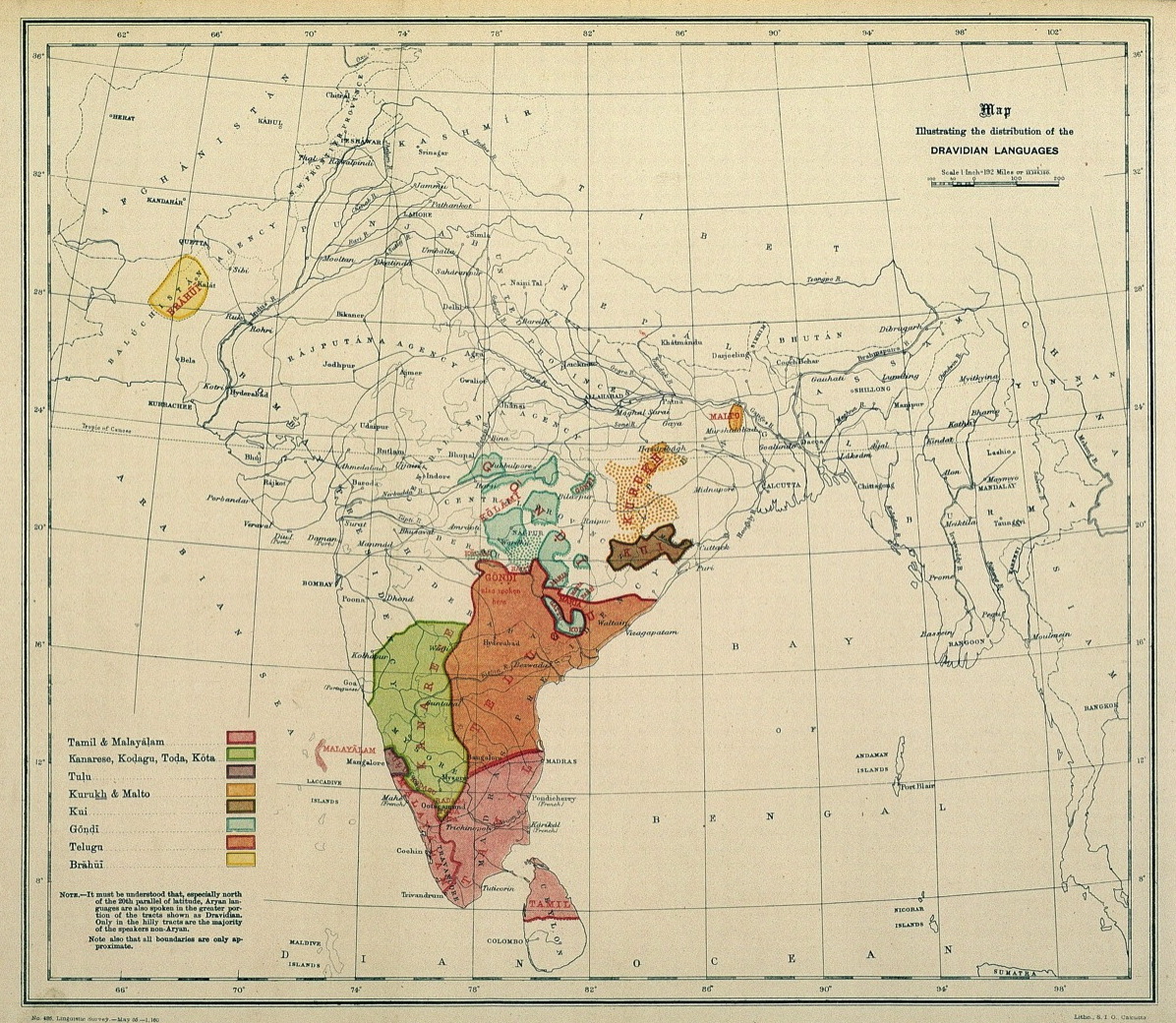
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Germanic Languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also referred to as the Nordic languages, a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish language, Danish, Faroese language, Faroese, Icelandic language, Icelandic, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and Swedish language, Swedish scholars and people. The term ''North Germanic languages'' is used in comparative linguistics, whereas the term Scandinavian languages appears in studies of the modern standard languages and the dialect continuum of Scandinavia. Danish, Norwegian and Swedish are close enough to form a strong mutual intelligibility where cross-border communication in native languages is very common, particularly between the latter two. Approximately 20 million people in the Nordic countries speak a Scandinavian language as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |