|
Montenegrin Cup (women)
The Montenegrin Cup for Women ( Montenegrin: ''Kup Crne Gore za žene'') is the national women's association football cup competition in Montenegro. It was founded in 2015, seven years after the formation of the Montenegrin Women's League. History After the establishment of Montenegrin Women's League in 2008, the Football Association of Montenegro organised the first edition of Montenegrin Women's Cup for the 2015-16 season. The inaugural season of the Montenegrin Women's Cup had seven participants, with the first round being the quarterfinals. The first winner of Montenegrin Cup was ŽFK Ekonomist. Finals The finals played so far are: Trophies by team See also * Montenegrin Women's League *Football Association of Montenegro *Football in Montenegro *Montenegrin Cup References External linksFootball Association of Montenegro {{Women's national association football cups Montenegro Cup Cup A cup is an open-top used to hold hot or cold liquids for pouring or drinkin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŽFK Ekonomist
ŽFK Ekonomist is a Women's association football, women's football club from Nikšić, Montenegro. It plays in the Montenegrin Women's League and is the league's inaugural champion. In 2012, the team became the first women's team from Montenegro to enter the UEFA Women's Champions League. Before the creation of the league, the team won the FSCG Trophy once. The team was founded in 2007. Titles * 4 Montenegrin Women's League : 2011–12, 2012–13, 2013–14, 2014–15 * 1 FSCG Trophy (Trofej FSCG) : 2011 Record in UEFA competitions Current squad * ''As of 6 May 2020. * ''Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.'' Former internationals * Montenegro women's national football team, Montenegro: Sladjana Bulatović, Jasna Djoković, Darija Đukić, Tatjana Djurković, Armisa Kuć, Jelena Sturanović, Ivona Turčinović, Andreja Vidić See also *Montenegrin Women's League *Football in Montenegro Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
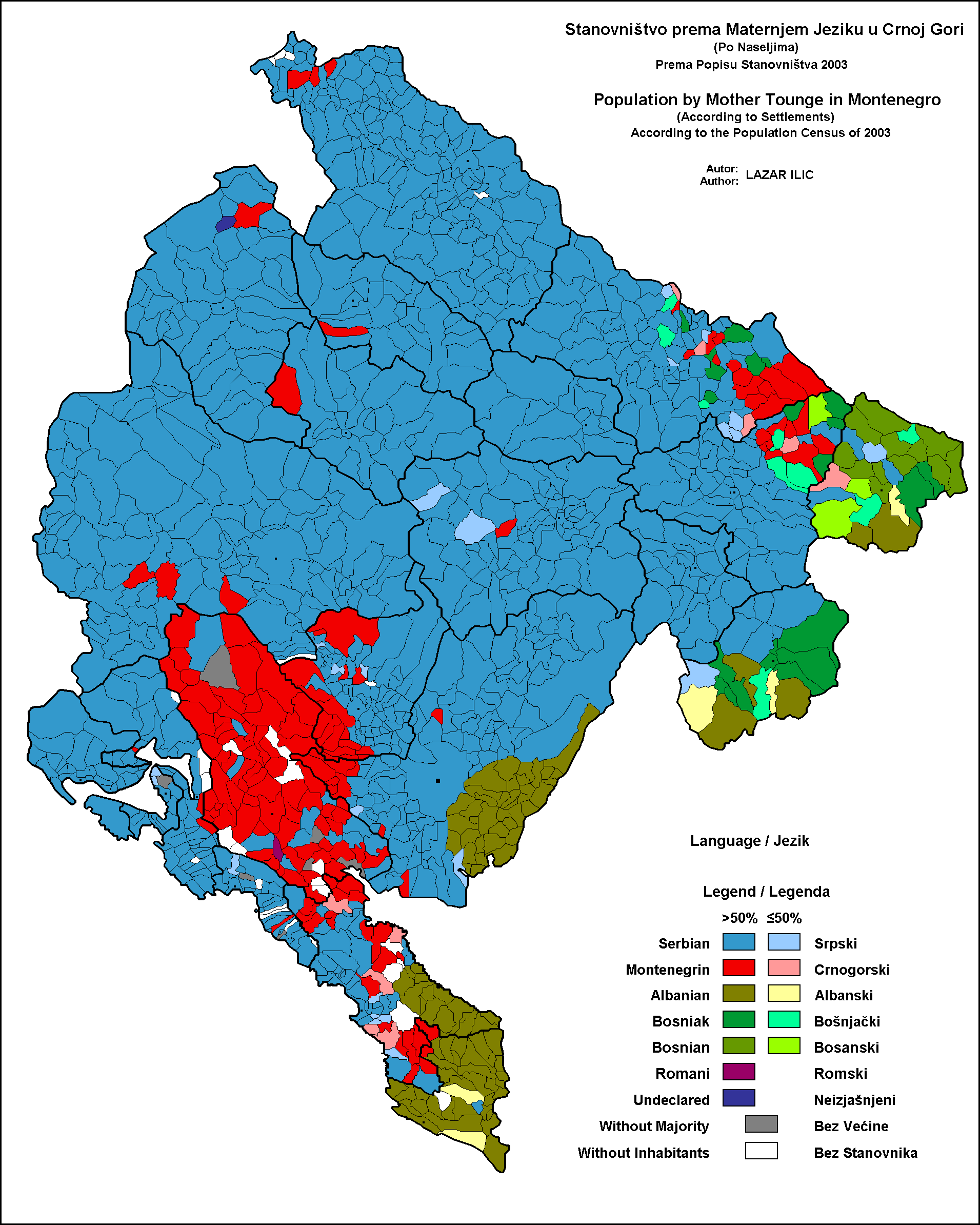
Montenegrin Language
Montenegrin ( ; cnr, label=none, / ) is a normative variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Montenegrins and is the official language of Montenegro. Montenegrin is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Croatian, Serbian, and Bosnian. Montenegro's language has historically and traditionally been called either Serbian or Montenegrin. The idea of a standardized Montenegrin standard language separate from Serbian appeared in the 1990s during the breakup of Yugoslavia, through proponents of Montenegrin independence from the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. Montenegrin became the official language of Montenegro with the ratification of a new constitution on 22 October 2007. Language standardization In January 2008, the government of Montenegro formed the Board (Council) for Standardization of the Montenegrin Language, which aims to standardize the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Association Football
Women's association football, more commonly known simply as women's football or women's soccer, is a team sport of association football when played by women only. It is played at the professional level in multiple countries and 176 national teams participate internationally. The history of women's football has seen competitions being launched at both the national and international levels. After the "first golden age" of women's football occurred in the United Kingdom in the 1920s, with one match attracting over 50,000 spectators, The Football Association instituted a ban from 1921 to 1970 in England that disallowed women's football on the grounds used by its member clubs. In many other nations, female footballers faced similarly hostile treatment and bans by male-dominated organisations. In the 1970s, international women's football tournaments were extremely popular and the oldest surviving continental championship was founded, the Women's Asian Cup. However, FIFA did not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegro
) , image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Podgorica , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Montenegrin , languages2_type = Languages in official use , languages2 = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2011 , religion = , religion_year = 2011 , demonym = Montenegrin , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Milo Đukanović , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Dritan Abazović (acting) , leader_title3 = Speaker , leader_name3 = Danijela Đurović , legislature = Skupština , sovereignty_type = Establishment history , established_event1 = Principality of Duklja , established_date1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegrin Women's League
The Montenegrin Women's Football league or 1. ŽFL is the top level women's football league of Montenegro. It is organized by the Football Association of Montenegro. The winning team of the league is eligible for a spot in the UEFA Women's Champions League. The first national women's football competition was held in the season 2008-09, but the league played its inaugural season in 2011-12. History Women's football history in Montenegro started in the period after the Montenegrin independence referendum. Beside the fact that the first women's club was founded in 2005, competitions started years after that. In 2008, Football Association of Montenegro founded national women's team and first women's competition - a yearly tournament called ''FSCG Trophy''. With its first season 2008-09, FSCG trophy matches lasted 60 minutes, with seven substitutes allowed. From season 2011-12, Montenegrin Women's First League is founded (commonly known as 1. ŽFL), with participation of the cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Football Association Of Montenegro
The Football Association of Montenegro ( Montenegrin: ''Fudbalski savez Crne Gore'', ''FSCG'' / Фудбалски савез Црне Горе, ФСЦГ) is the governing body of football in Montenegro. It is based in the capital, Podgorica. The FSCG organises the Montenegrin First, Second and Third Leagues, which between them contain 45 clubs. It also organises the Montenegrin Women's League and the men's and women's Montenegrin Cups, as well as the Montenegro national football team and the Montenegro national under-21 football team. The FSCG was established in 1931 as a sub-association within the Football Association of Yugoslavia. From 2003 until Montenegro declared independence in 2006, the FSCG was a sub-association within the Football Association of Serbia and Montenegro. It became a UEFA member in its own right in January 2007, and a FIFA member in May 2007. Former player Dejan Savićević has served as the FSCG's president since 2004. History The Football Associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2015–16 Montenegrin Cup (women)
The Montenegrin Cup 2015-16 was the first edition of the Montenegrin football tournament for women. Seven football clubs participated in the event. The winner of the competition was ŽFK Ekonomist Nikšić. Format The competition started October 15, 2015, and finished with the final game on May 16, 2016. There were three rounds of competition: quarterfinals, semifinals and a final match. Results Quarterfinals Semifinals Final See also *Montenegrin Women's League *Football Association of Montenegro *Football in Montenegro References {{DEFAULTSORT:2015-16 Montenegrin Cup (women) Cup Women A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardl ... Women's sports competitions in Montenegro 2015–16 in Montenegrin football 2015 in women's association football 2016 in women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podgorica
Podgorica (Cyrillic: Подгорица, ; lit. 'under the hill') is the capital and largest city of Montenegro. The city was formerly known as Titograd (Cyrillic: Титоград, ) between 1946 and 1992—in the period that Montenegro formed, as the Socialist Republic of Montenegro in honour of Marshal Josip Broz Tito. The city was largely destroyed during the bombing of Podgorica in World War II and accordingly the city is now dominated by architecture from the following decades of communism. Further but less substantial damage was caused by the 1999 bombing by NATO forces. The surrounding landscape is predominantly mountainous terrain. The city is just north of the Lake Skadar and close to coastal destinations on the Adriatic Sea. Historically, it was Podgorica's position at the confluence of the Ribnica and Morača rivers and at the meeting-point of the fertile Zeta Plain and Bjelopavlići Valley that encouraged settlement. Etymology Podgorica is written in Cyrillic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Football In Montenegro
Montenegro was independent from the late middle ages until 1918, when it declared its union with Serbia and, subsequently, became part of various incarnations of Yugoslavia and the state union of Serbia and Montenegro. During this time, football in Montenegro was part of the wider Yugoslavian structures. As a result of the Montenegrin independence referendum held on May 21, 2006, Montenegro declared independence two weeks later, on June 3, and formed its own football association. History Pre-2006 Football in Montenegro, as part of Yugoslavia, was organised first by the Football Association of Yugoslavia, founded in 1919 and renamed the Football Association of Serbia and Montenegro in 2003. Yugoslavia, later Serbia and Montenegro, was one of the leading countries in European football. They twice reached the semi-finals of the World Cup (in 1930 and 1962) and twice finished runners-up in the European Championships (in 1960 and 1968). The first player from Montenegro to play in a Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegrin Cup
The Montenegrin Cup (Montenegrin language, Montenegrin and Serbian language, Serbian: ''Kup Crne Gore'') is the national football cup played in Montenegro, established in 2006. The winner of the cup is awarded a spot in the second qualifying round of the UEFA Europa League if they have not already gained a spot in the UEFA Champions League. Most successful participant until now was FK Rudar Pljevlja, FK Rudar with four titles, followed by FK Budućnost Podgorica, FK Budućnost with three and OFK Titograd who won it twice. History Before independence Since 1946, Montenegrin football clubs played in the SFR Yugoslavia football system, so in the period 1947-1992 they participated in Yugoslav Cup. From 1992 to 2006, teams from Montenegro played in the Cup competition of FR Yugoslavia and Serbia and Montenegro. Most successful participant was FK Budućnost Podgorica, FK Budućnost, who played twice in the finals of Yugoslav Cup (1964–65 Yugoslav Cup, 1964-65 and 1976–77 Yugoslav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's National Association Football Cups
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)