|
Mallory Body
In histopathology, a Mallory body, Mallory-Denk body, and Mallory's hyaline, is an inclusion found in the cytoplasm of liver cells. Mallory bodies are damaged intermediate filaments within the liver cells. Associated conditions Mallory bodies are classically found in the livers of people suffering from alcohol-induced liver disease and were once thought to be specific for that. They are most common in alcoholic hepatitis (prevalence of 65%) and alcoholic cirrhosis (prevalence of 51%). They are a recognized feature of Wilson's disease (25%), primary biliary cirrhosis (24%), non-alcoholic cirrhosis (24%), hepatocellular carcinoma (23%) and morbid obesity (8%), among other conditions. However, it has also been reported in certain other unrelated conditions. Appearance Mallory bodies are highly eosinophilic and thus appear pink on H&E stain. The bodies themselves are made up of intermediate cytokeratin 8/ 18 filament proteins that have been ubiquitinated, or bound by othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive fat build-up in the liver without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), with the latter also including liver inflammation. Non-alcoholic fatty liver is less dangerous than NASH and usually does not progress to NASH. When NAFL does progress to NASH, it may eventually lead to complications such as cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, or cardiovascular disease. Obesity and type 2 diabetes are strong risk factors for NAFLD. Other risks include being overweight, metabolic syndrome (defined as at least three of the five following medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum HDL cholesterol), a diet high in fructose, and older age. NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease are typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallory Body High Mag Cropped
Mallory is an Irish surname derived from the Gaelic ''Ó Mallairígh''. Spelling variants include Mallary, Mallery, Malorie, Mallorie, Mallerie and Mallorey. Mallory and Mallerie are also given names derived from the surname. Surname * Arenia Mallory (1904–1977), American founder and head of what is now Saints Academy in Lexington, Mississippi, United States * Benajah Mallory (c. 1764–1853), farmer, merchant and political figure in Upper Canada * Bill Mallory (1935–), American football head coach * Boots Mallory (1913–1958), American film actress, dancer and model * Caitlin Mallory (1987–), American ice dancer who competes internationally for Estonia * Carole Mallory (1942–), American film actress and former model * Clare Mallory, the penname of American children's author Winifred Constance McQuilkan Hall (1913–1991) * Edward Mallory, born Edward Ralph Martz (1930–2007), American actor * Francis Mallory (1807–1860), American naval officer, physician, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
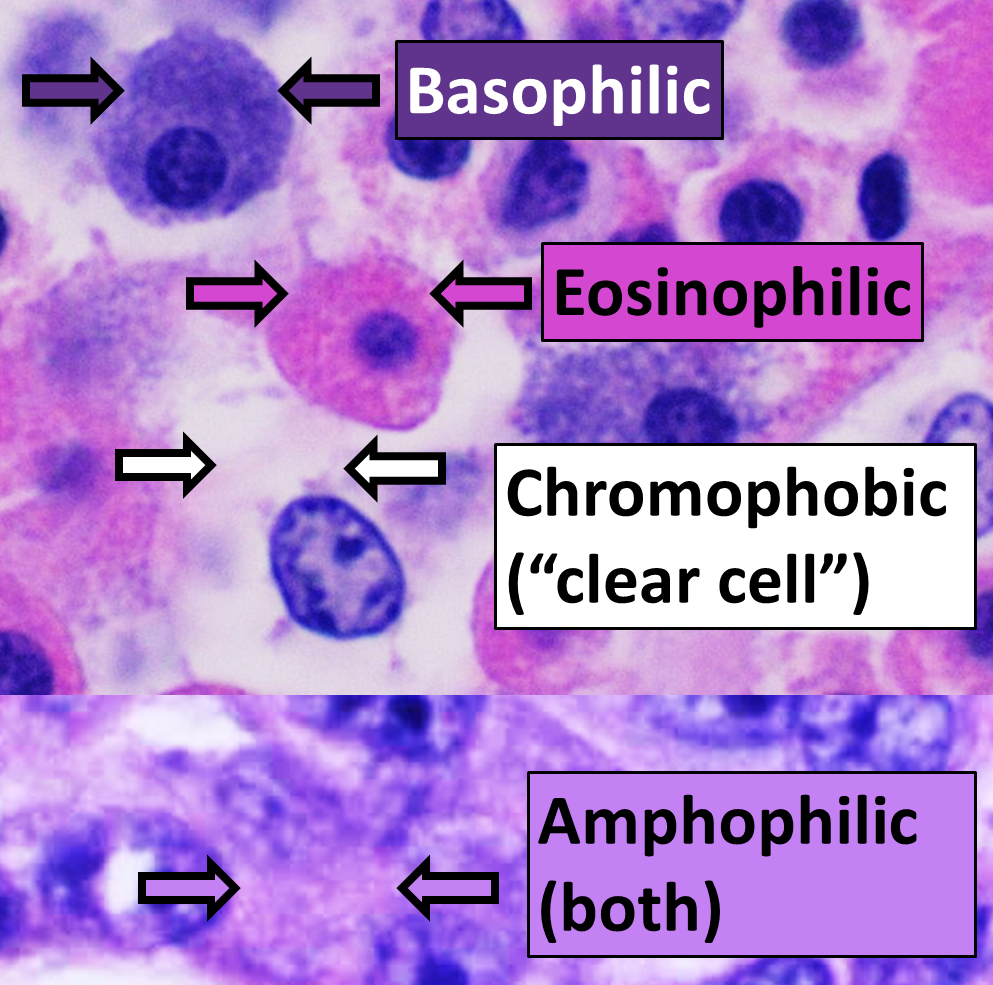
Eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye. Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''Eosinophilic'' describes the appearance of cells and structures seen in histological sections that take up the staining dye eosin. Such eosinophilic structures are, in general, composed of protein. Eosin is usually combined with a stain called hematoxylin to produce a hematoxylin- and eosin-stained section (also called an H&E stain, HE or H+E section). It is the most widely used histological stain for a medical diagnosis. When a pathologist examines a biopsy of a suspected cancer, they will stain the biopsy with H&E. Some structures seen inside cells are described as being eosinophilic; for example, Lewy and Mallory bodies. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichrome Stain
Trichrome staining is a histological staining method that uses two or more acid dyes in conjunction with a polyacid. Staining differentiates tissues by tinting them in contrasting colours. It increases the contrast of microscopic features in cells and tissues, which makes them easier to see when viewed through a microscope. The word ''trichrome'' means "three colours". The first staining protocol that was described as "trichrome" was Mallory's trichrome stain, which differentially stained erythrocytes to a red colour, muscle tissue to a red colour, and collagen to a blue colour. Some other trichrome staining protocols are the Masson's trichrome stain, Lillie's trichrome, and the Gömöri trichrome stain. Purpose Without trichrome staining, discerning one feature from another can be extremely difficult. Smooth muscle tissue, for example, is hard to differentiate from collagen. A trichrome stain can colour the muscle tissue red, and the collagen fibres green or blue. Liver bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of fatty liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver. Mere deposition of fat in the liver is termed steatosis, and together these constitute fatty liver changes. There are two main types of fatty liver disease: alcohol-related fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Risk factors for NAFLD include diabetes, obesity and metabolic syndrome. When inflammation is present it is referred to as alcoholic steatohepatitis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Steatohepatitis of either cause may progress to cirrhosis, and NASH is now believed to be a frequent cause of unexplained cirrhosis (at least in Western societies). NASH is also associated with lysosomal acid lipase deficiency. The word is from ''steato-'', meaning "fat" and ''hepatitis'', meaning "inflammation of the liver". Alcoholic steatohepatitis Chronic alcohol intake commonly causes steatohepatitis. Non-alcoh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballooning Degeneration
In histopathology, ballooning degeneration, formally ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes, is a form of liver parenchymal cell (i.e. hepatocyte) death. The name is derived from the fact that the cells undergoing this form of cell death increase in size (balloon). It is generally considered a form of apoptosis, and is a descriptor used in the context of inflamed fatty liver ( steatohepatitis) (which may be due to obesity or alcohol), as well as viral hepatitis. The histomorphological appearance of ballooning degeneration is not pathognomonic for steatohepatitis, but usage of the term is generally confined to the condition, i.e. in the context of other histopathological findings the label ''ballooning degeneration'' is not used for cell death with cytoplasmic clearing and cell swelling. Appearance Ballooned cells are typically two to three times the size of adjacent hepatocytes and are characterized by a wispy cleared cytoplasm on H&E stained sections. They can be dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Burr Mallory
Frank Burr Mallory (November 12, 1862 – September 27, 1941) was an American pathologist at the Boston City Hospital and Professor of Pathology at Harvard Medical School, after whom the Mallory body is named. The Pathology Department at Boston City Hospital, the Mallory Institute of Pathology, was named after him. Early life and career Mallory was born in Cleveland, Ohio on 12 November 1862 to George Burr and Anne (Faragher) Mallory, and received his medical degree in 1890 from Harvard Medical School. He became an assistant pathologist at Boston City Hospital in 1891, working under William Thomas Councilman. He married Persis McClain Tracy of Chautauqua, New York in 1893.Haythorn, Samuel R."Frank Burr Mallory. 1862–1941 ''The Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology'', Volume 54, Issue 2, pages 263–267, April 1942 In 1893 Mallory traveled to Europe to train under Hans Chiari in Prague and Ernst Ziegler in Freiburg. After returning to Harvard, he became an Assistant Prof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequestosome 1
Sequestosome-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SQSTM1'' gene. Also known as the ubiquitin-binding protein p62, it is an autophagosome cargo protein that targets other proteins that bind to it for selective autophagy. By interacting with GATA4 and targeting it for degradation, it can inhibit GATA-4 associated senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of SQSTM1 function. A conditional knockout mouse line, called ''Sqstm1tm1a(KOMP)Wtsi'' was generated as part of the International Knockout Mouse Consortium program — a high-throughput mutagenesis project to generate and distribute animal models of disease to interested scientists. Male and female animals underwent a standardized phenotypic screen to determine the effects of deletion. Twenty two tests were carried out on homozygous mutant mice and one significant abnormality was observed: females had abnormal complete blood count paramete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shock Protein
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are a family of proteins produced by cells in response to exposure to stressful conditions. They were first described in relation to heat shock, but are now known to also be expressed during other stresses including exposure to cold, UV light and during wound healing or tissue remodeling. Many members of this group perform chaperone functions by stabilizing new proteins to ensure correct folding or by helping to refold proteins that were damaged by the cell stress. This increase in expression is transcriptionally regulated. The dramatic upregulation of the heat shock proteins is a key part of the heat shock response and is induced primarily by heat shock factor (HSF). HSPs are found in virtually all living organisms, from bacteria to humans. Heat-shock proteins are named according to their molecular weight. For example, Hsp60, Hsp70 and Hsp90 (the most widely studied HSPs) refer to families of heat shock proteins on the order of 60, 70 and 90 kilodal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or, alternatively, ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |