|
Mycosis
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is a disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected: superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet and beard, and yeast infections such as pityriasis versicolor. Subcutaneous types include eumycetoma and chromoblastomycosis, which generally affect tissues in and beneath the skin. Systemic fungal infections are more serious and include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia, aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Signs and symptoms range widely. There is usually a rash with superficial infection. Fungal infection within the skin or under the skin may present with a lump and skin changes. Pneumonia-like symptoms or meningitis may occur with a deeper or systemic infection. Fungi are everywhere, but only some cause disease. Fungal infection occurs aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromoblastomycosis
Chromoblastomycosis is a long-term mycosis, fungal infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (a chronic (medicine), chronic subcutaneous mycosis). It can be caused by many different types of fungi which become implanted under the skin, often by thorns or splinters. Chromoblastomycosis spreads very slowly. It is rarely fatal and usually has a good prognosis, but it can be very difficult to cure. Several treatment options exist, including medication and surgery. The infection occurs most commonly in tropical or subtropical climates, often in rural areas. Signs and symptoms The initial trauma causing the infection is often forgotten or not noticed. The infection builds at the site over the years, and a small red papule (skin elevation) appears. The lesion is usually not painful, with few, if any, symptoms. Patients rarely seek medical care at this point. Several complications may occur. Usually, the infection slowly spreads to the surrounding tissue while remaining locali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mold that is breathed in frequently from the air, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung diseases such as asthma, cystic fibrosis or tuberculosis, or those who are immunocompromised such as those who have had a stem cell or organ transplant or those who take medications such as steroids and some cancer treatments which suppress the immune system. Rarely, it can affect skin. Aspergillosis occurs in humans, birds and other animals. Aspergillosis occurs in chronic or acute forms which are clinically very distinct. Most cases of acute aspergillosis occur in people with severely compromised immune systems such as those undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Chronic colonization or infection can cause complications in people with underlying respiratory illnesses, such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, or chronic obstructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
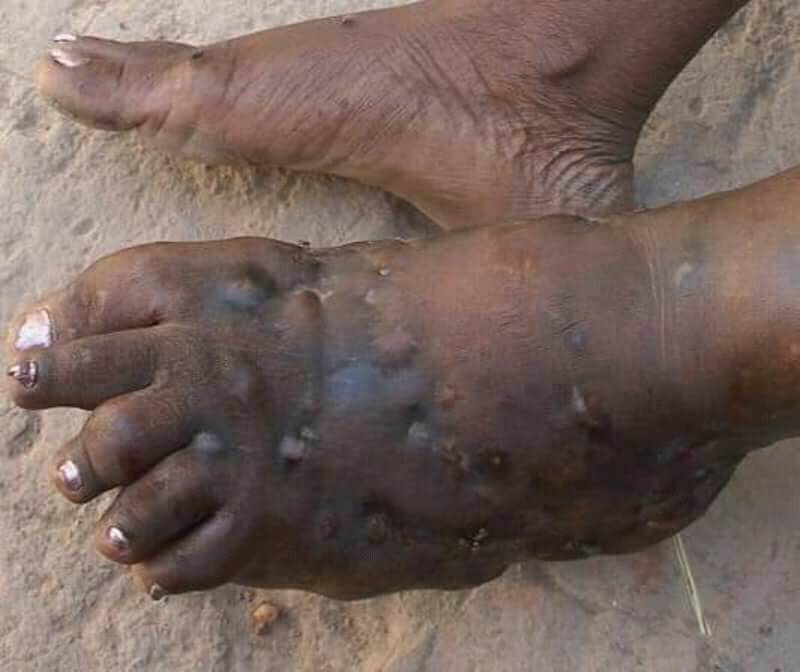
Eumycetoma
Eumycetoma, also known as Madura foot, is a persistent Mycoses, fungal infection of the skin and the tissues subcutaneous tissue, just under the skin, affecting most commonly the feet, although it can occur in hands and other body parts. It starts as a painless wet Nodule (medicine), nodule, which may be present for years before ulceration, swelling, grainy discharge and weeping from Sinus (anatomy), sinuses and fistulae, followed by bone deformity. Several fungi can cause eumycetoma, including: ''Madurella mycetomatis'', ''Madurella grisea'', ''Curvularia lunata'', ''Scedosporium species'', ''Acremonium'' and ''Fusarium'' species. Diagnosis is by biopsy, visualising the fungi microscopy, under the microscope and microbiological culture, culture. Medical imaging may reveal extent of bone involvement. Other tests include ELISA, immunodiffusion, and DNA Barcoding. Treatment includes Surgical debridement, surgical removal of affected tissue and Antifungal, antifungal medicines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Barbae
Tinea barbae is a fungal infection of the hair. Tinea barbae is due to a dermatophyte, dermatophytic infection around the bearded area of men. Generally, the infection occurs as a follicular inflammation, or as a cutaneous granulomatous lesion, i.e. a chronic inflammatory reaction. It is one of the causes of folliculitis. It is most common among agricultural workers, as the transmission is more common from animal-to-human than human-to-human. The most common causes are ''Trichophyton mentagrophytes'' and ''Trichophyton verrucosum, T. verrucosum''. Signs and symptoms Main symptoms that occur when affected with tinea barbae is pimple or blister amongst affected area, swelling and redness around infected area, red and lumpy skin on infected area. Crusting around hairs in infected area will occur, hairs on infected area will also be effortless to pull out. Tinea barbae can be itchy or painful to touch but these symptoms do not always occur. Transmission The transmission of tinea b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Pedis
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin (a dermatomycosis), that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause dermatophytosis. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Manuum
Tinea manuum is a fungal infection of the hand, mostly a type of dermatophytosis, often part of two feet-one hand syndrome. There is diffuse scaling on the palms or back of usually one hand and the palmar creases appear more prominent. When both hands are affected, the rash looks different on each hand, with palmar creases appearing whitish if the infection has been present for a long time. It can be itchy and look slightly raised. Nails may also be affected. The most common cause is ''Trichophyton rubrum''. The infection can result from touching another area of the body with a fungal infection such as athlete's foot or tinea cruris, fungal infection of the groin, contact with an infected person or animal, or contact with soil or contaminated towels. Risk factors include diabetes, hypertension, high blood pressure, immunosuppression, weak immune system, humid surroundings, excessive sweating, recurrent hand trauma and cracks in the feet. Pet owners and farmworkers are also at high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Cruris
Tinea cruris (TC), also known as jock itch, is a common type of contagious, superficial fungal infection of the groin and buttocks region, which occurs predominantly but not exclusively in men and in hot-humid climates. Typically, over the upper inner thighs, there is an intensely itchy red raised rash with a scaly well-defined curved border. It is often associated with athlete's foot and fungal nail infections, excessive sweating, and sharing of infected towels or sports clothing. It is uncommon in children. Its appearance may be similar to some other rashes that occur in skin folds including candidal intertrigo, erythrasma, inverse psoriasis and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Tests may include microscopy and culture of skin scrapings. Treatment is with topical antifungal medications and is particularly effective if symptoms have recent onset. Prevention of recurrences include treating concurrent fungal infections and taking measures to avoid moisture build-up including keeping the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
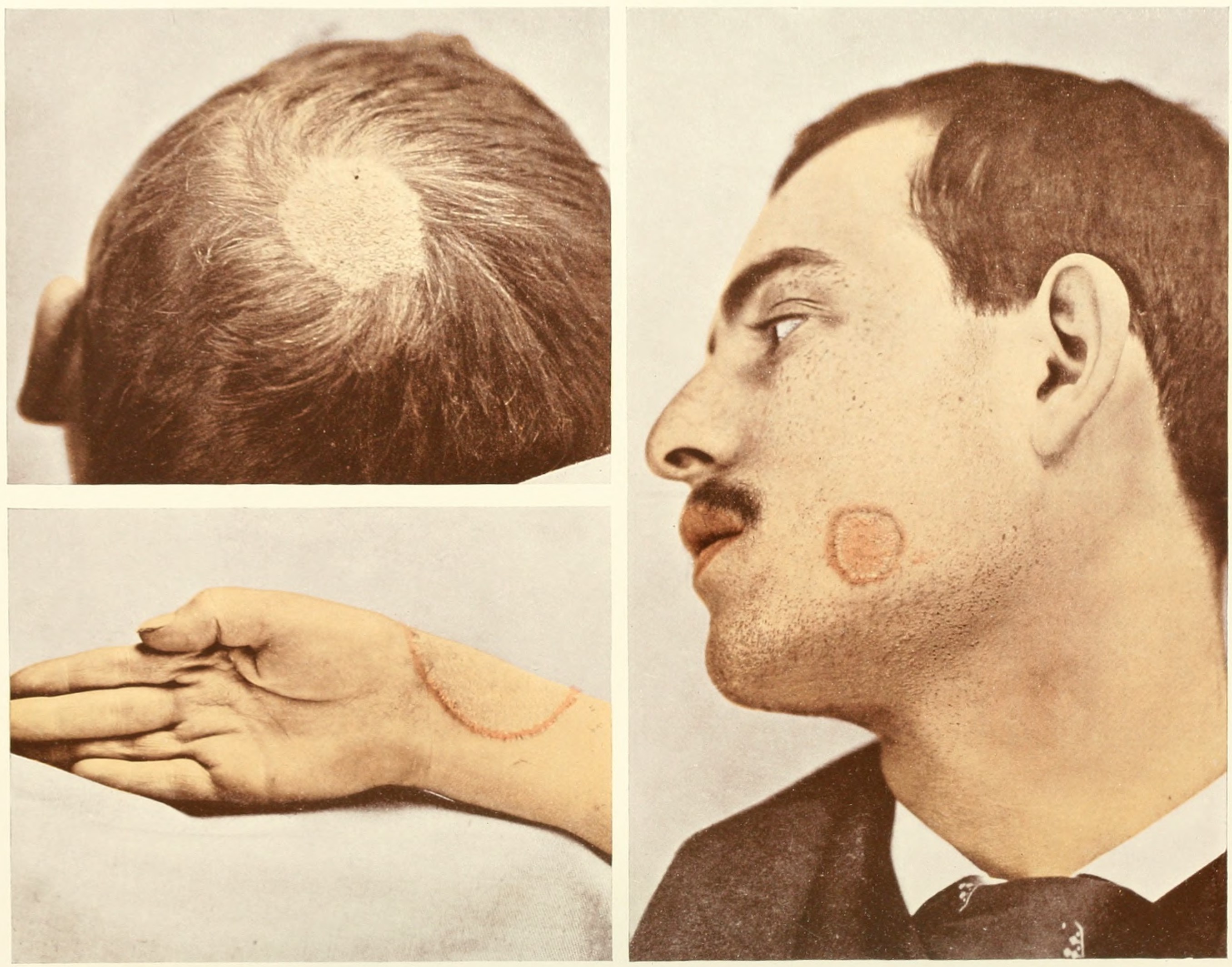
Tinea Corporis
Tinea corporis is a fungal infection of the body, similar to other forms of tinea. Specifically, it is a type of dermatophytosis (or ringworm) that appears on the arms and legs, especially on glabrous skin; however, it may occur on any superficial part of the body. Signs and symptoms It may have a variety of appearances; most easily identifiable are the enlarging raised red rings with a central area of clearing (ringworm). The same appearances of ringworm may also occur on the scalp (tinea capitis), beard area ( tinea barbae) or the groin ( tinea cruris, known as jock itch or dhobi itch). Other classic features of tinea corporis include: * Itching occurs on infected area. * The edge of the rash appears elevated and is scaly to touch. * Sometimes the skin surrounding the rash may be dry and flaky. * Almost invariably, there will be hair loss in areas of the infection. Causes Tinea corporis is caused by a tiny fungus known as dermatophyte. These tiny organisms normally live on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatophytoses
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin (a dermatomycosis), that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause dermatophytosis. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeasts
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Some yeast species have the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae, or quickly evolve into a multicellular cluster with specialised cell organelles function. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 μm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 μm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
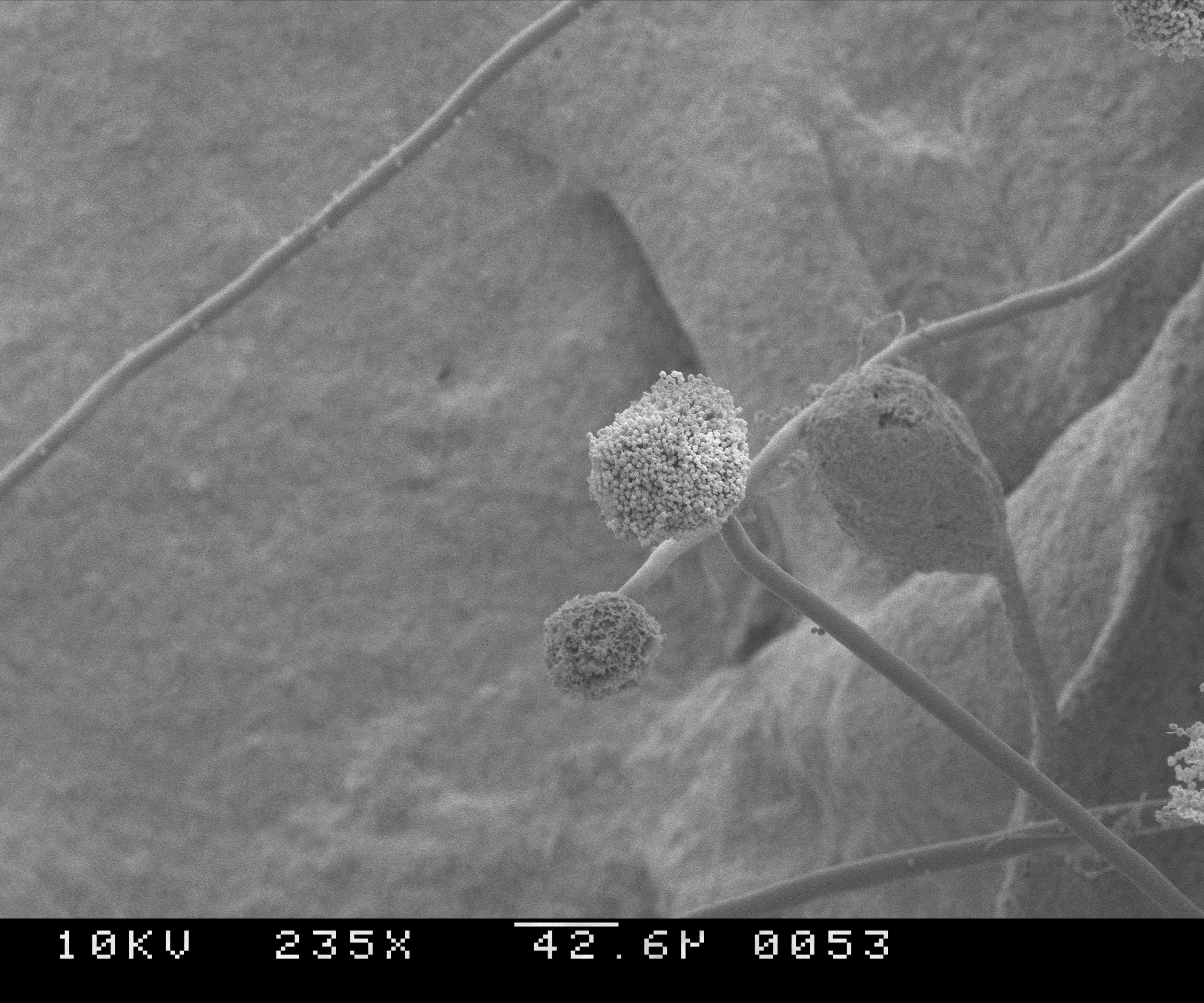
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical microscope, optical, electron microscope, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection (physics), reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the Laboratory specimen, specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscope, transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pityriasis Versicolor
Pityriasis commonly refers to flaking (or scaling) of the skin. The word comes from the Greek πίτυρον 'bran'. Classification Types include: * Pityriasis alba, dry, fine-scaled, pale patches on the face * Pityriasis lichenoides chronica, caused by a hypersensitivity reaction to infectious agents * Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta, a disease of the immune system * Pityriasis rosea, a type of skin rash ** Pityriasis circinata, * Pityriasis rubra pilaris, reddish-orange patches (Latin: ''rubra'') on the skin * Pityriasis versicolor, a skin eruption on the trunk and proximal extremities, usually caused by a fungus * Dandruff, historically called ''Pityriasis capitis'' * Pityriasis amiantacea, condition of the scalp in which thick tenaciously adherent scale infiltrates and surrounds the base of a group of scalp hairs See also * Desquamation * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |