|
Montenegro Fault
The Montenegro Fault ( es, Falla de Montenegro) is an oblique sinistral strike-slip fault in the department of Quindío in west-central Colombia. The fault is part of the megaregional Romeral Fault System and has a total length of and runs along an average northwest to southeast strike of 025.1 ± 9 in the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. Etymology The fault is named after Montenegro, Quindío.Paris et al., 2000a, p.20 Description The Montenegro Fault is part of the Romeral Fault System, running through the western slope of the Central Ranges. The fault is located to the west of the city of Armenia. The fault crosscuts and deforms the Pleistocene volcanic and volcano-sedimentary deposits of the Quindío Fan ( es, Abanico del Quindío), which covers about . The Montenegro Fault forms outstanding fault scarps as much as in height, beheaded streams, hanging valleys, ponded alluvium, aligned and offset drainages, as well as soil and rock slides on the face of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegro, Quindío
Montenegro () is a municipality in the western part of the department of Quindío, Colombia. It is located 10 km west of the departmental capital Armenia. Montenegro (literally: Black Mountain) was named for the dark green color of the trees that originally covered the hill above the current-day site of the township, which was visible from other parts of the region as it rose above the surrounding guadua forests. Between 1897 and 1904, Montenegro was officially known as Villa Quindío. The boundaries of Montenegro are principally formed by three rivers. To the north, the Roble River forms the limit with Quimbaya; to the east and south, the Espejo River forms the limit with Armenia and La Tebaida; and to the west La Vieja River is the limit with the neighboring department of Valle del Cauca. There is also a short boundary with Circasia in the northeast of the municipality. In 2005 it had an estimated population of 45,000, of which 36,400 live in the main urban zone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Faults
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to: Film and television * Normal (2003 film), ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson * Normal (2007 film), ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie * Normal (2009 film), ''Normal'' (2009 film), an adaptation of Anthony Neilson's 1991 play ''Normal: The Düsseldorf Ripper'' * ''Normal!'', a 2011 Algerian film * The Normals (film), ''The Normals'' (film), a 2012 American comedy film * Normal (New Girl), "Normal" (''New Girl''), an episode of the TV series Mathematics * Normal (geometry), an object such as a line or vector that is perpendicular to a given object * Normal basis (of a Galois extension), used heavily in cryptography * Normal bundle * Normal cone, of a subscheme in algebraic geometry * Normal coordinates, in differential geometry, local coordinates obtained from the exponential map (Riemannian geometry) * Normal distribution, the Gaussian continuo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Faults
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A '' fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
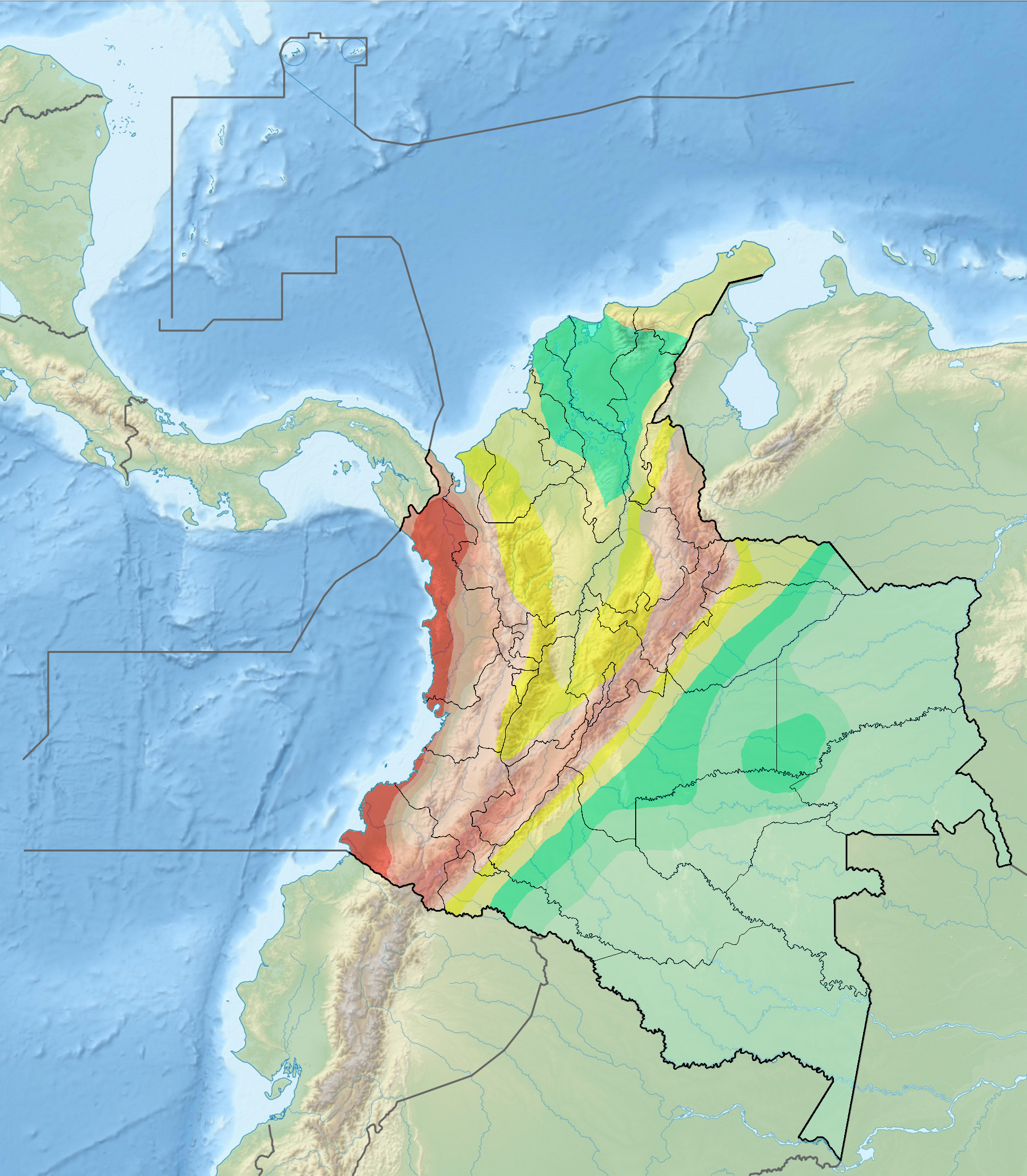
Seismic Faults Of Colombia
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning " earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INGEOMINAS
The Colombian Geological Survey (CGS) ( es, Servicio Geológico Colombiano; formerly known as INGEOMINAS) is a scientific agency of the Colombian government in charge of contributing to the socioeconomic development of the nation through research in basic and applied geosciences of the subsoil, the potential of its resources, evaluating and monitoring threats of geological origin, managing the geoscientific knowledge of the nation, and studying the nuclear and radioactive elements in Colombia. History The CGS was initially created as the ''National Scientific Commission'' ( es, Comisión Científica Nacional) by the Congress of Colombia on December 22, in 1916, with the mission of mapping the geological resources of the nation and exploring the national territory in search of mineral deposits. Following a series of earthquakes throughout the nation in the early 1920s, the eruption of the Galeras volcano in 1925, and the growing mining and petroleum industry, the Colombian gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia Fault
The Armenia Fault ( es, Falla de Armenia) is an oblique sinistral strike-slip fault in the department of Quindío in west-central Colombia. The fault is part of the megaregional Romeral Fault System and has a total length of approximately and runs along an average northwest to southeast strike of 023.2 ± 11 in the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault shows Holocene activity with a surface rupture produced in 2001. Etymology The fault is named after Armenia, the capital of Quindío.Paris et al., 2000a, p.21 Description The Armenia Fault is part of the Romeral Fault System on the western slope of the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault crosses the city of Armenia and displaces Pliocene to Pleistocene volcanic and volcano-sedimentary deposits of the Quindío Fan ( es, Abanico del Quindío), which covers about . The geometric and neotectonic features of the Montenegro and Armenia Faults are very similar. The fault forms well-developed fault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In Colombia
This is a list of earthquakes in Colombia. Colombia is a seismically active country and has a large seismic risk in many areas of its territory due to its location at the boundaries of the Malpelo, Panama, Caribbean, North Andes (where most earthquakes occurred) and South American Plates along the Pacific Ring of Fire. The southeastern and extreme eastern portions of Colombia are not as seismically active as the rest of the country. The first historically registered earthquake felt in Colombia occurred on September 11, 1530, around 10:00 AM, probably with the epicentre near Cumaná, Venezuela. The earthquake was documented by Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés in his work ''La Historia general de las Indias'' and by friar Bartolomé de las Casas in his book ''Historia de Las Indias''.Ramírez, 1975, p.63 The first documented earthquake with its epicentre in present-day Colombia territory took place in 1566,Ramírez, 1975, p.65 with the epicentre estimated around San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Espejo River
Espejo may refer to: Media *''El Espejo'', 1943 Argentine drama film *''Espejo de paciencia'', 1608 epic poem by Spanish writer Silvestre de Balboa *'' Espejo de sombras'', 1960 Mexican telenovela *''La mujer en el espejo'', 2004–2005 Colombian soap opera People with the surname * Antonio Espejo (other), multiple people * Carlos Espejo (1923–2014), Argentine swimmer * Dani Espejo (born 1993), Spanish footballer * Diego Espejo (born 2002), Spanish footballer * Elvira Espejo Ayca (born 1981), indigenous Bolivian artist and curator * Eugenio Espejo (1747–1795), Spanish physician and writer * Eva Espejo (born 1986), Mexican football manager * Francisca Espejo (born 1989), Chilean volleyball player * Francisco Espejo (1758–1812), Venezuelan lawyer, revolutionary, politician and President of Venezuela * Francisco de Cárdenas Espejo (1817–1898), Spanish lawyer, journalist and politician * Gianfranco Espejo (1988–2011), Peruvian footballer * Jerónimo Espejo (1801– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debris Flow
Debris flows are geological phenomena in which water-laden masses of soil and fragmented Rock (geology), rock rush down mountainsides, funnel into stream channels, entrain objects in their paths, and form thick, muddy deposits on valley floors. They generally have bulk density, bulk densities comparable to those of rock avalanches and other types of landslide classification, landslides (roughly 2000 kilograms per cubic meter), but owing to widespread sediment liquefaction caused by high pore pressure, pore-fluid pressures, they can flow almost as fluidly as water. Debris flows descending steep channels commonly attain speeds that surpass 10 m/s (36 km/h), although some large flows can reach speeds that are much greater. Debris flows with volumes ranging up to about 100,000 cubic meters occur frequently in mountainous regions worldwide. The largest prehistoric flows have had volumes exceeding 1 billion cubic meters (i.e., 1 cubic kilometer). As a result of their hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |