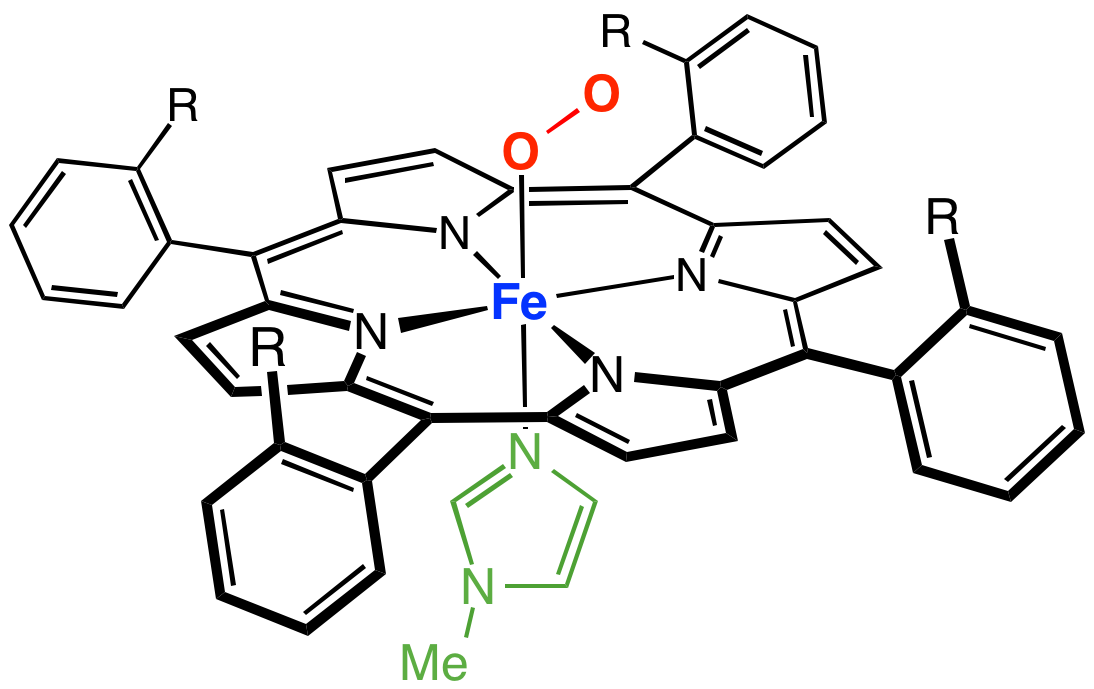
|
Metmyoglobin
Metmyoglobin is the oxidized form of the oxygen-carrying hemeprotein myoglobin. Metmyoglobin is the cause of the characteristic brown colouration of meat that occurs as it ages. In living muscle, the concentration of metmyoglobin is vanishingly small, due to the presence of the enzyme metmyoglobin reductase, which, in the presence of the Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor NADH and the coenzyme cytochrome b4 converts the Iron, Fe3+ in the heme, heme prosthetic group of metmyoglobin back to the Fe2+ of normal myoglobin. In meat, which is dead muscle, the normal processes of removing metmyoglobin are prevented from effecting this repair, or alternatively the rate of metmyoglobin formation exceeds their capacity, so that there is a net accumulation of metmyoglobin as the meat ages. Metmyoglobin reduction helps limit the oxidation of myoglobin and the oxidation of myoglobin is specific to each species. In other words, metmyoglobin gains electrons in order to limit myoglobin from losing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metmyoglobin Reductase
Metmyoglobin is the oxidized form of the oxygen-carrying hemeprotein myoglobin. Metmyoglobin is the cause of the characteristic brown colouration of meat that occurs as it ages. In living muscle, the concentration of metmyoglobin is vanishingly small, due to the presence of the enzyme metmyoglobin reductase, which, in the presence of the cofactor NADH and the coenzyme cytochrome b4 converts the Fe3+ in the heme prosthetic group of metmyoglobin back to the Fe2+ of normal myoglobin. In meat, which is dead muscle Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ..., the normal processes of removing metmyoglobin are prevented from effecting this repair, or alternatively the rate of metmyoglobin formation exceeds their capacity, so that there is a net accumulation of metmyoglobin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidized
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemeprotein
A hemeprotein (or haemprotein; also hemoprotein or haemoprotein), or heme protein, is a protein that contains a heme prosthetic group. They are a very large class of metalloproteins. The heme group confers functionality, which can include oxygen carrying, oxygen reduction, electron transfer, and other processes. Heme is bound to the protein either covalently or noncovalently or both. The heme consists of iron cation bound at the center of the conjugate base of the porphyrin, as well as other ligands attached to the "axial sites" of the iron. The porphyrin ring is a planar dianionic, tetradentate ligand. The iron is typically Fe2+ or Fe3+. One or two ligands are attached at the axial sites. The porphyrin ring has 4 nitrogen atoms that bind to the iron, leaving two other coordination positions of the iron available for bonding to the histidine of the protein and a divalent atom. Hemeproteins probably evolved to incorporate the iron atom contained within the protoporphyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding with oxygen like hemoglobin does. In humans, myoglobin is only found in the bloodstream after muscle injury. (Google books link is the 2008 edition) High concentrations of myoglobin in muscle cells allow organisms to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Diving mammals such as whales and seals have muscles with particularly high abundance of myoglobin. Myoglobin is found in Type I muscle, Type II A, and Type II B; although many texts consider myoglobin not to be found in smooth muscle, this has proved erroneous: there is also myoglobin in smooth muscle cells. Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed by X-ray crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chickens, sheep, rabbits, pigs, and cattle. This eventually led to their use in meat production on a |