|
Megabyzus (leafhopper)
Megabyzus (, a folk-etymological alteration of Old Persian Bagabuxša, meaning "God saved") was an Achaemenid Persian general, son of Zopyrus, satrap of Babylonia, and grandson of Megabyzus I, one of the seven conspirators who had put Darius I on the throne. His father was killed when the satrapy rebelled in 484 BCE, and Megabyzus led the forces that recaptured the city, after which the statue of the god Marduk was destroyed to prevent future revolts. Megabyzus subsequently took part in the Second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BCE). Herodotus claims that he refused to act on orders to pillage Delphi, but it is doubtful such orders were ever given. Conspiracy of Artabanes According to Ctesias, who is not especially reliable but is often our only source, Amytis, wife of Megabyzus and daughter of Xerxes, was accused of adultery shortly afterwards. As such, Megabyzus took part in the conspiracy of Artabanus to assassinate the emperor, but betrayed him before he could kill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was the son of Darius the Great and Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great. In Western history, Xerxes is best known for his Second Persian invasion of Greece, invasion of Greece in 480 BC, which ended in Persian defeat. Xerxes was designated successor by Darius over his elder brother Artobazan and inherited a large, multi-ethnic empire upon his father's death. He consolidated his power by crushing revolts in Twenty-seventh Dynasty of Egypt, Egypt and Babylonian revolts (484 BC), Babylon, and renewed his father's campaign to subjugate Ancient Greece, Greece and punish Classical Athens, Athens and its allies for their interference in the Ionian Revolt. In 480 BC, Xerxes personally led a large army and crossed the Dardanelles, Hellespont into Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica
Attica (, ''Attikḗ'' (Ancient Greek) or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the entire Athens metropolitan area, which consists of the city of Athens, the capital city, capital of Greece and the core city of the metropolitan area, as well as its surrounding suburban cities and towns. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean Sea, bordering on Boeotia to the north and Megaris to the west. The southern tip of the peninsula, known as Laurion, Lavrio, was an important Mines of Laurion, mining region. The history of Attica is closely linked with that of Athens. In ancient times, Attica corresponded with the Athens city-state. It was the most prominent region in Ancient Greece, specifically during the Golden Age of Athens in the Classical Greece, classical period. Classical Athens, Ancient Attica (the classical Classical Athens, Athens city-state) was divided into deme, demoi, or municipalities, from the reform of Cleisthenes in 508/7 BC, gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabazus
Megabazus (Old Persian: ''Bagavazdā'' or ''Bagabāzu'', ), son of Megabates, was a highly regarded Persian general under Darius, to whom he was a first-degree cousin. Most of the information about Megabazus comes from '' The Histories'' by Herodotus. Scythian campaign (513 BC) Megabazus led the army of the Persian King Darius I in 513 BC during his European Scythian campaign. After this had to be discontinued without result, Megabazos was left as commander-in-chief of an 80,000-man army in Europe, with the mission of subjugating the Greek cities on the Hellespont. The Persian troops first subjugated gold-rich Thrace after capturing Perinthos and the coastal Greek cities, and then defeated the powerful Paeonians, many of whom he deported to Phrygia. Subjugation of Macedon Finally, Megabazus sent envoys to Amyntas I, king of Macedon, demanding acceptance of Persian domination, which the king accepted. Megabazus received the present of " Earth and Water" from Amyntas, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenes
Achaemenes ( ; ; ) was the progenitor ( apical ancestor) of the Achaemenid dynasty of rulers of Persia. Other than his role as an apical ancestor, nothing is known of his life or actions. It is quite possible that Achaemenes was only the mythical ancestor of the Persian royal house, but if Achaemenes was a historical person, he would have lived around the end of the 8th century and the beginning of the 7th century BC.. Name The name used in European languages ( ('), ) ultimately derives from Old Persian ' (), as found together with Elamite (''Ha-ak-ka-man-nu-iš'' or ''Hâkamannuiš'') and Akkadian (''A-ḫa-ma-ni-iš-ʾ'') in the non-contemporaneous trilingual Behistun Inscription of Darius I. The Old Persian proper name is traditionally derived from ' "friend" and ' "thinking power", yielding "having a friend's mind." A more recent interpretation reads ' as "follower", giving "characterized by a follower's spirit.". The name is spelled (''Haxâmaneš'') in Modern Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Egypt
The history of Persian Egypt refers to the two periods when ancient Egypt was controlled by the Achaemenid Empire: * Twenty-seventh Dynasty of Egypt (525–404 BC), established by the first Achaemenid conquest of Egypt. * Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt (343–332 BC), established by the second Achaemenid conquest of Egypt. These two periods of satrapies were punctuated by a brief interval of Egyptian independence from 404 BC to 343 BC. Background In the 6th century BC, Persian rulers, particularly Cyrus the Great, sought to expand their imperialist agenda to include Egypt. Expansionism was a key strategy for empires of the ancient world to establish military and economic dominance, and Egypt was a priority of Cyrus the Great's, in large part due to the desirability of the Nile river and valley as economic assets. The contemporaneous Egyptian pharaoh, Amasis, attempted to ward off the occupation by forming alliances with neighbouring rulers, in particular Polycrates of Samos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area within the north of modern Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Bactria was strategically located south of Sogdia and the western part of the Pamir Mountains. The extensive mountain ranges acted as protective "walls" on three sides, with the Pamir on the north and the Hindu Kush on south forming a junction with the Karakoram, Karakoram range towards the east. Called "beautiful Bactria, crowned with flags" by the Avesta, the region is considered, in the Zoroastrianism, Zoroastrian faith, to be one of the "Avestan geography, sixteen perfect Iranian lands" that the supreme deity, Ahura Mazda, had created. It was once a small and independent kingdom struggling to exist against nomadic Turya (Avesta), Turanians. One of the early centres of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
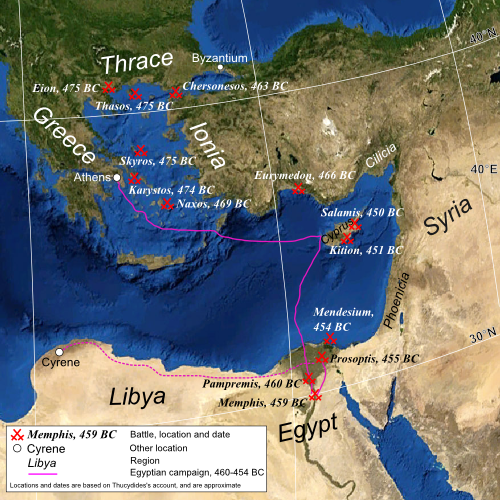
Inarus
Inaros (II), also known as Inarus, (fl. 460 BC) was an Egyptian rebel ruler who was the son of an Egyptian prince named Psamtik, presumably of the old Saite line, and grandson of Psamtik III. In 460 BC, he revolted against the Persians with the help of his Athenian allies under Admiral Charitimides, and defeated the Persian army commanded by satrap Achaemenes. The Persians retreated to Memphis, but the Athenians were finally defeated in 454 BC by the Persian army led by Megabyzus, satrap of Syria, and Artabazus, satrap of Phrygia, after a two-year siege. Inaros was captured and carried away to Susa where he was reportedly crucified in 454 BC. Revolt and aftermath He held a kingship over the Libyans from Mareia (above Pharos) and the part of the Nile Delta around Sais. With help from Amyrtaeus, also from Sais, who took the northern marshes, Inarus drove out the tax-collectors while collecting mercenaries. These actions started a revolt in Egypt at the beginning of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; , ''Phrygía'') was a kingdom in the west-central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. Stories of the heroic age of Greek mythology tell of several legendary Phrygian kings: * Gordias, whose Gordian Knot would later be cut by Alexander the Great * Midas, who turned whatever he touched to gold * Mygdon, who warred with the Amazons According to Homer's ''Iliad'', the Phrygians participated in the Trojan War as close allies of the Trojans, fighting against the Achaeans. Phrygian power reached its peak in the late 8th century BC under another historical king, Midas, who dominated most of western and central Anatolia and rivaled Assyria and Urartu for power in eastern Anatolia. This later Midas was, however, also the last independent king of Phrygia before Cimmerians sacked the Phrygian capital, Gordium, around 695 BC. Phrygia then became subject to Lydia, and then successivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
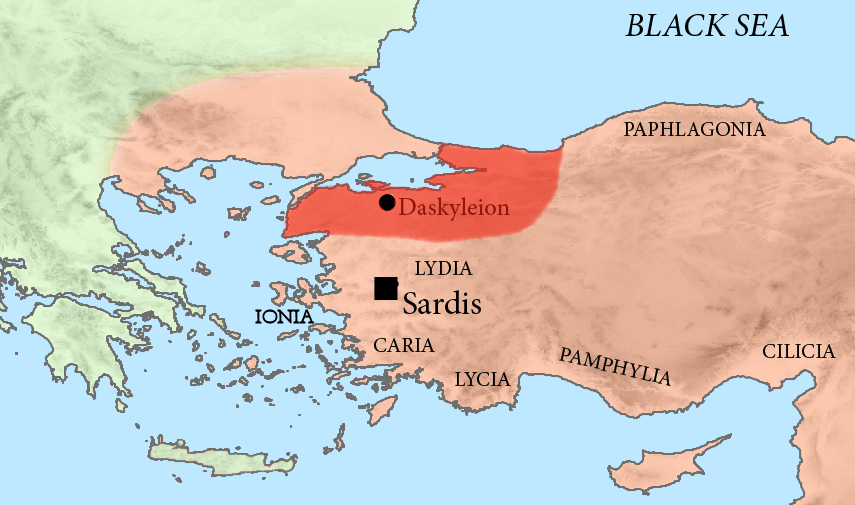
Artabazos I Of Phrygia
Artabazos (; 480 BC - 455 BC) was a Persian people, Persian general in the army of Xerxes I, and later satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia (now northwest Turkey) under the Achaemenid dynasty, founder of the Pharnacid dynasty of satraps. He was the son of Pharnaces (son of Arsames), Pharnaces, who was the younger brother of Hystaspes (father of Darius I), Hystaspes, father of Darius I. Artabazos was therefore a first cousin of the great Achaemenid ruler Darius I. General in the Second Persian invasion of Greece Artabazus was one of the generals of Xerxes I, Xerxes in the 480 BC Second Persian invasion of Greece, in command of the Parthians and the Chorasmians in the Achaemenid army. He was particularly in charge of the reserve forces guarding the route back to Asia, and responsible for suppressing a revolt in Potidaea. The invasion ended the following year with the commander-in-chief Mardonius (general), Mardonius, ignoring advice from Artabazus and others, meeting the Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria (region)
Syria, ( or ''Shaam'') also known as Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine, is a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in West Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. However, in modern times, the term "Syria" alone is used to refer to the Syria, Syrian Arab Republic. The term is originally derived from Assyria, an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic-speaking civilization centered in northern Mesopotamia, modern-day Iraq. During the Hellenistic period, the term Syria was applied to the entire Levant as Coele-Syria. Under Roman Empire, Roman rule, the term was used to refer to the Roman Syria, province of Syria, later divided into Phoenice (Roman province), Syria Phoenicia and Coele-Syria, Coele Syria, and to the province of Syria Palaestina. Under the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines, the provinces of Syria Prima and Syria Secunda emerged out of Coele Syria. After the Muslim conquest of the Levant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
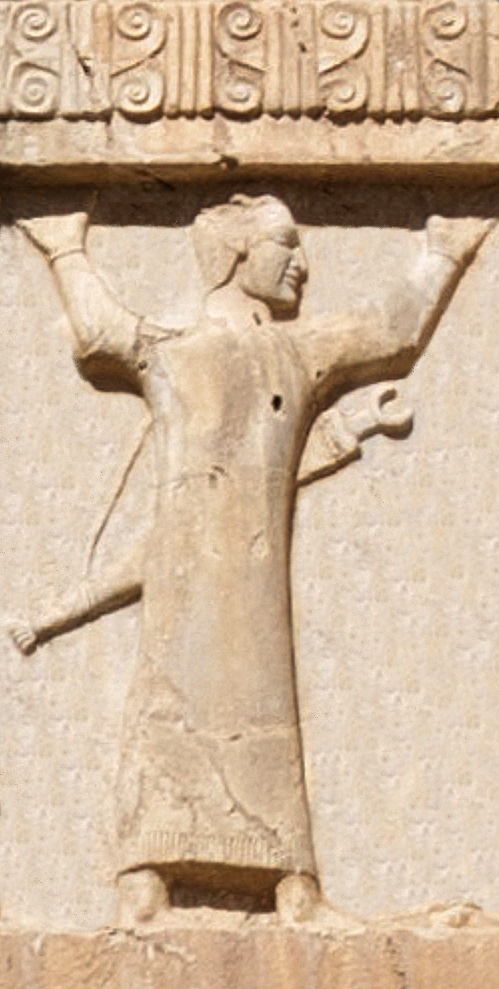
Xerxes I Tomb Egyptian Soldier Circa 470 BCE
Xerxes ( ) may refer to: People * Xerxes I of Persia, "Xerxes the Great", reigned 486–465 BC * Xerxes II of Persia, briefly reigned 424 BC * Xerxes of Sophene, ruler of Sophene and Commagene, 228–201 BC * Xerxes (Sasanian prince), 6th-century prince and general * Xerxes (name), a list of people with the name Fiction, stage and video *'' Il Xerse'' (''Xerxès'' in its 1660 French version), a 1654 opera by Francesco Cavalli * ''Xerse'' (Bononcini), a 1694 opera by Giovanni Bononcini *''Serse'' (''Xerxes''), a 1738 opera by George Frideric Handel *''Xerxes'', a 1919 novel by Louis Couperus * ''Xerxes'' (TV series), a 1988 Swedish TV series about young adults * ''Xerxes'' (graphic novel), a 2018 graphic novel by Frank Miller Other *Xerxes Peak, a mountain in the Canadian Rockies *XerxesDZB, a Dutch professional football team based in Rotterdam *Roksan Xerxes, a series of record turntables from Roksan Audio (UK) *XerXeS, a denial-of-service attack tool developed by The Jester * X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |