|
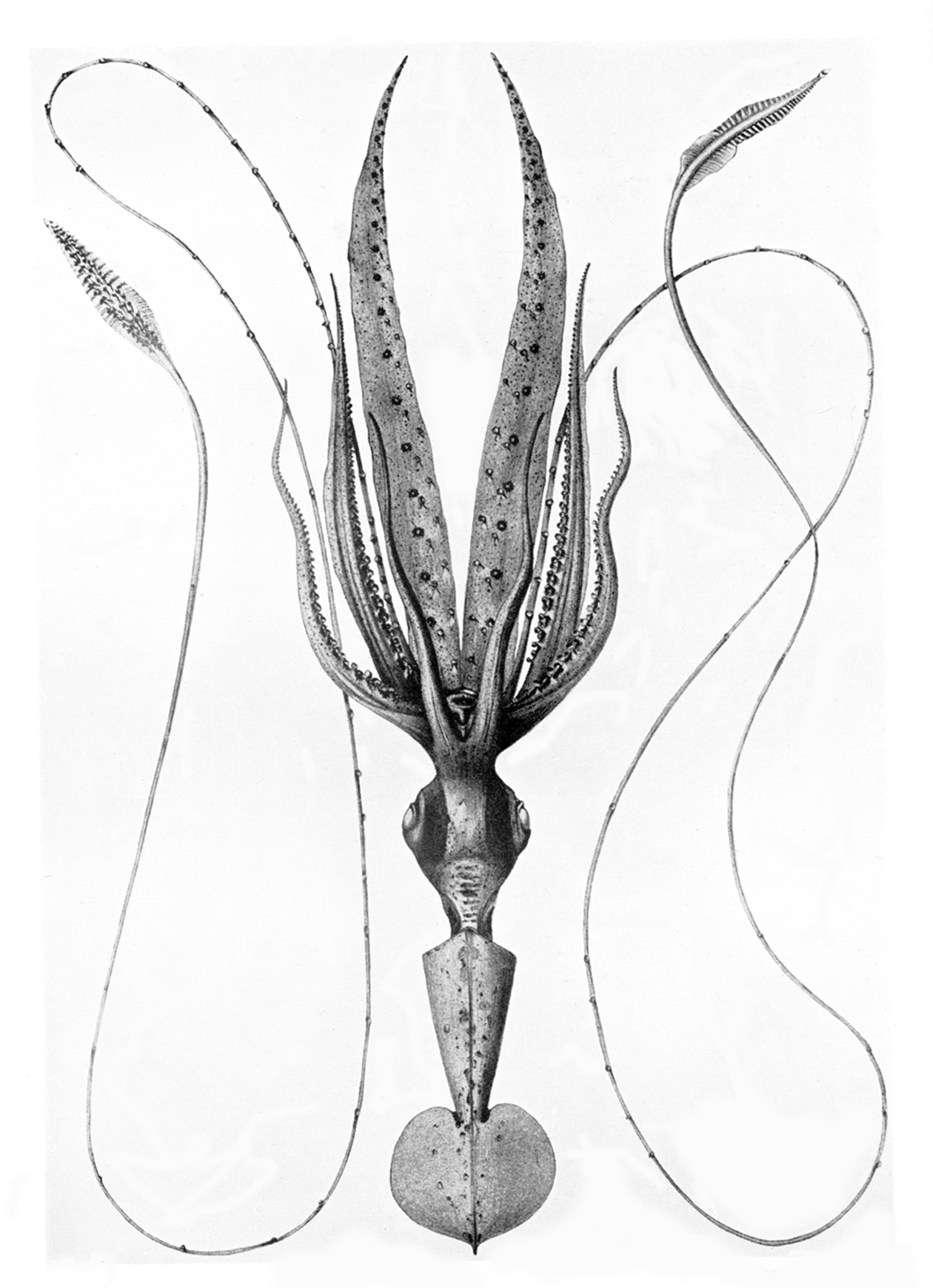
Liocranchia Valdiviae
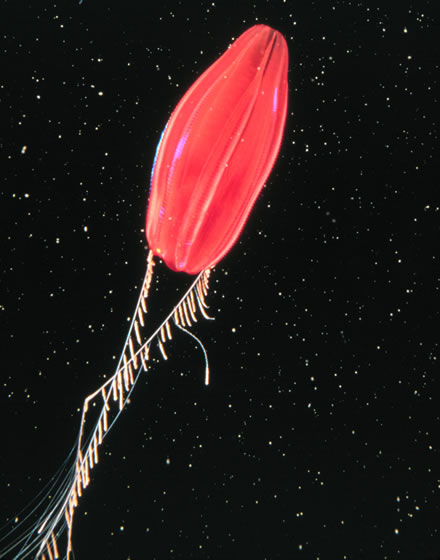
''Liocranchia'' is a genus of glass squid from the family Cranchiidae. They are moderate-sized with a long, spindle-shaped mantle which tapers to a point at the rear and they can attain mantle lengths of 250 mm. The species in ''Liocranchia'' have a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical and subtropical oceans although it has been suggested that on especies, ''Liocranchia reinhardti'' is associated with land masses. In seas off Hawaii waters ''L. reinhardti'' undergoes vertical migrations while '' L. valdiviae'' occurs in deep water is sedentary. They are eaten by many oceanic predator species. Characteristics ''Liocranchia'' species are characterised by having two rows of cartilagenous tubercules starting at each funnel-mantle fusion which diverge from each other along their length, each funnel having a valve and a very large ventral pad. The tentacles have duckers and pads in two series on distal 2/3 of tentacle stalk. In the paralarvae the eyes are not mounted on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Johann Pfeffer
Georg Johann Pfeffer (1854–1931) was a German zoologist, primarily a malacologist, a scientist who studies mollusks. Pfeffer was born in Berlin. In 1887 he became curator of the , which was established in 1843 and destroyed during World War II. Pfeffer's published writings were mainly about cephalopods. The World Register of Marine Species database lists 133 marine taxa named by Pfeffer When Pfeffer's name is listed as an authority for a taxon such as the land snail genus ''Lamellaxis'' Strebel & Pfeffer, 1882, his name is ''not'' simply an orthographic error for the more commonly encountered molluscan authority Pfeiffer, i.e. Ludwig Karl Georg Pfeiffer, who lived 50 years earlier, from 1805 to 1877. Georg Johann Pfeffer also studied amphibians and reptiles, naming several new species. Two species of reptiles are named in his honor, ''Calamaria pfefferi Pfeffer's reed snake, ''Calamaria pfefferi'', is a species of dwarf snake in the family Colubridae. The spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant cloak or cape, see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for example, the siphon. Mantle cavity The ''mantle cavity'' is a central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon Inquirendum
In biological classification, a ''species inquirenda'' is a species of doubtful identity requiring further investigation. The use of the term in English-language biological literature dates back to at least the early nineteenth century. The term taxon inquirendum is broader in meaning and refers to an incompletely defined taxon of which the taxonomic validity is uncertain or disputed by different experts or is impossible to identify the taxon. Further characterization is required. See also * Glossary of scientific naming * '' Candidatus'', a proposed taxa based on incomplete evidence * '' incertae sedis'', a taxon of uncertain position in a classification * ''nomen dubium In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application. Zoology In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a s ...'', a name of unknown or doubtful application * Open nome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Chun
Carl Chun (1 October 1852 – 11 April 1914) was a German marine biologist. Chun was born in Höchst, today a part of Frankfurt, and studied zoology at the University of Leipzig, where from 1878 to 1883 he was privat-docent of zoology and an assistant to Rudolf Leuckart. After professorial posts in Königsberg (1883–1891) and Breslau (1891–1898), he returned to Leipzig as a professor of zoology.UNI Leipzig Professorenkatalog (biographical sketch) In 1888, Chun described seasonal vertical migration (SVM) which has a periodicity of ca. 1 year. Chun examined depth-stratified net samples from the |
Liocranchia Valdiviae
''Liocranchia'' is a genus of glass squid from the family Cranchiidae. They are moderate-sized with a long, spindle-shaped mantle which tapers to a point at the rear and they can attain mantle lengths of 250 mm. The species in ''Liocranchia'' have a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical and subtropical oceans although it has been suggested that on especies, ''Liocranchia reinhardti'' is associated with land masses. In seas off Hawaii waters ''L. reinhardti'' undergoes vertical migrations while '' L. valdiviae'' occurs in deep water is sedentary. They are eaten by many oceanic predator species. Characteristics ''Liocranchia'' species are characterised by having two rows of cartilagenous tubercules starting at each funnel-mantle fusion which diverge from each other along their length, each funnel having a valve and a very large ventral pad. The tentacles have duckers and pads in two series on distal 2/3 of tentacle stalk. In the paralarvae the eyes are not mounted on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Coburn Robson
Guy Coburn Robson (1888–1945) was a British zoologist, specializing in Mollusca, who first named and described ''Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni'', the colossal squid. Robson studied at the marine biological station in Naples, and joined the staff of the Natural History Museum in 1911, becoming Deputy Keeper of the Zoology Department from 1931 to 1936. Evolution Robson is best known for his major book ''The Variations of Animals in Nature'' (co-authored with O. W. Richards, 1936) which argued that although the fact of evolution is well established, the mechanisms are largely hypothetical and undemonstrated.Allee, W. C. (1937)''The Variation of Animals in Nature: A Critical Summary and Judgment of Evolutionary Theories by G. C. Robson, O. W. Richards'' ''American Journal of Sociology'' 42 (4): 596–597. The book claims that most differences among animal populations and related species are non-adaptive. It was published before major developments in the modern synthesis and contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liocranchia Gardineri
''Liocranchia'' is a genus of glass squid from the family Cranchiidae. They are moderate-sized with a long, spindle-shaped mantle which tapers to a point at the rear and they can attain mantle lengths of 250 mm. The species in ''Liocranchia'' have a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical and subtropical oceans although it has been suggested that on especies, ''Liocranchia reinhardti'' is associated with land masses. In seas off Hawaii waters ''L. reinhardti'' undergoes vertical migrations while '' L. valdiviae'' occurs in deep water is sedentary. They are eaten by many oceanic predator species. Characteristics ''Liocranchia'' species are characterised by having two rows of cartilagenous tubercules starting at each funnel-mantle fusion which diverge from each other along their length, each funnel having a valve and a very large ventral pad. The tentacles have duckers and pads in two series on distal 2/3 of tentacle stalk. In the paralarvae the eyes are not mounted on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectocotylized
A hectocotylus (plural: ''hectocotyli'') is one of the arms of male cephalopods that is specialized to store and transfer spermatophores to the female. Structurally, hectocotyli are muscular hydrostats. Depending on the species, the male may use it merely as a conduit to the female, analogously to a penis in other animals, or he may wrench it off and present it to the female. The hectocotyl arm was first described in Aristotle's biological works. Although Aristotle knew of its use in mating, he was doubtful that a tentacle could deliver sperm. The name ''hectocotylus'' was devised by Georges Cuvier, who first found one embedded in the mantle of a female argonaut. Supposing it to be a parasitic worm, in 1829 Cuvier gave it a generic name, combining the Greek word for "hundred" and Latin word for "hollow thing". Anatomy Generalized anatomy of squid and octopod hectocotyli: Variability Hectocotyli are shaped in many distinctive ways, and vary considerably between species. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladius (cephalopod)
The gladius (plural: ''gladii''), or pen, is a hard internal bodypart found in many cephalopods of the superorder Decapodiformes (particularly squids) and in a single extant member of the Octopodiformes, the vampire squid (''Vampyroteuthis infernalis''). It is so named for its superficial resemblance to the Roman short sword of the same name, and is a vestige of the ancestral mollusc shell, which was external. The gladius is located dorsally within the mantle and usually extends for its entire length. Composed primarily of chitin, it lies within the shell sac, which is responsible for its secretion. Gladii are known from a number of extinct cephalopod groups, including teudopseids (''e.g.'' '' Actinosepia'', '' Glyphiteuthis'', '' Muensterella'', '' Palaeololigo'', '' Teudopsinia'', '' Teudopsis'', and '' Trachyteuthis''), loligosepiids (''e.g.'' '' Geopeltis'', '' Jeletzkyteuthis'', and '' Loligosepia''), and prototeuthids (''e.g.'' '' Dorateuthis'', '' Paraplesioteuthis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralarvae
Paralarvae (singular: ''paralarva'') are young cephalopods in the planktonic stages between hatchling and subadult. This stage differs from the larval stage of animals that undergo true metamorphosis Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse .... Paralarvae have been observed only in members of the orders Octopoda and Teuthida. The term was first introduced by Richard E. Young and Robert F. Harman in 1988. Paralarvae usually spend an uncertain amount of time in the plankton and then typically descend to an adult habitat in the mesopelagic or bathypelagic zone. Their population abundance is dependent on the variation of mortality rates during the planktonic period. See also * Larva * Crustacean larvae References Further reading *Bigelow, Keith A. "Age and growth in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentacles
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions. A tentacle is similar to a cirrus, but a cirrus is an organ that usually lacks the tentacle's strength, size, flexibility, or sensitivity. A nautilus has cirri, but a squid has tentacles. Invertebrates Molluscs Many molluscs have tentacles of one form or another. The most familiar are those of the pulmonate land snails, which usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |