|
Diel Vertical Migration
Diel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The adjective "diel" ( IPA: , ) comes from , and refers to a 24-hour period. The migration occurs when organisms move up to the uppermost layer of the water at night and return to the bottom of the daylight zone of the oceans or to the dense, bottom layer of lakes during the day. DVM is important to the functioning of deep-sea food webs and the biologically-driven sequestration of carbon. In terms of biomass, DVM is the largest synchronous migration in the world. It is not restricted to any one taxon, as examples are known from crustaceans (copepods), molluscs (squid), and ray-finned fishes (trout). The phenomenon may be advantageous for a number of reasons, most typically to access food and to avoid predators. It is triggered by various stimuli, the most prominent being changes in light-inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animation Of Diel Migration
Animation is a filmmaking technique whereby image, still images are manipulated to create Motion picture, moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on cel, transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animation has been recognised as an artistic medium, specifically within the Entertainment#Industry, entertainment industry. Many animations are either traditional animations or computer animations made with computer-generated imagery (CGI). Stop motion animation, in particular claymation, has continued to exist alongside these other forms. Animation is contrasted with live action, although the two do not exist in isolation. Many moviemakers have produced Live-action animation, films that are a hybrid of the two. As CGI increasingly Photorealism, approximates photographic imagery, filmmakers can easily Compositing, composite 3D animations into their film rather than using practical effects for showy visual effects (VFX). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trout
Trout (: trout) is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used for some similar-shaped but non-salmonid fish, such as the spotted seatrout/speckled trout (''Cynoscion nebulosus'', which is actually a croaker). Trout are closely related to salmon and have similar migratory life cycles. Most trout are strictly potamodromous, spending their entire lives exclusively in freshwater lakes, rivers and wetlands and migrating upstream to spawn in the shallow gravel beds of smaller headwater creeks. The hatched fry and juvenile trout, known as ''alevin'' and ''parr'', will stay upstream growing for years before migrating down to larger waterbodies as maturing adults. There are some anadromous species of trout, such as the steelhead (a coastal subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scripps Institution Of Oceanography
Scripps Institution of Oceanography (SIO) is the center for oceanography and Earth science at the University of California, San Diego. Its main campus is located in La Jolla, with additional facilities in Point Loma. Founded in 1903 and incorporated into the University of California system in 1912, the institution has since broadened its research focus to encompass the physics, chemistry, geology, biology, and climate of the Earth. The institution awards the Nierenberg Prize annually to recognize researchers with exceptional contributions to science in public interest. History Founding Scripps Institution of Oceanography can trace its beginnings back to William Ritter, a biologist originally from Wisconsin. In 1891, Ritter was offered a job teaching biology at the University of California, Berkeley and married Mary Bennett. Their honeymoon and subsequent biological studies took them to San Diego, where Ritter met a local physician and naturalist, Fred Baker, who would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin W
Martin may refer to: Places Antarctica * Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land * Port Martin, Adelie Land * Point Martin, South Orkney Islands Europe * Martin, Croatia, a village * Martin, Slovakia, a city * Martín del Río, Aragón, Spain * Martín River, a tributary of the Ebro river in Spain * Martin (Val Poschiavo), Switzerland England * Martin, Hampshire * Martin, Kent * Martin, East Lindsey, Lincolnshire, a hamlet and former parish * Martin, North Kesteven, Lincolnshire, a village and parish * Martin Hussingtree, Worcestershire * Martin Mere, a lake in Lancashire ** WWT Martin Mere, a wetland nature reserve that includes the lake and surrounding areas North America Canada * Rural Municipality of Martin No. 122, Saskatchewan, Canada * Martin Islands, Nunavut, Canada United States * Martin, Florida * Martin, Georgia * Martin, Indiana * Martin, Kentucky * Martin, Louisiana * Martin, Michigan * Martin, Nebraska * Martin, North Dakota * Martin, Ohio * Martin, South Caro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echo Sounding
Echo sounding or depth sounding is the use of sonar for ranging, normally to determine the depth (coordinate), depth of water (bathymetry). It involves transmitting acoustic waves into water and recording the time interval between emission and return of a pulse; the resulting time of flight, along with knowledge of the speed of sound in water, allows determining the distance between sonar and target. This information is then typically used for navigation purposes or in order to obtain depths for Nautical chart, charting purposes. Echo sounding can also be used for ranging to other targets, such as fish schools. Hydroacoustic assessments have traditionally employed mobile surveys from boats to evaluate fish biomass and spatial distributions. Conversely, fixed-location techniques use stationary transducers to monitor passing fish. The word ''Depth sounding, sounding'' is used for all types of depth measurements, including those that don't use sound, and is unrelated in origin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Scattering Layer
The deep scattering layer, sometimes referred to as the sound scattering layer, is a layer in the ocean consisting of a variety of marine animals. It was discovered through the use of sonar, as ships found a layer that scattered the sound and was thus sometimes mistaken for the seabed. For this reason it is sometimes called the false bottom or phantom bottom. It can be seen to rise and fall each day in keeping with diel vertical migration. Sonar operators, using the newly developed sonar technology during World War II, were puzzled by what appeared to be a false sea floor 300–500 metres (980–1,640 ft) deep at day, and less deep at night. Initially, this mysterious phenomenon was called the ECR layer using the initials of its three discoverers. It turned out to be due to millions of marine organisms, most particularly small mesopelagic fish, with swim bladders that reflected the sonar. These organisms migrate up into shallower water at dusk to feed on plankton. The laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and sodar (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low ( infrasonic) to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish, and baleen whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, microscopic fungi, and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. fresh water, Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in lakes and rivers. Mostly, plankton just drift where currents take them, though some, like jellyfish, swim slowly but not fast enough to generally overcome the influence of currents. Although plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, there are also airborne versions that live part of their lives drifting in the at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the Order (biology), order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their Saltation (gait), saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to Fresh water, freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are ''Daphnia pulex, D. pulex'' (small and most common) and ''Daphnia magna, D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae group instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, although this division is not visible. The hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in natural sciences research in the early 19th century and was instrumental in establishing the fields of comparative anatomy and paleontology through his work in comparing living animals with fossils. Cuvier's work is considered the foundation of vertebrate paleontology, and he expanded Linnaean taxonomy by grouping classes into phylum, phyla and incorporating both fossils and living species into the classification. Cuvier is also known for establishing extinction as a fact—at the time, extinction was considered by many of Cuvier's contemporaries to be merely controversial speculation. In his ''Essay on the Theory of the Earth'' (1813) Cuvier proposed that now-extinct species had been wiped out by periodic catastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
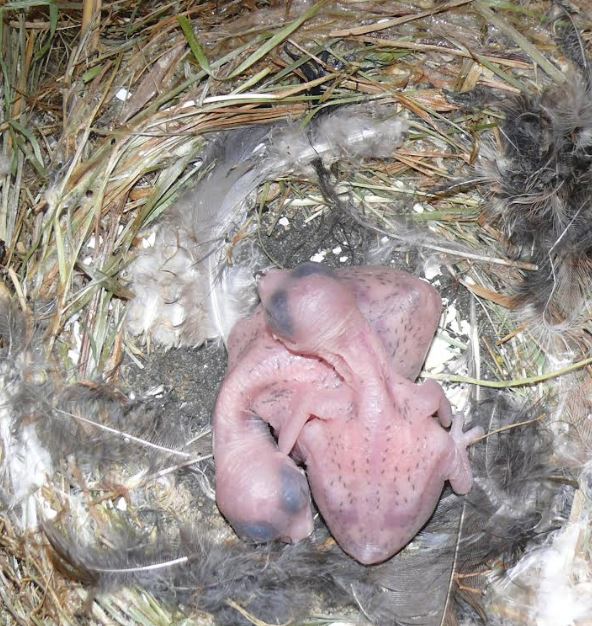
Common Swift
The common swift (''Apus apus'') is a medium-sized bird, superficially similar to the barn swallow or Common house martin, house martin but somewhat larger, though not stemming from those passerine species, being in the order Apodiformes. The resemblances between the groups are due to convergent evolution, reflecting similar contextual development. The swifts' nearest relatives are the New World hummingbirds and the Southeast Asian treeswifts. Its scientific name ''Apus'' is Latin for a swift, thought by the ancients to be a type of swallow with no feet (from Ancient Greek α, ''a'', "without", and πούς, ''pous'', "foot"). Swifts have very short legs which they use primarily for clinging to vertical surfaces (hence the German name ''Mauersegler'', literally meaning "wall-glider"). They never settle voluntarily on the ground where they would be vulnerable to accidents and predation, and non-breeding individuals may spend up to ten months in continuous flight. Taxonomy The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |