|
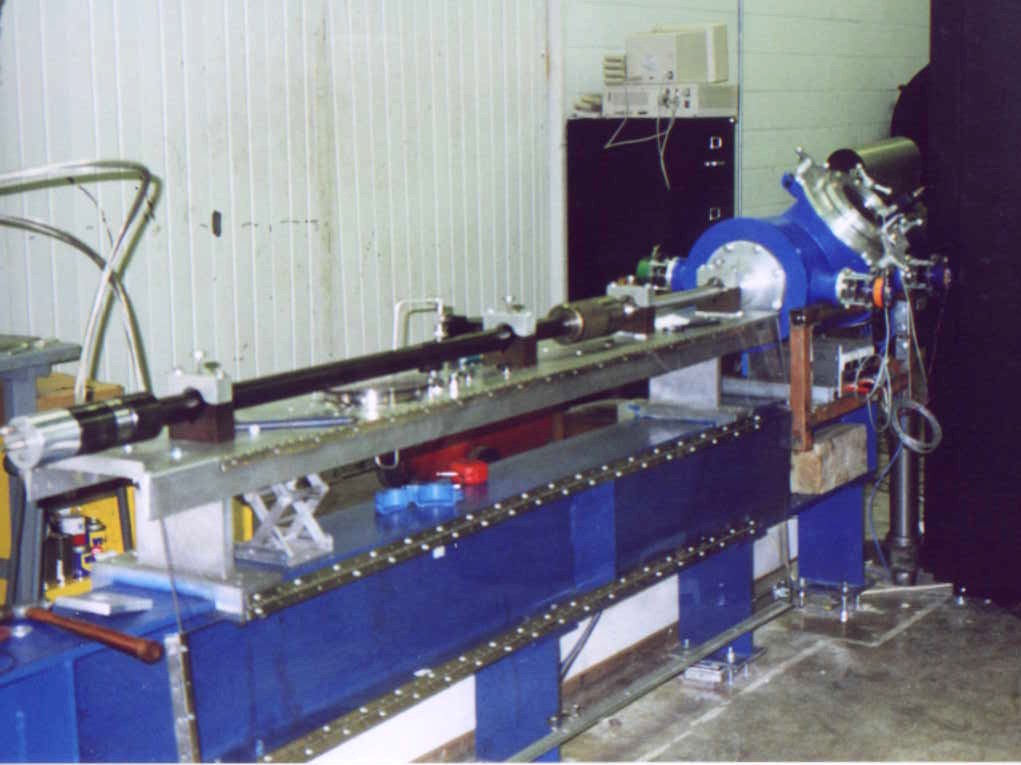
Light-gas Gun
The light-gas gun is an apparatus for physics experiments. It is a highly specialized gun designed to generate extremely high velocities. It is usually used to study high-speed impact phenomena ( hypervelocity research), such as the formation of impact craters by meteorites or the erosion of materials by micrometeoroids. Some basic material research relies on projectile impact to create high pressure; such systems are capable of forcing liquid hydrogen into a metallic state. Operation A light-gas gun works on the same principle as a spring piston airgun. A large-diameter piston is used to force a gaseous working fluid through a smaller-diameter barrel containing the projectile to be accelerated. This reduction in diameter acts as a lever, increasing the speed while decreasing the pressure. In an airgun, the large piston is powered by a spring or compressed air, and the working fluid is atmospheric air. In a light-gas gun, the piston is powered by a chemical reaction (usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield Gun
image:Us machine gunner.jpg, A United States Marine Corps, U.S. Marine manning an M240 machine gun equipped with a gun shield A gun shield is a flat (or sometimes 14 cm/50 3rd Year Type naval gun, curved) piece of armor designed to be mounted on a crew-served weapon such as a machine gun, automatic grenade launcher, or artillery piece. Military Some mounted machine guns and artillery pieces are equipped with metal armor plates to protect the gunners from Small Arms and Light Weapons, small arms fire and Fragmentation (weaponry), shrapnel from explosions. They were fitted to some armored fighting vehicles and patrol boats during the Vietnam War. Gun shields fell out of widespread use after the Vietnam War, but they have seen a resurgence in popularity during the 1980s and 1990s. Israel Defense Forces, Israeli military analysts began urging the use of gun shields, pointing to the grave risk to soldiers exposed to fire from automatic weapons. In particular, it was noted that many c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-density Polyethylene
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or " polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, HDPE is used in the production of plastic bottles, corrosion-resistant piping, geomembranes and plastic lumber. HDPE is commonly recycled, and has the number "2" as its resin identification code. In 2008, the global HDPE market reached a volume of more than 30 million tons. Properties HDPE is known for its high strength-to-density ratio. The density of HDPE ranges from 930 to 970 kg/m3. Although the density of HDPE is only marginally higher than that of low-density polyethylene, HDPE has little branching, giving it stronger intermolecular forces and tensile strength (38 MPa versus 21 MPa) than LDPE. The difference in strength exceeds the difference in density, giving HDPE a higher specific strength. It is also harder and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDIO KEW Lexan Projectile , an organization set up to oversee the Strategic Defense Initiative; now known as the Missile Defense Agency.
{{disambig ...
SDIO may refer to: * Secure Digital Input Output, a type of Secure Digital card interface. It can be used as an interface for input or output devices. * Strategic Defense Initiative Organization The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic nuclear missiles. The program was announced in 1983, by President Ronald Reagan. Reagan called for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiabatic Process
An adiabatic process (''adiabatic'' ) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat between the thermodynamic system and its Environment (systems), environment. Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transfers energy to the surroundings only as Work (thermodynamics), work and/or mass flow.. A translation may be founhere. Also a mostly reliabltranslation is to be foundin As a key concept in thermodynamics, the adiabatic process supports the theory that explains the first law of thermodynamics. The opposite term to "adiabatic" is ''diabatic''. Some chemical and physical processes occur too rapidly for energy to enter or leave the system as heat, allowing a convenient "adiabatic approximation".Bailyn, M. (1994), pp. 52–53. For example, the adiabatic flame temperature uses this approximation to calculate the upper limit of fire, flame temperature by assuming combustion loses no heat to its surroundings. In meteorology, adiabatic expansion an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell–Boltzmann Distribution
In physics (in particular in statistical mechanics), the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution, or Maxwell(ian) distribution, is a particular probability distribution named after James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann. It was first defined and used for describing particle speeds in ideal gas, idealized gases, where the particles move freely inside a stationary container without interacting with one another, except for very brief collisions in which they exchange energy and momentum with each other or with their thermal environment. The term "particle" in this context refers to gaseous particles only (atoms or molecules), and the system of particles is assumed to have reached thermodynamic equilibrium. The energies of such particles follow what is known as Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics, and the statistical distribution of speeds is derived by equating particle energies with kinetic energy. Mathematically, the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution is the chi distribution with three degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Theory Of Gases
The kinetic theory of gases is a simple classical model of the thermodynamic behavior of gases. Its introduction allowed many principal concepts of thermodynamics to be established. It treats a gas as composed of numerous particles, too small to be seen with a microscope, in constant, random motion. These particles are now known to be the atoms or molecules of the gas. The kinetic theory of gases uses their collisions with each other and with the walls of their container to explain the relationship between the macroscopic properties of gases, such as volume, pressure, and temperature, as well as transport properties such as viscosity, thermal conductivity and mass diffusivity. The basic version of the model describes an ideal gas. It treats the collisions as perfectly elastic and as the only interaction between the particles, which are additionally assumed to be much smaller than their average distance apart. Due to the time reversibility of microscopic dynamics ( microsco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elasticity (solid mechanics), elastic medium. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At , the speed of sound in dry air (sea level 14.7 psi) is about . The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in dry air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In colloquial speech, ''speed of sound'' refers to the speed of sound waves in Earth's atmosphere, air. However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at in air, it travels at in water (almost 4.3 times a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firearm
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions). The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes containing gunpowder and pellet projectiles were mounted on spears to make the portable fire lance, operable by a single person, which was later used effectively as a shock weapon in the siege of De'an in 1132. In the 13th century, fire lance barrels were replaced with metal tubes and transformed into the metal-barreled hand cannon. The technology gradually spread throughout Eurasia during the 14th century. Older firearms typically used black powder as a propellant, but modern firearms use smokeless powder or other explosive propellants. Most modern firearms (with the notable exception of smoothbore shotguns) have rifled barrels to impart spin to the projectile for improved flight stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airgun
An air gun or airgun is a gun that uses energy from compressed air or other gases that are mechanically pressurized and then released to propel and accelerate projectiles, similar to the principle of the primitive blowgun. This is in contrast to a firearm, which shoots projectiles using energy generated via exothermic combustion ( detonation) of chemical propellants, most often black powder or smokeless powder. Air guns come in both long gun (air rifle) and handgun (air pistol) forms. Both types typically propel metallic projectiles that are either diabolo-shaped pellets or spherical shots called BBs, although in recent years Minié ball-shaped cylindro-conoidal projectiles called slugs are gaining more popularity. Certain types of air guns (usually air rifles) may also launch fin-stabilized projectile such as darts (e.g., tranquilizer guns) or hollow-shaft arrows (so-called "airbows"). The first air guns were developed as early as the 16th century, and have s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Range-G
AEDC Range G is a two-stage light-gas gun owned by the United States Air Force. History Constructed in 1962, the AEDC Range-G is the largest routinely operated light-gas gun in the United States. It is located at Arnold Engineering Development Complex on Arnold Air Force Base. The design of the range came from collaboration between German and American scientists after World War II. Range-G has played a crucial role in lethality development for many defense programs. The range has performed more than 7,000 high speed launches. Capabilities Range G is capable of launching projectiles up to speeds of 7 km/s (22,965 ft/s). The gun has an interchangeable barrel that can accommodate projectile diameters of 3.3 inches, 4.0 inches, and 8.0 inches. The projectile is launched into a 10 ft diameter test chamber that is approximately 1000 ft long. This chamber can be conditioned to pressures from 0.2 torr (26.7 pascals) to 1.7 atmospheres (172 kilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Air Force Base
Arnold Air Force Base (Arnold AFB) is a United States Air Force base located in Coffee County, Tennessee, Coffee and Franklin County, Tennessee, Franklin counties, Tennessee, adjacent to the city of Tullahoma, Tennessee, Tullahoma. It is named for Henry H. Arnold, General Henry "Hap" Arnold, the father of the U.S. Air Force. The airfield was closed in 2009 but has since reopened. The first landing since 2009 took place in May 2023. Army aviation assets (helicopters) continue to utilize Arnold as part of missions supporting Fort Campbell, Kentucky or the Tennessee Army National Guard. The base is home to the Arnold Engineering Development Complex (AEDC), the most advanced and largest complex of flight simulation test facilities in the world. The center operates 58 aerodynamic and propulsion wind tunnels, rocket and turbine engine test cells, space environmental chambers, arc heaters, ballistic ranges and other specialized units. AEDC is an Air Force Test Center organization. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AEDC Range-G Launcher Facility
The Arnold Engineering Development Complex (AEDC), Arnold Engineering Development Center before July 2012, is an Air Force Materiel Command facility under the control of the Air Force Test Center (AFTC). Named for General Henry "Hap" Arnold, the father of the U.S. Air Force, AEDC is the most advanced and largest complex of flight simulation test facilities in the world. Headquartered at Arnold Air Force Base, Tennessee, the Complex also operates from geographically separated units at Ames Research Center, Mountain View and Edwards AFB, California; Peterson AFB, Colorado; Eglin AFB, Florida; the Federal Research Center at White Oak, Maryland; Holloman AFB, Kirtland AFB, and White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico; Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio, and Hill AFB, Utah. AEDC operates more than 68 test facilities, including, but not limited to, aerodynamic and propulsion wind tunnels, rocket and turbine engine test cells, environmental chambers, arc heaters, ballistic ranges, sled tracks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |