|
Licking
Licking is the action (philosophy), action of passing the tongue over a surface, typically either to deposit saliva onto the surface, or to collect liquid, food or minerals onto the tongue for ingestion, or to animal communication, communicate with other animals. Many animals both personal grooming, groom themselves and Eating, eat or drinking, drink by licking. In animals Grooming: Animals commonly clean themselves through licking. In mammals, licking helps keep the fur clean and untangled. The tongues of many mammals have a rough upper surface that acts like a brush when the animal licks its fur. Certain reptiles, such as geckos, clean their eyes by licking them. Mammals typically lick their offspring clean immediately after birth; in many species this is necessary to free the newborn from the amniotic sac. The licking not only cleans and dries the offspring's fur, but also stimulates its breathing and digestion, digestive processes. Food and water acquisition: Hummingbir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lipase and amylase), antiseptic, antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes). The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay. Saliva also performs a lubricating function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the oral mucosa from desiccation, drying out. Various animal species have special uses for saliva that go beyond predigestion. Some Swift (bird), swifts use their gummy saliva to build nests. ''Aerodramus'' bird nest, nests form the basis of edible bird's ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
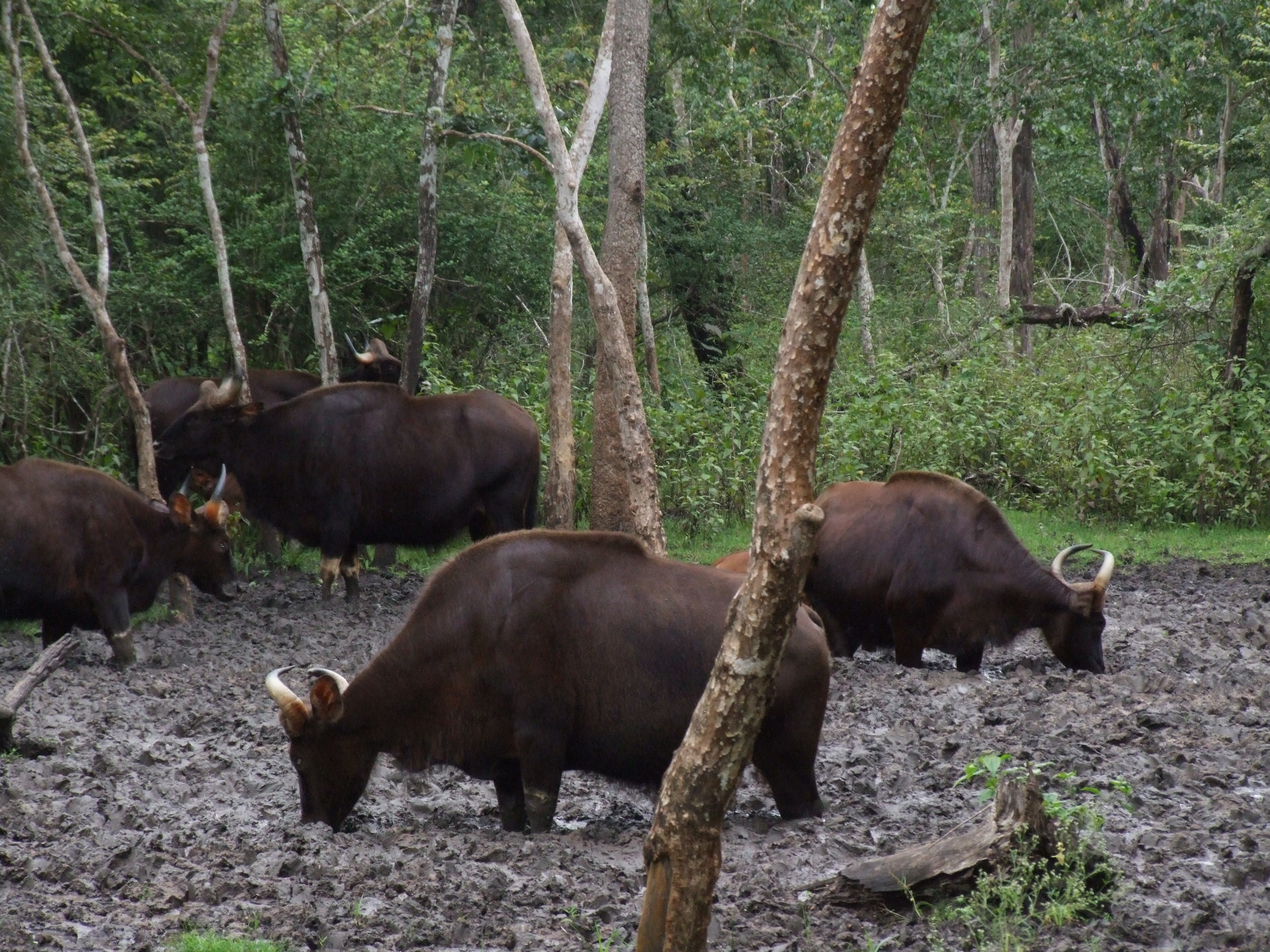
Mineral Lick
A mineral lick (also known as a salt lick) is a place where animals can go to lick essential mineral nutrients from a deposit of salts and other minerals. Mineral licks can be naturally occurring or artificial (such as blocks of salt that farmers place in pastures for livestock to lick). Natural licks are common, and they provide essential elements such as phosphorus and the biometals (sodium, calcium, iron, zinc, and trace elements) required in the springtime for bone, muscle and other growth in deer and other wildlife, such as moose, elephants, tapirs, cattle, woodchucks, domestic sheep, fox squirrels, mountain goats and porcupines. Such licks are especially important in ecosystems with poor general availability of nutrients. Harsh weather exposes salty mineral deposits that draw animals from miles away for a taste of needed nutrients. It is thought that certain fauna can detect calcium in salt licks. Overview Many animals regularly visit mineral licks to consume clay, suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gecko
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates throughout the world. They range from . Geckos are unique among lizards for their vocalisations, which differ from species to species. Most geckos in the family Gekkonidae use chirping or clicking sounds in their social interactions. Tokay geckos (''Gekko gecko'') are known for their loud mating calls, and some other species are capable of making hissing noises when alarmed or threatened. They are the most species-rich group of lizards, with about 1,500 different species worldwide. All geckos, except species in the family Eublepharidae lack eyelids; instead, the outer surface of the eyeball has a transparent membrane, the cornea. They have a fixed lens within each iris that enlarges in darkness to let in more light. Since they cannot blink, species without eyelids generally l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
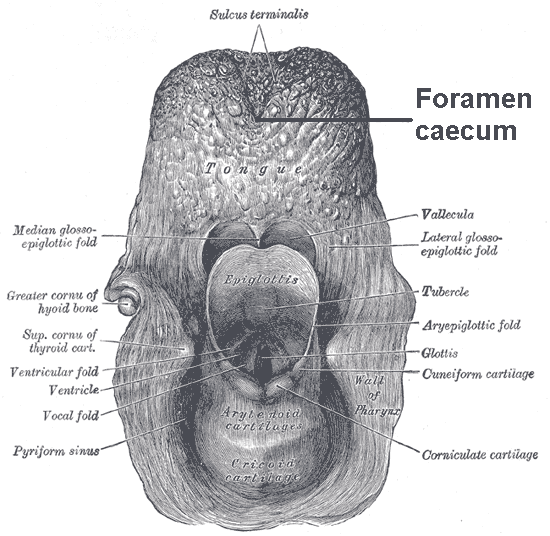
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of muscles of the tongue. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to bone. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 Order (biology), orders. The largest Order (biology), orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, pinniped, seals, and others). In terms of cladistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the fetus at a developmental stage when it is ready to feed and breathe. In some species the offspring is precocial and can move around almost immediately after birth but in others it is altricial and completely dependent on parenting. In marsupials, the fetus is born at a very immature stage after a short gestation and develops further in its mother's womb pouch. It is not only mammals that give birth. Some reptiles, amphibians, fish and invertebrates carry their developing young inside them. Some of these are ovoviviparous, with the eggs being hatched inside the mother's body, and others are viviparous, with the embryo developing inside her body, as in the case of mammals. Mammals Large mammals, such as primates, cattle, horses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongues
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of muscles of the tongue. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomeronasal Organ
The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum, in the nasal cavity just above the roof of the mouth (the hard palate) in various tetrapods. The name is derived from the fact that it lies adjacent to the unpaired vomer bone (from Latin 'plowshare', for its shape) in the nasal septum. It is present and functional in all snakes and lizards, and in many mammals, including cats, dogs, cattle, pigs, and some primates. Some humans may have physical remnants of a VNO, but it is vestigial and non-functional. The VNO contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons which have receptors that detect specific non-volatile (liquid) organic compounds which are conveyed to them from the environment. These compounds emanate from prey, predators, and the compounds called sex pheromones from potential mates. Activation of the VNO triggers an appropriate behavioral response to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangaroo Licking Itself To Cool
Kangaroos are four marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern grey kangaroo, and western grey kangaroo. Kangaroos are indigenous to Australia and New Guinea. The Australian government estimates that 42.8 million kangaroos lived within the commercial harvest areas of Australia in 2019, down from 53.2 million in 2013. As with the terms "wallaroo" and "wallaby", "kangaroo" refers to a paraphyletic grouping of species. All three terms refer to members of the same taxonomic family, Macropodidae, and are distinguished according to size. The largest species in the family are called "kangaroos" and the smallest are generally called "wallabies". The term "wallaroos" refers to species of an intermediate size. There are also the tree-kangaroos, another type of macropod, which inhabit the tropical ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of muscles of the tongue. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to bone. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flehmen
The flehmen response (; from German ''flehmen'', to bare the upper teeth, and Upper Saxon German ''flemmen'', to look spiteful), also called the flehmen position, flehmen reaction, flehmen grimace, flehming, or flehmening, is a behavior in which an animal curls back its upper lip exposing its front teeth, inhales with the nostrils usually closed, and then often holds this position for several seconds. It may be performed over a sight or substance of particular interest to the animal, or may be performed with the neck stretched and the head held high in the air. Flehmen is performed by a wide range of mammals, including ungulates and felids. The behavior facilitates the transfer of pheromones and other scents into the vomeronasal organ (VNO, or Jacobson's organ) located above the roof of the mouth via a duct which exits just behind the front teeth of the animal. Etymology The word originates from the German verb ''flehmen'', to bare the upper teeth. It comes from the Upper Saxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suction
Suction is the colloquial term to describe the air pressure differential between areas. Removing air from a space results in a pressure differential. Suction pressure is therefore limited by external air pressure. Even a perfect vacuum cannot suck with more pressure than is available in the surrounding environment. Suctions can form on the sea, for example, when a ship founders. When the pressure in one part of a physical system is reduced relative to another, the fluid in the higher pressure region will exert a force relative to the region of lowered pressure, referred to as pressure-gradient force. Pressure reduction may be static, as in a piston and cylinder arrangement, or dynamic, as in the case of a vacuum cleaner when air flow results in a reduced pressure region. When animals breathe, the diaphragm and muscles around the rib cage cause a change of volume in the lungs. The increased volume of the chest cavity decreases the pressure inside, creating an imbalance wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)