Suction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
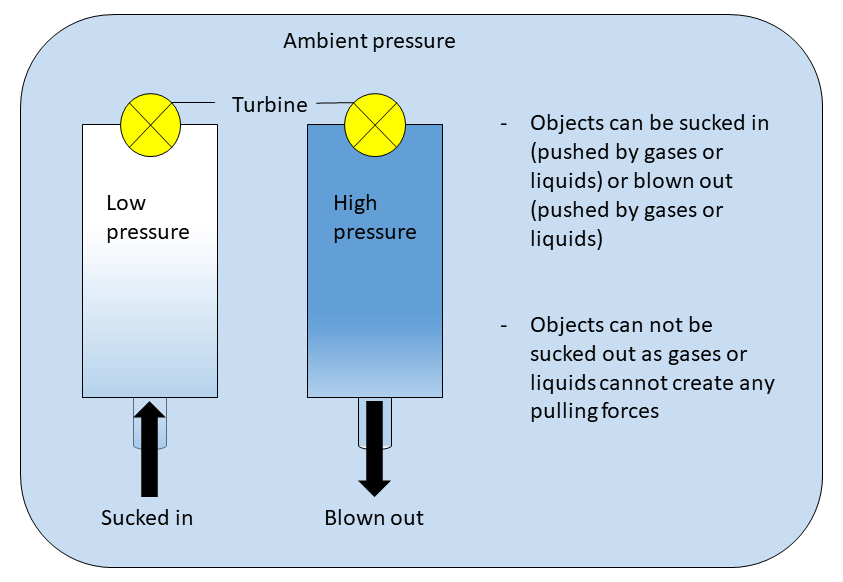 Suction is the day-to-day term for the movement of gases or
Suction is the day-to-day term for the movement of gases or
 Suction is the day-to-day term for the movement of gases or
Suction is the day-to-day term for the movement of gases or liquid
Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The density of a liquid is usually close to th ...
s along a pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
gradient with the implication that the movement occurs because the lower pressure pulls the gas or liquid. However, the forces acting in this case do not originate from just the lower pressure side, but also from the side of the higher pressure, as a reaction to the pressure difference.
When the pressure in one part of a physical system
A physical system is a collection of physical objects under study. The collection differs from a set: all the objects must coexist and have some physical relationship.
In other words, it is a portion of the physical universe chosen for analys ...
is reduced relative to another, the fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are M ...
or gas in the higher pressure region will exert a force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
relative to the region of lowered pressure, referred to as pressure-gradient force. If all gas or fluid is removed the result is a perfect vacuum in which the pressure is zero. Hence, no negative pressure forces can be generated. Accordingly, from a physics point of view, the objects are not pulled but pushed.
Examples
Pressure reduction may be static, as in apiston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder a ...
and cylinder arrangement, or dynamic, as in the case of a vacuum cleaner
A vacuum cleaner, also known simply as a vacuum, is a device that uses suction, and often agitation, in order to remove dirt and other debris from carpets, hard floors, and other surfaces.
The dirt is collected into a dust bag or a plastic bin. ...
when air flow results in a reduced pressure region.
When animals breathe, the diaphragm and muscles around the rib cage cause a change of volume in the lungs. The increased volume of the chest cavity decreases the pressure inside, creating an imbalance with the ambient air pressure, resulting in suction. Similarly, when a straw is used to suck a liquid from a glass into the mouth, the atmospheric pressure on the fluid in the glass pushes the liquid up through the straw along the pressure gradient.
A common semantic mistake in aviation accident reporting is describing people or objects as being 'sucked out' during rapid decompression events, when physically they are 'blown out' by the higher internal cabin pressure rushing toward the lower ambient pressure outside the plane — the opposite phenomenon to what happens when an object is placed too close to a running jet engine creating the risk of being sucked in.
See also
*Pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
* Vacuum pump
* Suction devices used in medicine
* Implosion
* Suction cup
* Suction cupping
References
{{reflist Physical quantities Units of pressure Vacuum