|
Kosmos 869
Kosmos 869 (russian: Космос 869 meaning ''Cosmos 869'') was an uncrewed spacecraft, uncrewed military Soyuz spacecraft, Soyuz 7K-S test. It was a somewhat successful mission. This was the third and final test flight of a new Soyuz spacecraft type 7K-S. It was designed to be a spaceship for military solo missions. At the time of the launch the program had already been discontinued. The completed spaceships were launched as uncrewed test flights: Kosmos 670, Kosmos 772 and Kosmos 869. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S. *Mass: 6800 kg. *Crew: None. *Launched: November 29, 1976. *Landed: December 17, 1976 10:31 UTC. *Perigee: 209 km. *Apogee: 289 km. *Inclination: 51.7 deg. *Duration: 17.99 days. Maneuver Summary *196 km X 290 km orbit to 187 km X 335 km orbit. Delta V: 15 m/s. *187 km X 335 km orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncrewed Spacecraft
Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board, used for robotic spaceflight. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be remote controlled, remote guided or even autonomous, meaning they have a pre-programmed list of operations, which they will execute unless otherwise instructed. Many habitable spacecraft also have varying levels of robotic features. For example, the space stations Salyut 7 and Mir, and the International Space Station module Zarya, were capable of remote guided station-keeping and docking maneuvers with both resupply craft and new modules. The most common uncrewed spacecraft categories are robotic spacecraft, unmanned resupply spacecraft, space probed space observatories. Not every uncrewed spacecraft is a robotic spacecraft; for example, a reflector ball is a non-robotic uncrewed spacecraft. Examples Selected lunar probes * Luna program — USSR Lunar exploration (1959 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-25
Soyuz TM-25 was a crewed Soyuz spaceflight, which launched on February 10, 1997.The mission report is available here: http://www.spacefacts.de/mission/english/soyuz-TM-25.htm It transported Russian cosmonauts Vasily Tsibliyev, Aleksandr Lazutkin, and German cosmonaut Reinhold Ewald to Mir. Crew Mission highlights This was the 30th expedition to Mir. An ESA , owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (120 ... astronaut from Germany was included on the mission. Soyuz TM-25 is a Russian spacecraft that was launched to carry astronauts and supplies to Mir station. It was launched by a Soyuz-U rocket from Baykonur cosmodrome at 14:09 UT to ferry three cosmonauts for a 162-day stay at the station; it docked with the station at 15:51 UT on 12 February 97. Within meters of automatic appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1976 In The Soviet Union
The following lists events that happened during 1976 in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Incumbents * General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union: Leonid Brezhnev * Premier of the Soviet Union: Alexei Kosygin * Chairman of the Russian SFSR: Mikhail Solomentsev Events January February * February 24 - 25th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union March April May June * June 1 - The Philippine government opens relations with the Soviet Union. July September October November December Births * 9 August – Sergei Tyumentsev, former Russian professional football player * 31 August – Alikhan Ramazanov, former Russian professional football player Deaths * 11 January – Aleksey Sorokin, member of Soviet cosmonaut program (b. 1931) * 26 April – Andrei Grechko, Soviet general, Marshal of the Soviet Union and Minister of Defense (b. 1903) * 30 November – Ivan Yakubovsky, Marshal of the Soviet Union (b. 1912) See also *1976 in fine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Uncrewed Test Flights
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Military Spacecraft
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos Satellites
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity. The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering scientific, religious or philosophical aspects of the cosmos and its nature. Religious and philosophical approaches may include the cosmos among spiritual entities or other matters deemed to exist outside the physical universe. Etymology The philosopher Pythagoras first used the term ''kosmos'' ( grc, κόσμος, Latinized ''kósmos'') for the order of the universe. Greek κόσμος "order, good order, orderly arrangement" is a word with several main senses rooted in those notions. The verb κοσμεῖν (''κοσμεῖν'') meant generally "to dispose, prepare", but especially "to order and arrange (troops for battle), to set (an army) in array"; also "to establish (a government or regime)" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos 772
Kosmos 772 (russian: Космос 772 meaning ''Cosmos 772'') was an uncrewed military Soyuz 7K-S test. It was an unsuccessful mission as only one transmitter worked. Only the 166 MHz frequency transmitter operated, all of the other normal Soyuz wavelengths transmitters failed. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S *Mass: 6750 kg *Crew: None *Launched: September 29, 1975 *Landed: October 3, 1975 4:10 UTC *Perigee: 154 km *Apogee: 245 km *Inclination: 51.8 deg *Duration: 3.99 days Maneuver Summary *193 km X 270 km orbit to 195 km X 300 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s. *196 km X 300 km orbit to 196 km X 328 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s. Total Delta V: 16 m/s. See also *Soyuz 7K-OK *Soyuz TM-25 Soyuz TM-25 was a crewed Soyuz spaceflight, which launched on February 10, 1997.The mission report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos 670
Kosmos 670 (russian: Космос 670 meaning ''Cosmos 670'') was an unmanned Soyuz 7K-S test. It used a new and unique inclination of 50.6 degree. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: 7K-S *Mass: 6700 kg *Crew: None *Launched: August 6, 1974 *Landed: August 8, 1974 23:59 UTC. *Perigee: 221 km *Apogee: 294 km *Inclination: 50.6 deg *Duration: 2.99 days See also *Cosmos 772 Kosmos 772 (russian: Космос 772 meaning ''Cosmos 772'') was an uncrewed military Soyuz 7K-S test. It was an unsuccessful mission as only one transmitter worked. Only the 166 MHz frequency transmitter operated, all of the other normal Soyuz w ... * Cosmos 869 References Kosmos 0670 1974 in the Soviet Union Spacecraft launched in 1974 Soyuz uncrewed test flights {{USSR-spacecraft-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-OK
Soyuz 7K-OK was the first generation of Soyuz spacecraft and was flown between 1967 and 1971. The 7K-OK was used for the first ferry flights to the Salyut space station program, beginning a long history of space station service that continues today with the International Space Station (ISS). , the 7K-OK is notable for the only fatalities of the Soyuz programme, with Soyuz 1 in 1967 (sole crew-member killed by parachute failure) and Soyuz 11 in 1971 (three crew killed by depressurisation during reentry). The first uncrewed automated docking in the history of spaceflight was achieved between 7K-OK spacecraft Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188 in 1967. Additionally firsts include the first docking between two crewed spacecraft (Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5), the longest crewed flight involving only one spacecraft (the 18-day flight of Soyuz 9 in 1970), and the first successful transfer of crew to the first space station in the history of space flight (Soyuz 11 and Salyut 1 in 1971). Descript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
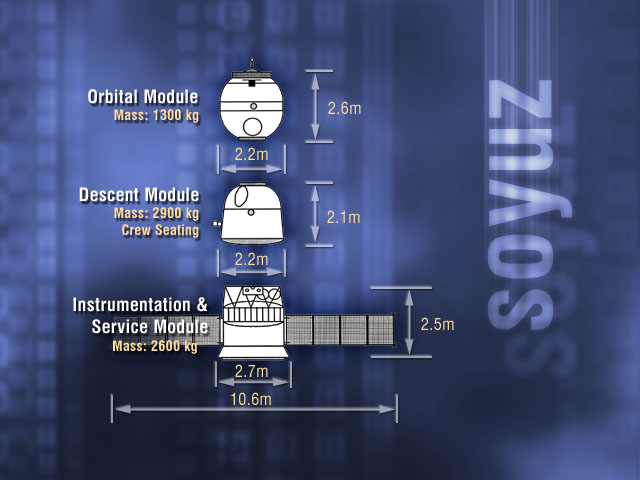
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)