|
Soyuz TM-25
Soyuz TM-25 was a crewed Soyuz spaceflight, which launched on February 10, 1997.The mission report is available here: http://www.spacefacts.de/mission/english/soyuz-TM-25.htm It transported Russian cosmonauts Vasily Tsibliyev, Aleksandr Lazutkin, and German cosmonaut Reinhold Ewald to Mir. Crew Mission highlights This was the 30th expedition to Mir. An ESA , owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (120 ... astronaut from Germany was included on the mission. Soyuz TM-25 is a Russian spacecraft that was launched to carry astronauts and supplies to Mir station. It was launched by a Soyuz-U rocket from Baykonur cosmodrome at 14:09 UT to ferry three cosmonauts for a 162-day stay at the station; it docked with the station at 15:51 UT on 12 February 97. Within meters of automatic appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosaviakosmos
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency, which was established on 25 February 1992russian: Российское космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (russian: РКА). and restructured in 1999 and 2004, as the Russian Aviation and Space Agencyrussian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never more than about one-third of the radius of Earth. The term ''LEO region'' is also used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. All crewed space stations to date have been within LEO. From 1968 to 1972, the Apollo program's lunar missions sent humans beyond LEO. Since the end of the Apollo program, no human spaceflights have been beyond LEO. Defining characteristics A wide variety of sources define LEO in terms of altitude. The altitude of an object in an elliptic orbit can vary significantly along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily Tsibliyev
Vasily Vasiliyevich Tsibliyev (russian: Василий Василиевич Циблиев); born on February 20, 1954) is retired Russian cosmonaut and former head of the Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center. Life He was selected as a cosmonaut on March 26, 1987. Tsibliyev flew as Commander on Soyuz TM-17 from July 1, 1993 to January 14, 1994 and on Soyuz TM-25 from February 2, 1997 to August 14 of the same year. He retired as a cosmonaut on June 19, 1998. From 2003 to 2009, he headed the Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center. Tsibliyev is married with two children. Tsibliyev was the commander in charge of ''Mir'' when it was hit by a ''Progress'' spacecraft in 1997. Honours and awards * Hero of the Russian Federation (14 January 1994) - for courage and heroism displayed during spaceflight on the orbital scientific research complex ''Mir'' * Order of Merit for the Fatherland, 3rd class (10 April 1998) - for courage and heroism displayed during prolonged space flight on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps astronauts and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Programme
The Soyuz programme ( , ; russian: link=no, Союз , meaning "Union") is a human spaceflight programme initiated by the Soviet Union in the early 1960s. The Soyuz spacecraft was originally part of a Moon landing project intended to put a Soviet cosmonaut on the Moon. It was the third Soviet human spaceflight programme after the Vostok (1961–1963) and Voskhod (1964–1965) programmes. The programme consists of the Soyuz capsule and the Soyuz rocket and is now the responsibility of the Russian Roscosmos. After the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011, Soyuz was the only way for humans to get to the International Space Station (ISS) until 30 May 2020, when Crew Dragon flew to the ISS for the first time with astronauts. Soyuz rocket The launch vehicles used in the Soyuz expendable launch system are manufactured at the Progress State Research and Production Rocket Space Center (TsSKB-Progress) in Samara, Russia. As well as being used in the Soyuz programme as the lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-26
Soyuz TM-26 was a Russian spaceflight that ferried cosmonauts and supplies to Mir. It was the 32nd expedition to Mir. It was launched by a Soyuz-U rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome on August 5, 1997. The main mission was to transport two specially-trained cosmonauts to repair or salvage the troubled space station. TM-26 docked with Mir on August 7 by manual control. The crew repaired the power cable and harness/connectors in the severely damaged Spektr module and restored much of the lost power; they also repaired and replaced the oxygen generators in Mir. The hole(s) in that module that caused total depressurization of the module could not be located during their spacewalk inside that module. During the flight a television advertisement starring Vasily Tsibliyev was filmed on the station. The ad, for Tnuva's brand of UHT Ultra-high temperature processing (UHT), ultra-heat treatment, or ultra-pasteurization is a food processing technology that sterilizes liquid food by hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-24
Soyuz TM-24 was the 27th expedition to Mir. Soyuz TM-24 carried a crew of three. The crew consisted of Cosmonauts Valery Korzun and Aleksandr Kaleri, and the first French woman in space, Claudie André-Deshays. They joined American astronaut Shannon Lucid and Mir 21 crewmates Yuri Onufriyenko Col. Yuri Ivanovich Onufrienko (russian: Юрий Иванович Онуфриенко, ua, Юрій Іванович Онуфрієнко; born 6 February 1961) is a retired Russian cosmonaut. He is a veteran of two extended spaceflights, aboa ... and Yuri Usachev. André-Deshays carried out biological and medical experiments on Mir for 16 days (the ''Cassiopée'' mission) before returning to Earth with Onufriyenko and Usachev. Crew References {{coord, 47, 49, N, 69, 24, E, display=title Crewed Soyuz missions Spacecraft launched in 1996 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocentric Orbit
A geocentric orbit or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA estimated there were approximately 2,465 artificial satellite payloads orbiting Earth and 6,216 pieces of space debris as tracked by the Goddard Space Flight Center. More than 16,291 objects previously launched have undergone orbital decay and entered Earth's atmosphere. A spacecraft enters orbit when its centripetal acceleration due to gravity is less than or equal to the centrifugal acceleration due to the horizontal component of its velocity. For a low Earth orbit, this velocity is about ; by contrast, the fastest crewed airplane speed ever achieved (excluding speeds achieved by deorbiting spacecraft) was in 1967 by the North American X-15. The energy required to reach Earth orbital velocity at an altitude of is about 36 MJ/kg, which is six times the energy needed merely to climb to the corresponding altitude. Spacecraft with a perigee belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
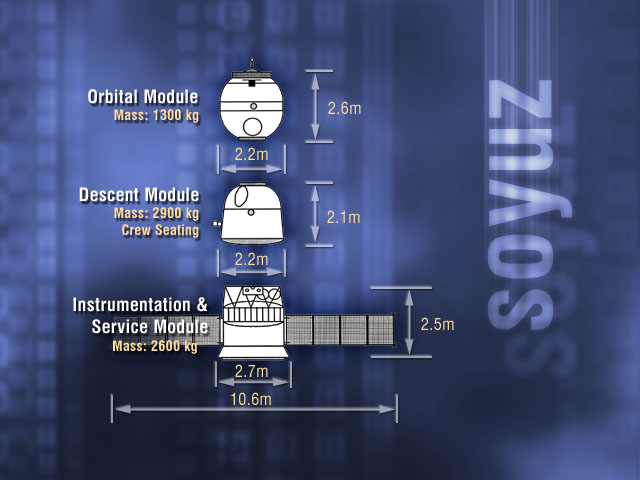
Soyuz-TM
The Soyuz-TM were fourth generation (1986–2002) Soyuz spacecraft used for ferry flights to the Mir and ISS space stations. The Soyuz spacecraft consisted of three parts, the Orbital Module, the Descent Module and the Service Module. The first launch of the spacecraft was the uncrewed Soyuz TM-1 on May 21, 1986, where it docked with the Mir space station. The final flight was Soyuz TM-34, which docked with the International Space Station and landed November 10, 2002. Background After the Apollo-Soyuz Test project in 1976, the Soyuz for crewed flights had the singular mission of supporting crewed space stations. The original Soyuz had a limited endurance when docked with a station, only about 60 to 90 days. There were two avenues for extending the duration of missions past this. The first avenue was to make upgrades to increase the Soyuz spacecraft's endurance. The Soyuz-T could last 120 days and the Soyuz-TM could last 180 days. The other was to use a Visiting Expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CMa or α CMa. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, Sirius is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. Sirius is a binary star consisting of a main-sequence star of spectral type A0 or A1, termed Sirius A, and a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type DA2, termed Sirius B. The distance between the two varies between 8.2 and 31.5 astronomical units as they orbit every 50 years. Sirius appears bright because of its intrinsic luminosity and its proximity to the Solar System. At a distance of , the Sirius system is one of Earth's nearest neighbours. Sirius is gradually moving closer to the Solar System, so it is expected to increase in brightness slightly over the next 60,000 years, reaching a peak magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhold Ewald
Reinhold Ewald (born 18 December 1956) is a German physicist and ESA astronaut. Biography Born in Mönchengladbach, West Germany, he received a Diploma in experimental physics from the University of Cologne in 1983 and a Ph.D. in 1986, with a minor degree in human physiology. In 1990, he was selected to the German astronaut team, training for the Mir '92 mission. He was the backup of Klaus-Dietrich Flade for the Soyuz TM-14 mission. In 1995 he began training for the second German Mir mission. In February 1997 he flew to the space station Mir with Soyuz TM-25, spending 20 days in space. He performed experiments in biomedical and material sciences, and carried out operational tests in preparation for the International Space Station. In February 1999, he joined the European Astronaut Corps at the European Astronaut Centre (EAC) in Cologne, Germany. From 2006 to 2011, Ewald headed the Flight Operations Division within ESA's ISS Operations department at the Columbus Control Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)

