|
KEYBOARD.SYS
This article lists notable commands provided by the MS-DOS disk operating system (DOS), especially as used on an IBM PC compatible computer. Other DOS variants as well as the legacy Windows shell, Command Prompt (cmd.exe), provide many of these commands. Many other DOS variants are informally called ''DOS'', but are not included in the scope of the list. The highly related variant, IBM PC DOS, is included. The list is not intended to be exhaustive, but does include commands covering the various releases. Each command is implemented either as built-in to the command interpreter, COMMAND.COM, or as an external program. Although prevailing style is to write command names in all caps, the interpreter matches ignoring case. Commands APPEND Sets the path to be searched for data files or displays the current search path. The APPEND command is similar to the PATH command that tells DOS where to search for program files (files with a .COM, . EXE, or .BAT file name extension). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command (computing)
In computing, a command is an instruction received via an external Interface (computing), interface that directs the behavior of a computer program. Commonly, commands are sent to a program via a command-line interface, a scripting language, script, a network protocol, or as an event triggered in a graphical user interface. Many commands support arguments to specify input and to modify default behavior. Terminology and syntax varies but there are notable common approaches. Typically, an option or a flag is a name (without Whitespace character, whitespace) with a prefix such as dash or Slash (punctuation), slash that modifies default behavior. An option might have a required value that follows it. Typically, flag refers to an option that does not have a following value. A parameter is an argument that specifies input to the command and its meaning is based on its position in the command line relative to other parameters; generally ignoring options. A parameter can specify anything ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to: Science and technology * BASIC, a computer programming language * Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base * Basic access authentication, in HTTP Entertainment * Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film * Basic, one of the Galactic Basic, languages in ''Star Wars'' Music * Basic (Glen Campbell album), ''Basic'' (Glen Campbell album), 1978 * Basic (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), ''Basic'' (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), 1984 * B.A.S.I.C. (Alpinestars album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (Alpinestars album), 2000 * Basic (Brown Eyed Girls album), ''Basic'' (Brown Eyed Girls album), 2015 * B.A.S.I.C. (The Basics album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (The Basics album), 2019 Places * Basic, Mississippi, a community in the US * BASIC countries, Brazil, South Africa, India and China in climate change negotiations Organizations * BASIC Bank Limited, government owned bank in Bangladesh * Basic Books, an American publisher Other uses * Basic (cigarette), a brand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novell DOS
DR-DOS is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles, originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research, Inc. and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS that attempted to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS-DOS. Its first release was version 3.31, named so that it would match MS-DOS's then-current version. DR DOS 5.0 was released in 1990 as the first to be sold in retail; it was critically acclaimed and led to DR DOS becoming the main rival to Microsoft's MS-DOS, who quickly responded with its own MS-DOS 5.0 but releasing over a year later. It introduced a graphical user interface layer called ViewMAX. DR DOS 6.0 was released in 1991; then with Novell's acquisition of Digital Research, the following version was named Novell DOS 7.0 in 1994. After another sale, to Caldera, updated versions were released partly open-source under the Caldera moniker, and briefly as Ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Sector
In computer disk storage, a sector is a subdivision of a track on a magnetic disk or optical disc. For most disks, each sector stores a fixed amount of user-accessible data, traditionally 512 bytes for hard disk drives (HDDs), and 2048 bytes for CD-ROMs, DVD-ROMs and BD-ROMs. Newer HDDs and SSDs use 4096 byte (4 KiB) sectors, which are known as the Advanced Format (AF). The sector is the minimum storage unit of a hard drive. Most disk partitioning schemes are designed to have files occupy an integral number of sectors regardless of the file's actual size. Files that do not fill a whole sector will have the remainder of their last sector filled with zeroes. In practice, operating systems typically operate on blocks of data, which may span multiple sectors. Geometrically, the word sector means a portion of a disk between a center, two radii and a corresponding arc (see Figure 1, item B), which is shaped like a slice of a pie. Thus, the ''disk sector'' (Figure 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
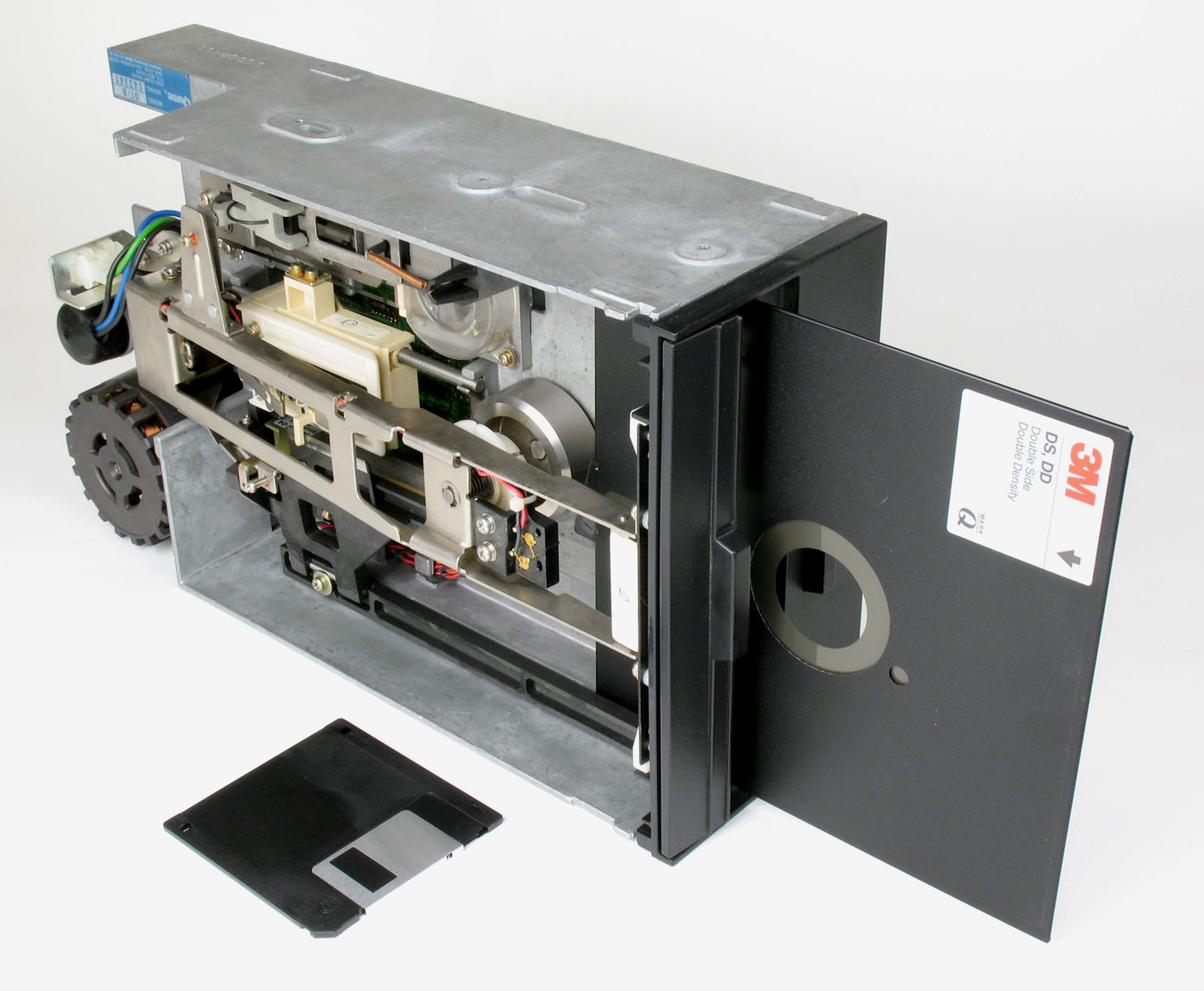
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Partitioning
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk after a partitioning scheme is chosen for the new disk before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with disk read-and-write head, magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual Block (data storage), blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small disk enclosure, rectangular box. Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, and were the dominant secondary storage device for History of general-purpose CPUs, general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
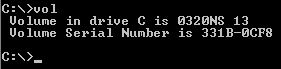
Volume (computing)
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically (though not necessarily) resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition. Differences from partition A volume is not the same thing as a partition. For example, a floppy disk might be accessible as a volume, even though it does not contain a partition, as floppy disks cannot be partitioned with most modern computer software. Also, an OS can recognize a partition without recognizing any volume associated with it, as when the OS cannot interpret the filesystem stored there. This situation occurs, for example, when Windows NT-based OSes encounter disks with non-Microsoft OS partitions, such as the ext4 filesystem commonly used with Linux. Another example occurs in the Intel world wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MODE
Mode ( meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to: Arts and entertainment * MO''D''E (magazine), a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine * ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is the setting for the ABC series ''Ugly Betty'' * ''Mode'' (video game), a 1996 video game * Mode Records, a record label * Mode Media, a defunct digital media company * ''Mode'' (book series), a quartet of novels by Piers Anthony * Modern Organization for Dance Evolvement, known as MODE, a 1970s modern dance organisation in New York * ''Mode'', a defunct Indonesian women's magazine Music * Mode (music), a system of musical tonality involving a type of scale coupled with a set of characteristic melodic behaviors ** Modus (medieval music) *** Gregorian mode, a system of modes used in Gregorian chant (as opposed to ancient Greek modes or Byzantine octoechos) * "Mode", a song by PRhyme from the 2015 soundtrack '' Southpaw: Music from and Inspired by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Win32 Console
Windows Console is a GUI application for running console applications in Windows. Windows Console is used for running text-based programs such as operating system shells (e.g. Command Prompt and PowerShell), utilities (e.g. Far Manager) and some, generally older, applications (e.g. Midnight Commander). Windows Terminal was introduced in Windows 10 as a replacement for Windows Console. In 2019, the console host was open-sourced under the MIT License, alongside Windows Terminal. Use Full-screen mode Windows Console runs in either window or full-screen mode. The mode can be toggled by pressing . In window mode, the console writes text in a window and uses an operating system's font rendering. In this mode, an application's user interaction is controlled by the windowing system; analogous to X Window System applications such as xterm. In Windows XP and earlier, the full-screen console uses a hardware text mode and uploads a raster font to the video adapter; analogo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyph
A glyph ( ) is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A grapheme, or part of a grapheme (such as a diacritic), or sometimes several graphemes in combination (a composed glyph) can be represented by a glyph. Glyphs, graphemes and characters In modern English, symbols like letters and numerical digits are each both single graphemes and single glyphs. In most languages written in any variety of the Latin alphabet except English, the use of diacritics to signify a sound mutation is common. For example, the grapheme requires two glyphs: the basic and the grave accent . In general, a diacritic is regarded as a glyph, even if it is contiguous with the rest of the character like a cedilla in French, Catalan or Portuguese, the ogonek in several languages, or the stroke on a Polish . Altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Code Page
Windows code pages are sets of characters or code pages (known as character encodings in other operating systems) used in Microsoft Windows from the 1980s and 1990s. Windows code pages were gradually superseded when Unicode was implemented in Windows, although they are still supported both within Windows and other platforms, and still apply when Alt code shortcuts are used. Current Windows versions support Unicode, new Windows applications should use Unicode (UTF-8) and not 8-bit character encodings. There are two groups of system code pages in Windows systems: OEM and Windows-native ("ANSI") code pages. (ANSI is the American National Standards Institute.) Code pages in both of these groups are extended ASCII code pages. Additional code pages are supported by standard Windows conversion routines, but not used as either type of system code page. ANSI code page ANSI code pages (officially called "Windows code pages" after Microsoft accepted the former term being a misnomer) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |