hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition.
Differences from partition
A volume is not the same thing as a partition. For example, afloppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a ...
might be accessible as a volume, even though it does not contain a partition, as floppy disks cannot be partitioned with most modern computer software. Also, an OS can recognize a partition without recognizing any volume associated with it, as when the OS cannot interpret the filesystem stored there. This situation occurs, for example, when Windows NT-based OSes encounter disks with non-Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
OS partitions, such as the ext4
ext4 (fourth extended filesystem) is a journaling file system for Linux, developed as the successor to ext3.
ext4 was initially a series of backward-compatible extensions to ext3, many of them originally developed by Cluster File Systems for ...
filesystem commonly used with Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
. Another example occurs in the Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
world with the "Extended Partition". While these are partitions, they cannot contain a filesystem directly. Instead, "logical drives" (also known as volumes) must be created within them. This is also the case with NetWare volumes residing inside of a single partition. In short, volumes exist at the logical OS level, and partitions exist at the physical, media specific level. Sometimes there is a one-to-one correspondence, but this is not guaranteed.
In Microsoft Windows Server 2008 and onward, the term "volume" is used as a superset that includes "partition" as well.
It isn't uncommon to see a volume packed into a single file. Examples include ISO9660 disc images (CD/DVD images, commonly called "ISOs"), and installer volumes for Mac OS X ( DMGs). As these volumes are files which reside within another volume, they certainly are ''not'' partitions.
Example
This example concerns aWindows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
system with two physical hard disks. The first hard disk has two partitions, the second has only one. The first partition of the first hard disk contains the operating system. Mount point
Mounting is a process by which a computer's operating system makes files and directories on a storage device (such as hard drive, CD-ROM, or network share) available for users to access via the computer's file system.
In general, the proce ...
s have been left at defaults.
In this example,
* "C:", "D:", and "E:" are volumes.
* Hard Disk 1 and Hard Disk 2 are physical disks.
* Any of these can be called a "drive".
Nomenclature
InLinux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
systems, volumes are usually handled by the Logical Volume Manager or the Enterprise Volume Management System and manipulated usinmount(8)
In NT-based versions of
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
, volumes are handled by the kernel and managed using the Disk Management MMC snap-in or the Diskpart command line tool.
Windows NT-based operating systems
Windows NT-based OSes do not have a single root directory. As a result, Windows will assign at least one path to each mounted volume, which will take one of two forms: * A drive letter, in the form of a single letter followed by a colon, such as "F:" * A mount-point on anNTFS
NT File System (NTFS) (commonly called ''New Technology File System'') is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft in the 1990s.
It was developed to overcome scalability, security and other limitations with File Allocation Tabl ...
volume having a drive letter, such as "C:\Music"
In these two examples, a file called "Track 1.mp3" stored in the root directory of the mounted volume could be referred to as "F:\Track 1.mp3" or "C:\Music\Track 1.mp3", respectively.
In order to assign a mount point for a volume as a path within another volume, the following criteria must be met:
* The mounted-to volume must be formatted NTFS.
* A directory must exist at the root path. (As of Windows Vista, it can be any subdirectory in a volume)
* That directory must be empty.
By default, Windows will assign drive letters to all drives, as follows:
* "A:" and "B:" to floppy disk drives, whether present or not
* "C:" and subsequent letters, as needed, to:
** Hard disks
** Removable disks, including optical media (e.g. CDs and DVDs)
Because of this legacy
Legacy or Legacies may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Comics
* " Batman: Legacy", a 1996 Batman storyline
* '' DC Universe: Legacies'', a comic book series from DC Comics
* ''Legacy'', a 1999 quarterly series from Antarctic Press
* ''Legacy ...
convention, the operating system startup
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship includes all new businesses including self-employment and businesses that do not intend to ...
drive is still most commonly assigned "C:", however this is not always the case. Since personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
s now no longer include floppies, and optical disc
An optical disc is a flat, usuallyNon-circular optical discs exist for fashion purposes; see shaped compact disc. disc-shaped object that stores information in the form of physical variations on its surface that can be read with the aid o ...
and other removable drives typically still start at "D:", letters A and B are available for manual assignment by a user with administrative privileges. This assignment will be remembered by the same OS on the same PC next time a removable volume is inserted, as long as there are no conflicts, and as long as the removable drive has not been reformatted on another computer (which changes its volume serial number), and as long as the OS has not been reinstalled on the computer.
On Windows XP, mount points may be managed through the Disk Management snap-in for the Microsoft Management Console. This can be most conveniently accessed through "Computer Management" in the "Administrative Tools" section of the Control Panel.
More than one drive letter can refer to a single volume, as when using the SUBST command.
Warning: removing drive letters or mount-points for a drive may break some programs, as some files may not be accessible under the known path. For example, if a program is installed at "D:\Program Files\Some Program", it may expect to find its data files at "D:\Program Files\Some Program\Data". If the logical disk previously called "D:" has its drive letter changed to "E:", "Some Program" won't be able to find its data at "D:\Program Files\Some Program\Data", since the drive letter "D:" no longer represents that volume.
Unix-like operating systems
InUnix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
operating systems, volumes other than the boot volume have a mount-point somewhere within the filesystem, represented by a path. Logically, the directory tree stored on the volume is grafted in at the mountpoint. By convention, mount-points will often be placed in a directory called '/mnt', though '/media' and other terms are sometimes used.
To use a given path as a mount-point for another volume, a directory (sometimes called a " folder") must exist there.
Unix-like operating systems use the command to manipulate mount points for volumes.
For example, if a CD-ROM drive containing a text file called 'info.txt' was mounted at '', the text file would be accessible at ''.
Data management speed
Files within a volume can generally be moved to any other place within that volume by manipulating the filesystem, without moving the actual data. However, if a file is to be moved outside the volume, the data itself must be relocated, which is a much more expensive operation. In order to better visualize this concept, one might consider the example of a large library. If a non-fiction work is originally classified as having the subject "plants", but then has to be moved to the subject "flora", one does not need to refile the book, whose position on the shelf would be static, but rather, one needs only to replace theindex card
An index card (or record card in British English and system cards in Australian English) consists of card stock (heavy paper) cut to a standard size, used for recording and storing small amounts of discrete data. A collection of such cards ei ...
. However, to move the book to another library, adjusting index cards alone is insufficient. The entire book must be moved.
Labels and serial numbers
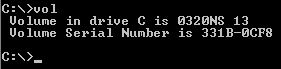 A volume label is the name given to a specific volume in a filesystem. In the
A volume label is the name given to a specific volume in a filesystem. In the FAT
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
filesystem, the volume label was traditionally restricted to 11 characters (reflecting the 8.3 restrictions, but not divided into name and extension fields) even when long file name
Long filename (LFN) support is Microsoft's backward-compatible extension of the 8.3 filename (short filename) naming scheme used in MS-DOS. Long filenames can be more descriptive, including longer filename extensions such as .jpeg, .tiff, an ...
was enabled, stored as an entry within a disk's root directory
In a Computing, computer file system, and primarily used in the Unix and Unix-like operating systems, the root directory is the first or top-most Directory (computing), directory in a hierarchy. It can be likened to the trunk of a Tree (data st ...
with a special volume-label attribute bit set, and also copied to an 11-byte field within the Extended BIOS Parameter Block
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volume ...
of the disk's boot sector. The label is always stored as uppercase
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''#Majuscule, majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally ''#Minuscule, minuscule'') in the written representation of certain langua ...
in FAT and VFAT filesystems, and cannot contain special characters that are also disallowed for regular filenames. In the NTFS filesystem, the length of its volume label is restricted to 32 characters, and can include lowercase characters and even Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Char ...
. In the exFAT filsystem, the length of its volume label is also restricted to 11 characters, but can include lowercase characters and Unicode. The command is used to change the label in DOS, Windows, and OS/2. For GUI systems like Windows Explorer
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application and default desktop environment that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user i ...
, can be pressed while the volume is highlighted, or a right-click on the name will bring up a context menu
A context menu (also called contextual, shortcut, and pop up or pop-up menu) is a menu in a graphical user interface (GUI) that appears upon user interaction, such as a right-click mouse operation. A context menu offers a limited set of choic ...
that allows it to be renamed, either of which is the same process as for renaming a file. Changing the label in Windows will also change the volume creation timestamp
A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. Timestamps do not have to be based on some absolu ...
to the current date and time for FAT filesystems. NTFS partitions have the System Volume Information directory, whose creation timestamp is set when Windows creates the partition, or when it first recognizes a repartitioning (the creation of a new volume) by a separate disk utility
A disk utility is a utility software, utility program that allows a user to perform various functions on a computer disk, such as disk partitioning and logical volume management, as well as multiple smaller tasks such as changing drive letters an ...
.
In contrast to the label, the volume serial number is generally unique and is not normally changed by the user, and thus acts as a more consistent and reliable identifier of when a volume has been changed (as when a disk is removed and another inserted). Disk formatting
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new f ...
changes the serial number, but relabeling does not. It originated in 1950s in mainframe computer
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise ...
operating systems. In OS/360
OS/360, officially known as IBM System/360 Operating System, is a discontinued batch processing operating system developed by IBM for their then-new System/360 mainframe computer, announced in 1964; it was influenced by the earlier IBSYS/IBJOB a ...
line it is human-configurable, has a maximum length of six characters, is in uppercase, must start with a letter, and identifies a volume to the system in unique manner. For example, "SYSRES" is often used for a ''system residence volume''. Operating systems may use the volume serial number as mountpoint name.
A volume serial number is a serial number
A serial number (SN) is a unique identifier used to ''uniquely'' identify an item, and is usually assigned incrementally or sequentially.
Despite being called serial "numbers", they do not need to be strictly numerical and may contain letters ...
assigned to a disk volume or tape volume.
In FAT
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
and NTFS
NT File System (NTFS) (commonly called ''New Technology File System'') is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft in the 1990s.
It was developed to overcome scalability, security and other limitations with File Allocation Tabl ...
file systems, a volume serial number is a feature used to determine if a disk is present in a drive or not, and to detect if it was exchanged with another one. This identification system was created
by Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
and IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
during their development of OS/2
OS/2 is a Proprietary software, proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was created and initially developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, ...
.
It was introduced in MS-DOS 4.01 in 1988.
The volume serial number is a 32-bit number determined by the date and time on the real-time clock on the current computer at the time of a disk's formatting. Previously, determination by the OS of whether a disk was swapped was done by reading the drive's ''volume label''. However, even at that time the volume label was not required to be unique and was optional. Therefore, many users had not given disks any meaningful name and the old method failed.
The command can be used from the command line
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user ...
to display the current label and serial number of a volume.
References
External links
* MSDN's article oHard Links and Junctions
{{DEFAULTSORT:Volume (Computing) Disk file systems