|
Jean Pierre Blanchard
Jean-Pierre rançoisBlanchard (4 July 1753 – 7 March 1809) was a French inventor, best known as a pioneer of gas balloon flight, who distinguished himself in the conquest of the air in a balloon, in particular the first crossing of the English Channel, on 7 January 1785. Biography 1784 - Flights in Paris Blanchard made his first successful balloon flight in Paris on 2 March 1784, in a hydrogen gas balloon launched from the Champ de Mars. The first successful manned balloon flight had taken place on 21 November 1783, when Pilâtre de Rozier and the Marquis d'Arlandes took off at Palace of Versailles in a free-flying hot air balloon constructed by the Montgolfier brothers. The first manned hydrogen balloon flight had taken place on 1 December 1783, when Professor Jacques Charles and Nicolas-Louis Robert launched '' La Charlière'' from the Jardin des Tuileries in Paris. Blanchard's flight nearly ended in disaster, when one spectator (Dupont de Chambon, a contemporary of Nap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Livesay
Richard Livesay (1750–1826) was a British portrait and landscape painter, and engraver. Life Livesay was a pupil of Benjamin West, and began his career in London, exhibiting for the first time at the Royal Academy in 1776. Between 1777 and 1785 he lodged with Jane Hogarth in Leicester Fields. Engaged by West to copy pictures at Windsor, Livesay moved there about 1790, and gave lessons in drawing to some of the royal children. In 1796 he was appointed drawing-master to the Royal Naval Academy at Portsmouth, and lived in Portsea. On an address card which he issued at that time he described himself as "Portrait, Landscape, and Marine Painter, Drawing-Master to the Royal Academy, Portsmouth, 61 Hanover Street, Portsea." Livesay died at Southsea in 1826. Works Livesay executed for Jane Hogarth a series of facsimiles of drawings by William Hogarth, her late husband, among them seven illustrating the well-known ''Tour'', published in 1782. While at Windsor he painted portraits of y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Brothers
Les Frères Robert were two French brothers. Anne-Jean Robert (1758–1820) and Nicolas-Louis Robert (1760–1820) were the engineers who built the world's first hydrogen balloon for professor Jacques Charles, which flew from central Paris on 27 August 1783. They went on to build the world's first manned hydrogen balloon, and on 1 December 1783 Nicolas-Louis accompanied Jacques Charles on a 2-hour, 5-minute flight. Their barometer and thermometer made it the first balloon flight to provide meteorological measurements of the atmosphere above the Earth's surface. The brothers subsequently experimented with an elongated elliptical shape for the hydrogen envelope in a balloon they attempted to power and steer by means of oars and umbrellas. In September 1784 the brothers flew 186 km from Paris to Beuvry, the world's first flight of more than 100 km. Career Background The Robert brothers were skilled engineers with a workshop at the ''Place des Victoires'' in Paris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
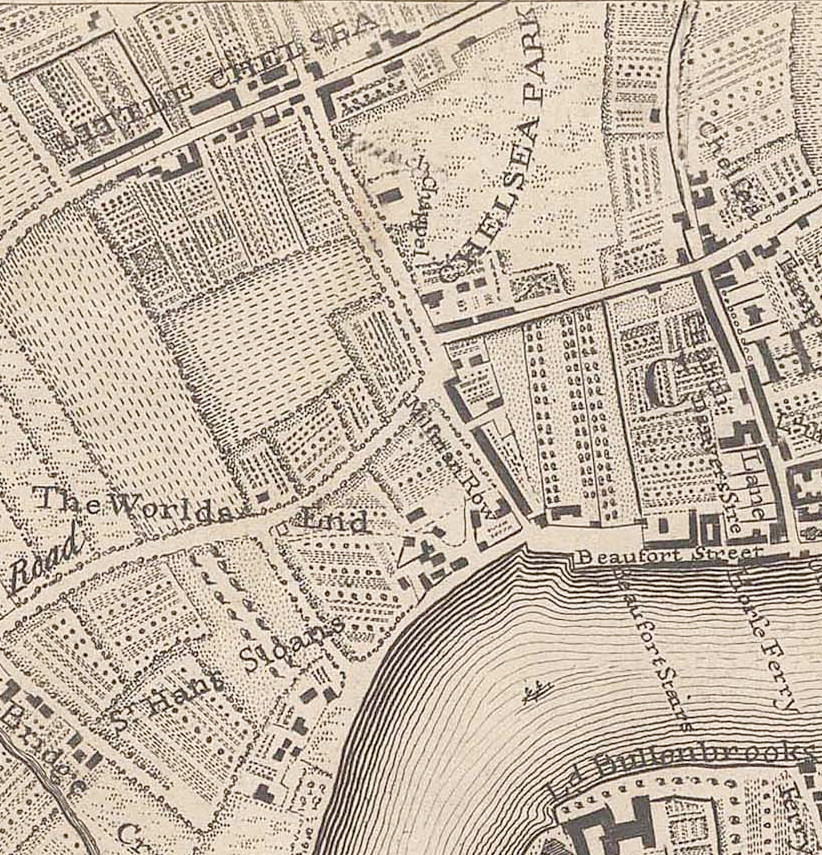
Lewis Lochée
Lewis Lochée (died 8 June 1791) was a military author born in the Austrian Netherlands. From the early 1770s, he was the proprietor and master of a military academy at Little Chelsea, at that time a rural hamlet near Westminster, in Great Britain. After closing his academy in 1790, Lochée returned to the Netherlands to fight for the freedom of the Province of Brabant from the Austrians. In 1791, shortly before his death in France, he published a history of the Revolution. Early life When Lochée was naturalised as a British subject by an Act of Parliament on 8 May 1780, he said he was the son of John and Theresa Lochée, had been born at Brussels in the Province of Brabant, and had "constantly professed the true Protestant Religion"; apart from this, his origins remain obscure.J. E. O. Screen, "The 'Royal Military Academy' of Lewis Lochée" in ''Journal of the Society for Army Historical Research'', Vol. 70, No. 283 (Autumn 1992), pp. 143-156 Life in England In the words of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ware, Hertfordshire
Ware is a town in Hertfordshire, England close to the county town of Hertford. It is also a civil parish in East Hertfordshire district. Location The town lies on the north–south A10 road which is partly shared with the east–west A414 (for Hertford to the west and Harlow to the east). There is a large viaduct over the River Lea at Kings Meads. The £3.6m two-mile bypass opened on 17 January 1979. At the north end of the bypass is the Wodson Park Sports and Leisure Centre and Hanbury Manor, a hotel and country club. The former route of the A10 through the town is now the A1170. The railway station is on the Hertford East Branch Line and operated by Greater Anglia and is on a short single track section of the otherwise double track line. History Archaeology has shown that Ware has been occupied since at least the Mesolithic period (which ended about 4000 BC). The Romans had a sizeable settlement here and foundations of several buildings, including a temple, and two cemeteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorfields
Moorfields was an open space, partly in the City of London, lying adjacent to – and outside – its northern wall, near the eponymous Moorgate. It was known for its marshy conditions, the result of the defensive wall acting like a dam, impeding the flow of the River Walbrook and its tributaries. Moorfields gives its name to the Moorfields Eye Hospital which occupied a site on the former fields from 1822–1899, and is still based close by, in the St Luke's area of the London Borough of Islington. Setting Moorfields is first recorded in the late 12th century, though not by name, as a ''great fen''. The fen was larger than the area subsequently known as Moorfields. Moorfields was contiguous with Finsbury Fields, Bunhill Fields and other open spaces, and until its eventual loss in the 19th century, was the innermost part of a green wedge of land which stretched from the wall, to the open countryside which lay close by. Moorfields separated the western and eastern growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincenzo Lunardi
Vincenzo Lunardi (11 January 1754 in Lucca – 1 August 1806 in Lisbon) was a pioneering Italian aeronaut, born in Lucca. Ascents in England Vincenzo Lunardi's family were of minor Tuscan nobility from Lucca, and his father had married late in life. Vincenzo was one of three children. He travelled in France in his early years before being called home, where he was put into the diplomatic service. Vincenzo Lunardi came to England as Secretary to Prince Caramanico, the Neapolitan Ambassador. 15 September 1784 There was a flying craze in France and Scotland with James Tytler, Scotland's first aeronaut and the first Briton to fly, but even so and after a year since the invention of the balloon, the English were still skeptical, and so George Biggin and 'Vincent' Lunardi, "The Daredevil Aeronaut", together decided to demonstrate a hydrogen balloon flight at the Artillery Ground of the Honourable Artillery Company in London on 15 September 1784. However, because the 200,000-strong c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
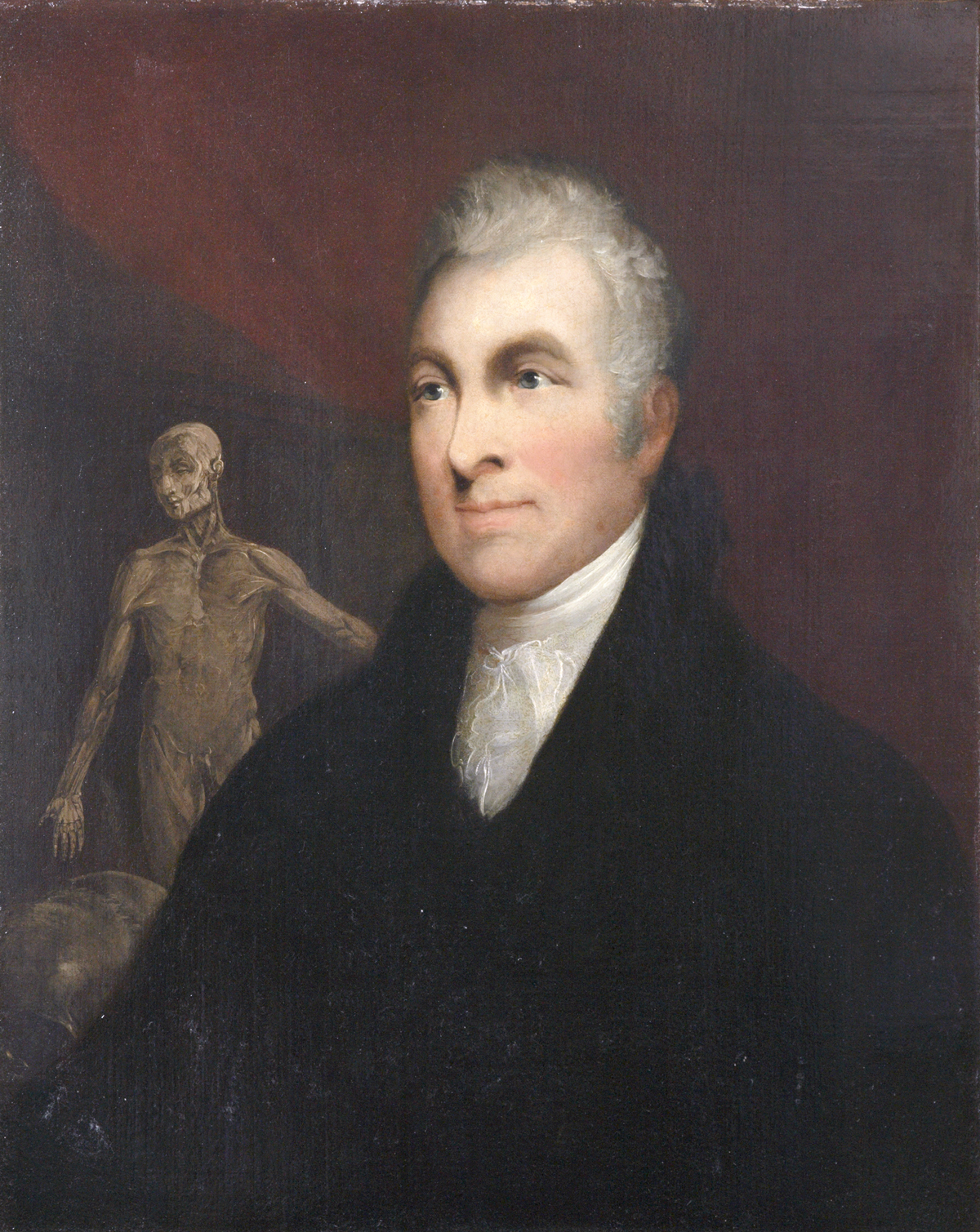
John Sheldon (anatomist)
John Sheldon (6 July 1752 – 8 October 1808) was an English surgeon and anatomist. Career Sheldon was born in London on 6 July 1752, and was apprenticed to Henry Watson, elected in 1766 the first professor of anatomy of the Surgeons' Company. Sheldon studied and taught anatomy at Watson's private museum in Tottenham Court Road, which was later wrecked by a mob. He received his diploma at the Surgeons' Company on 2 November 1775, and then lectured on anatomy at Great Windmill Street school under William Hunter. Sheldon was surgeon to the General Medical Asylum in Welbeck Street, and on 18 July 1782 he was appointed professor of anatomy to the Royal Academy in succession to Hunter. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society on 29 April 1784, and on 20 April 1786 he became surgeon to Westminster Hospital, a post he resigned two years later. Teacher In 1777 Sheldon opened a private theatre in Great Queen Street, where he taught anatomy, and pursued research. After the deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balloonomania
Balloonomania was a strong public interest or fad in balloons that originated in France in the late 18th century and continued into the 19th century, during the advent of balloon flights. The interest began with the first flights of the Montgolfier brothers in 1783 (in a balloon inflated with hot air). Soon afterwards Jacques Alexandre César Charles flew another type of balloon (inflated with hydrogen) and both types of balloon were in use from then on. The fad quickly spread in France and across the channel in England. Origins The science of lighter-than-air gases, and specifically the properties of oxygen, had been discovered as early as 1774 by Joseph Priestley, who noted its lightness and explosive qualities when heated. The chemistry of lighter-than-air and heated gasses was eventually put to the test by the Montgolfier brothers, two paper manufacturers in France, while experimenting with heated air caught in paper bags. Balloonomania saw its true origins, however, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motto
A motto (derived from the Latin , 'mutter', by way of Italian , 'word' or 'sentence') is a sentence or phrase expressing a belief or purpose, or the general motivation or intention of an individual, family, social group, or organisation. Mottos (or mottoes) are usually found predominantly in written form (unlike slogans, which may also be expressed orally), and may stem from long traditions of social foundations, or from significant events, such as a civil war or a revolution. A motto may be in any language, but Latin has been widely used, especially in the Western world. Heraldry In heraldry, a motto is often found below the shield in a banderole; this placement stems from the Middle Ages, in which the vast majority of nobles possessed a coat of arms complete with a motto. In the case of Scottish heraldry, it is mandated to appear above the crest. Spanish coats of arms may display a motto in the bordure of the shield. In heraldic literature, the terms 'rallying cry' r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sic Itur Ad Astra
''Ad astra'' is a Latin phrase meaning "to the stars". The phrase has origins with Virgil, who wrote in his ''Aeneid'': "''sic itur ad astra''" ('thus one journeys to the stars') and "''opta ardua pennis astra sequi''" ('desire to pursue the high hard to reachstars on wings'). Another origin is Seneca the Younger, who wrote in ''Hercules'': "''non est ad astra mollis e terris via''" ('there is no easy way from the earth to the stars'). Etymology ''Ad'' is a Latin preposition expressing direction toward in space or time (e.g. ''ad nauseam'', ''ad infinitum'', ''ad hoc'', '' ad libidem'', ''ad valorem'', ''ad hominem''). It is also used as a prefix in Latin word formation. ''Astra'' is the accusative plural form of the Latin word ''astrum'' 'star' (from Ancient Greek ἄστρον ''astron'' 'star', from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂ster-''). Mottos ''Ad astra'' is used as, or as part of, the motto of many organizations, most prominently, air forces. It has also been adopted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulogne-Billancourt
Boulogne-Billancourt (; often colloquially called simply Boulogne, until 1924 Boulogne-sur-Seine, ) is a wealthy and prestigious commune in the Parisian area, located from its centre. It is a subprefecture of the Hauts-de-Seine department and thus the seat of the larger arrondissement of Boulogne-Billancourt. Boulogne-Billancourt includes two large islands in the Seine: Île Saint-Germain and Île Seguin. With a population of 121,334 as of 2018, it is the most populous commune in Hauts-de-Seine and most populous suburb of Paris, as well as one of the most densely populated municipalities in Europe. Boulogne-Billancourt is one of the wealthiest regions in the Parisian area and in France. Formerly an important industrial site, it has successfully reconverted into business services and is now home to major communication companies headquartered in the Val de Seine business district. Etymology The original name of the commune was Boulogne-sur-Seine (meaning "Boulogne upon Seine"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seine
) , mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = Seine basin , basin_size = , tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle , tributaries_right = Ource, Aube, Marne, Oise, Epte The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre (and Honfleur on the left bank). It is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen, from the sea. Over 60 percent of its length, as far as Burgundy, is negotiable by large barges and most tour boats, and nearly its whole length is available for recreational boating; excursion boats offer sightseeing tours of the river banks in the capital city, Paris. There are 37 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Portrait_of_a_Naval_Lieutenant%2C_c.1795_-_BHC3117_-_Royal_Museums_Greenwich.jpg)