|
Jùjú Music
Jùjú is a style of Yoruba popular music, originated in Lagos, Nigeria. It first began developing in the 1920s with Tunde King (Abdulrafiu Babatunde King). Early styles of jùjú music consisted of banjo or acoustic guitar, drums, gourd rattle, tambourine, and vocals. Call-and-response singing is common in jùjú music along with harmonies, repetitive refrains, and Polyrhythm, polyrhythmic percussion. Other musical elements like improvisation and expressive vocal styles are often found. Although jùjú music was developing in the 1920s, a recognizable genre did not emerge until the mid-1930s. Jùjú music emerged in Lagos in 1932, and was influenced by palm wine guitar music. Jùjú was also strongly influenced by Asikò dance drumming, which is tied to Yoruba people, Yoruba Christianity, Christian communities. Lyrics include praise and storytelling, reflecting themes such as identity, community, life, spiritual beliefs and social commentary. Jùjú performances often lasted hours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
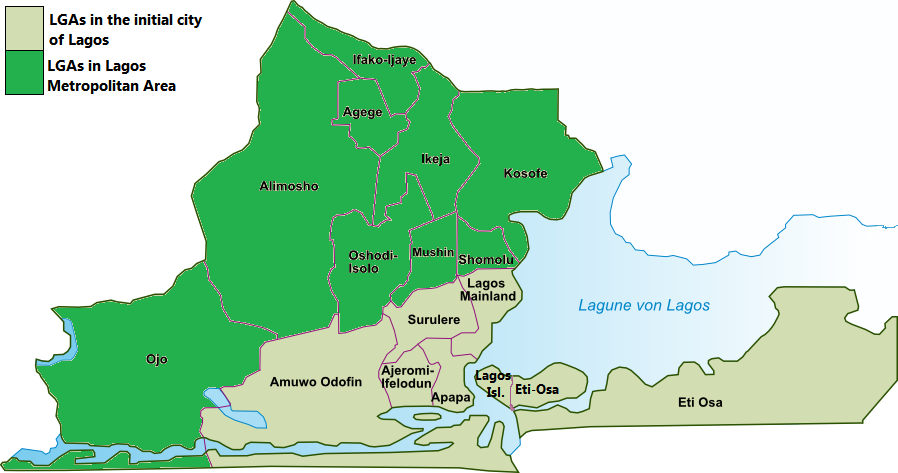
Lagos
Lagos ( ; ), or Lagos City, is a large metropolitan city in southwestern Nigeria. With an upper population estimated above 21 million dwellers, it is the largest city in Nigeria, the most populous urban area on the African continent, and one of the fastest-growing megacity, megacities in the world. Lagos was the national capital of Nigeria until the Government of Nigeria, government's December 1991 decision to move their capital to Abuja, in the centre of the country. Lagos is a major African financial center, financial centre and is the economic hub of Lagos State and Nigeria at large. The city has a significant influence on commerce, entertainment, technology, education, politics, tourism, art, and fashion in Africa. Lagos is also among the top ten of the world's fastest-growing cities and Urban area, urban areas. In 2024, Time Out (magazine), Time Out magazine ranked Lagos as the 19th best city to visit in the world. A megacity, it has the second-highest Gross domestic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuji Music
Fújì is a genre of Yoruba popular music that emerged in Nigeria in the 1960s. It evolved from the improvisational wéré music also known as ajísari (meaning "waking up for sari", performed to awaken Muslims before dawn during the fasting season of Ramadan. Fuji music was named after the Japanese stratovolcano-mountain, Mount Fuji by Alhaji Sikiru Ayinde Barrister (pioneer of wéré). It features energetic beats, diverse Yoruba rhythms, and call-and-response vocals. Fuji's influence extends into contemporary music, with its hooks and rhythms frequently appearing in Nigerian hip hop. In February 2024, professor and filmmaker Saheed Aderinto released the first episode of The Fuji Documentary titled "Mr. Fuji: Barry Wonder" which chronicles the story of Fuji music creator Sikiru Ayinde Barrister. Etymology Sikiru Ololade Ayinde Balogun Barrister significantly popularized wéré music during the 1950s and 1960s and later coined the term "fuji" for his new innovation ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Juju Musicians
This is a List of notable juju musicians in Nigeria. There are numerous genres of music in Nigeria. Some genres such as Jùjú music, Fuji music, Apala and Were music are peculiar to certain ethnic groups. A *Ayinde Bakare D * Dele Ojo * Dayo Kujure * Dele Taiwo * Dele Abiodun, Admiral E *Ebenezer Obey I * I. K. Dairo K *Kokoro *King Sunny Adé * Kayode Fashola M *Moses Olaiya (Baba Sala) P * Prince Adekunle S * Segun Adewale *Shina Peters *Sonny Okosun * Sunny Melody T * Tunde King *Tunde Nightingale Earnest Olatunde Thomas (10 December 1922 – 1981), known as Tunde Nightingale or The Western Nightingale, was a Nigerian singer and guitarist, best known for his unique jùjú music style, following in the tradition of Tunde King. Early l ... See also * List of Nigerian highlife musicians References {{DEFAULTSORT:Juju musicians Yoruba musicians Nigerian composers Lists of Nigerian musicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Nigeria
The music of Nigeria includes many kinds of folk and popular music. Little of the country's music history prior to European contact has been preserved, although bronze carvings dating back to the 16th and 17th centuries have been found depicting musicians and their instruments. The country's most internationally renowned genres are Indigenous, Apala, Aurrebbe music, Rara music, Were music, Ogene, Fuji, Jùjú, Afrobeat, Afrobeats, Igbo highlife, Afro-juju, Waka, Igbo rap, Gospel, Nigerian pop and Yo-pop. Styles of folk music are related to the over 250 ethnic groups in the country, each with their own techniques, instruments, and songs. The largest ethnic groups are the Igbo, Hausa and Yoruba. Traditional music from Nigeria and throughout Africa is often functional; in other words, it is performed to mark a ritual such as the wedding or funeral and not to achieve artistic goals. Although some Nigerians, especially children and the elderly, play instruments for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proverb
A proverb (from ) or an adage is a simple, traditional saying that expresses a perceived truth based on common sense or experience. Proverbs are often metaphorical and are an example of formulaic speech, formulaic language. A proverbial phrase or a proverbial expression is a type of a conventional saying similar to proverbs and transmitted by oral tradition. The difference is that a proverb is a fixed expression, while a proverbial phrase permits alterations to fit the grammar of the context. Collectively, they form a folklore genre, genre of folklore. Some proverbs exist in more than one language because people borrow them from languages and cultures with which they are in contact. In the West, the Bible (including, but not limited to the Book of Proverbs) and medieval Latin (aided by the work of Erasmus) have played a considerable role in distributing proverbs. Not all Biblical proverbs, however, were distributed to the same extent: one scholar has gathered evidence to show th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica during the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its Jamaican diaspora, diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, "Do the Reggay", was the first popular song to use the word ''reggae'', effectively naming the genre and introducing it to a global audience. Reggae is rooted in traditional Jamaican Kumina, Pukkumina, Revival Zion, Nyabinghi, and burru drumming. Jamaican reggae music evolved out of the earlier genres mento, ska and rocksteady. Reggae usually relates news, social gossip, and political commentary. It is recognizable from the counterpoint between the bass and drum downbeat and the offbeat rhythm section. The immediate origins of reggae were in ska and rocksteady; from the latter, reggae took over the use of the bass as a percussion instrument. Stylistically, reggae incorporates some of the musical elements of rhythm and blues, jazz, mento (a celebratory, rural folk form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funk
Funk is a music genre that originated in African-American communities in the mid-1960s when musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of various music genres that were popular among African-Americans in the mid-20th century. It deemphasizes melody and chord progressions and focuses on a strong rhythmic groove of a bassline played by an electric bassist and a drum part played by a percussionist, often at slower tempos than other popular music. Funk typically consists of a complex percussive groove with rhythm instruments playing interlocking grooves that create a "hypnotic" and "danceable" feel. It uses the same richly colored extended chords found in bebop jazz, such as minor chords with added sevenths and elevenths, and dominant seventh chords with altered ninths and thirteenths. Funk originated in the mid-1960s, with James Brown's development of a signature groove that emphasized the downbeat—with a heavy emphasis on the first be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Music
Rock is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in the United States as "rock and roll" in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of styles from the mid-1960s, primarily in the United States and the United Kingdom. It has its roots in rock and roll, a style that drew from the black musical genres of blues and rhythm and blues, as well as from country music. Rock also drew strongly from genres such as electric blues and folk music, folk, and incorporated influences from jazz and other styles. Rock is typically centered on the electric guitar, usually as part of a rock group with electric bass guitar, drum kit, drums, and one or more singers. Usually, rock is song-based music with a Time signature, time signature and using a verse–chorus form; however, the genre has become extremely diverse. Like pop music, lyrics often stress romantic love but also address a wide variety of other themes that are frequently social or political. Rock was the most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agidigbo
The ''agidigbo'' or ‘’’molo’’’ is a large traditional plucked lamellophone thumb piano used by the Yoruba people of Nigeria to play apala music. It is a box, big enough to sit on a musician’s lap, with 4 to 5 strips of metal set up side by side on top like keys on a piano keyboard. The tongues are designed to vibrate. The musician uses their fingers to pluck them, the left hand plucking one or two rhythmic tongues, the right hand plucking the three melodic tongues. "The best players use as many fingers as possible." Players also tap the side of the instrument with a thick ring or the top with their thumbs or knuckles. The instrument produces sonorous tones. Because of the Yoruba language's nature as a tonal language, the agidigbo can act as a musical “speech surrogate”, conveying language through its tones. Characteristics The instrument consists of five metal tongues mounted onto the top of a box, approximately 2 ft x 2.5 ft and 9 inches high (esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Sunny Ade
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws. Kings are Hereditary monarchy, hereditary monarchs when they inherit power by birthright and Elective monarchy, elective monarchs when chosen to ascend the throne. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European languages, Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (cf. Indic ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish ''rí'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as ''rex (king), rex'' and in Greek as ''archon'' or ''basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |