|
Indricothere
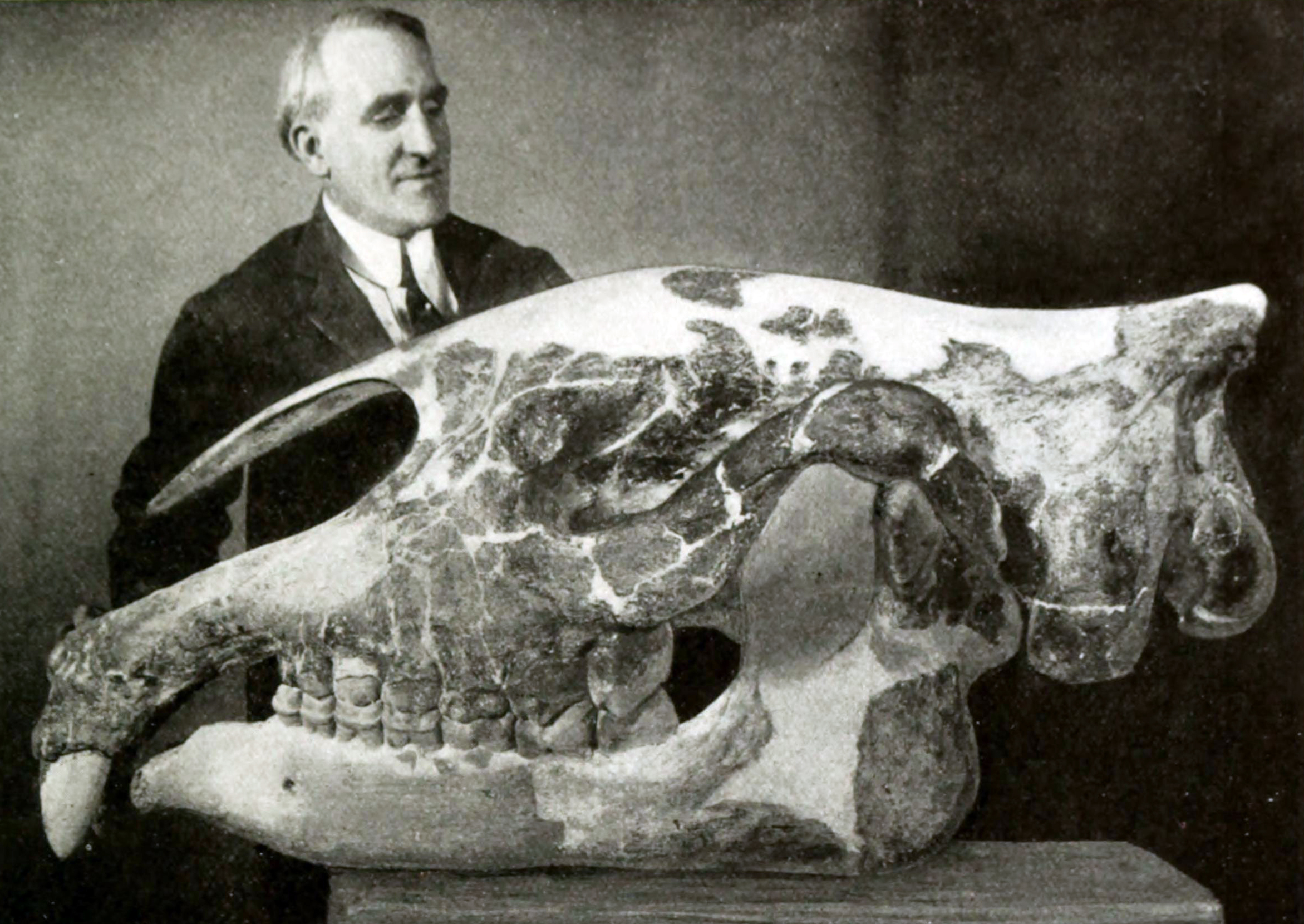
Paraceratheriidae is an extinct family of long-limbed, hornless rhinocerotoids, native to Asia and Eastern Europe that originated in the Eocene epoch and lived until the end of the Oligocene. They represent some of the largest terrestrial mammals to have ever lived. Description The necks and limbs of paraceratheriids are elongate relative to those of living rhinoceroses. The earliest paraceratheres like ''Juxia'' were comparable in size with living rhinoceroses with a body mass of three quarters to one and a half tons, while later members grew substantially larger, with the largest representatives (''Paraceratherium'', '' Dzungariotherium'') estimated to have a body mass of 17 to possibly over 20 tonnes, making them the largest land mammals to have ever lived (though possibly equalled or exceeded by some proboscideans in body mass). Non-fostercoopine paraceratheriids are united by the possession of a retracted nasal notch, a lack of contact between the premaxilla and nasal bones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraceratherium
''Paraceratherium'' is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids belonging to the family Paraceratheriidae. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch (34–23 million years ago). The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. ''Paraceratherium'' means "near the hornless beast", in reference to '' Aceratherium'', the genus in which the type species ''P. bugtiense'' was originally placed. The exact size of ''Paraceratherium'' is unknown because of the incompleteness of the fossils. The shoulder height was about , and the length about . Its weight is estimated to have been about . The long neck supported a skull that was about long. It had large, tusk-like incisors and a nasal incision that suggests it had a prehensile upper lip or proboscis (trunk). The legs were long and pillar-like. The lifestyle of ''Paracera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forstercooperia
''Forstercooperia'' is an extinct genus of forstercooperiine indricotheriinae, paraceratheriid rhinocerotoids from the Middle Eocene of Asia. Description ''Forstercooperia'' is known from a vast amount of cranial material, although only some scant postcranial remains. The average size of the genus is about equal with a large dog, even though later genera like ''Juxia'' and ''Paraceratherium'' reached sizes of a cow and even much larger. Like primitive rhinocerotoids, ''Forstercooperia'' possesses blunt ends on the tips of its nasals, above the nasal incision. Unlike all modern rhinoceroses, the nasals of ''Forstercooperia'', as well as many related genera, lack rugosities, which suggests that they lacked any form of horn. The nasal incision extends fairly far into the upper jaw, ending just posterior to the canine. ''Forstercooperia'' possesses a small post-insicor diastema, not as large as its descendants, and similar in size to that of ''Hyracodon''. Taxonomy ''Forstercooperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
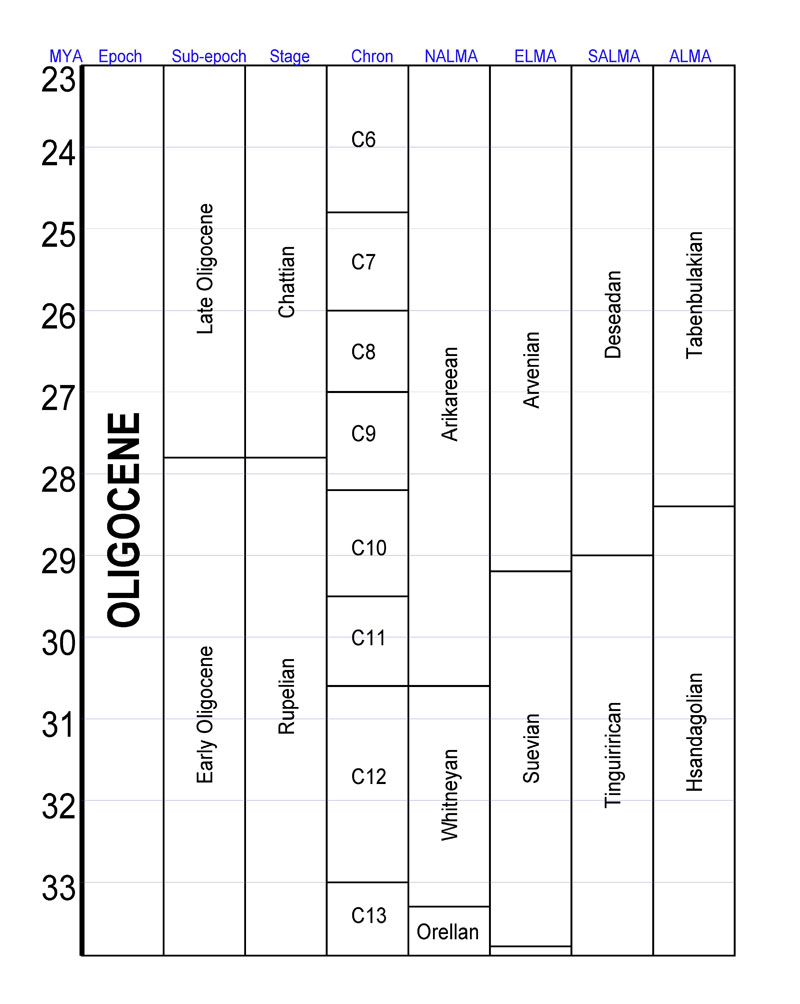
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aralotherium
''Aralotherium'' is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids closely related to ''Paraceratherium'', one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed. It lived in China and Kazakhstan during the late Oligocene epoch (28–23 million years ago). It is classified as a member of the Paraceratheriidae Paraceratheriidae is an extinct family of long-limbed, hornless rhinocerotoids, native to Asia and Eastern Europe that originated in the Eocene epoch and lived until the end of the Oligocene. They represent some of the largest terrestrial mammals ... subfamily Paraceratheriinae. Two species are known, ''A. prohorovi'' and ''A. sui''. References Paraceratheriidae Oligocene rhinoceroses Chattian genus extinctions Prehistoric placental genera Chattian genus first appearances Prehistoric rhinoceroses Fossil taxa described in 1939 {{Paleo-oddtoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzungariotherium
''Dzungariotherium'' is a genus of paraceratheriid, an extinct group of large, hornless rhinocerotoids, which lived during the middle and late Oligocene of northwest China. The type species ''D. orgosense'' was described in 1973 based on fossilsmainly teethfrom Dzungaria in Xinjiang, northwest China. Description The teeth of ''D. orgosense'' (from which that species is mainly known) are 25 percent larger than those of '' Paraceratherium transouralicum'', indicating that it was one of the largest known paraceratheriids,Prothero, 2013. pp. 67–86 but the teeth and skull were proportionally large compared to the body, making it smaller overall. Skull length range is 126-143 cm. The mass of a ''D. sp'' specimen was estimated to be ~ 20.6 metric tons. ''Paraceratherium bugtiense'' and ''D. orgosense'' share features such as relatively slender maxillae In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', ' Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos, anteaters and other animals in the order Edentata have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisors are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitanian Extinctions
Aquitanian may refer to: * Aquitanian (stage), a geological age, the first stage of the Miocene Epoch * Aquitanian language, an ancient language spoken in the region later known as Gascony * Aquitani (or Aquitanians), were a people living in what is now Nouvelle-Aquitaine and southwestern Midi-Pyrenees, France * Anything originating from Aquitaine Aquitaine (, ; ; ; ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne (), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former Regions of France, administrative region. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the administ ..., a region of France {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraceratheriidae
Paraceratheriidae is an extinct family of long-limbed, hornless rhinocerotoids, native to Asia and Eastern Europe that originated in the Eocene epoch and lived until the end of the Oligocene. They represent some of the largest terrestrial mammals to have ever lived. Description The necks and limbs of paraceratheriids are elongate relative to those of living rhinoceroses. The earliest paraceratheres like '' Juxia'' were comparable in size with living rhinoceroses with a body mass of three quarters to one and a half tons, while later members grew substantially larger, with the largest representatives (''Paraceratherium'', '' Dzungariotherium'') estimated to have a body mass of 17 to possibly over 20 tonnes, making them the largest land mammals to have ever lived (though possibly equalled or exceeded by some proboscideans in body mass). Non-fostercoopine paraceratheriids are united by the possession of a retracted nasal notch, a lack of contact between the premaxilla and nasal bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert M
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald R
Donald is a Scottish masculine given name. It is derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers. A short form of Donald is Don, and pet forms of Donald include Donnie and Donny. The feminine given name Donella is derived from Donald. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name '' Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of many ancient and medieval Gaelic kings and noblemen: * Dyfnwal Moelmud (Dunvallo Molmutius), legendary kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |