|
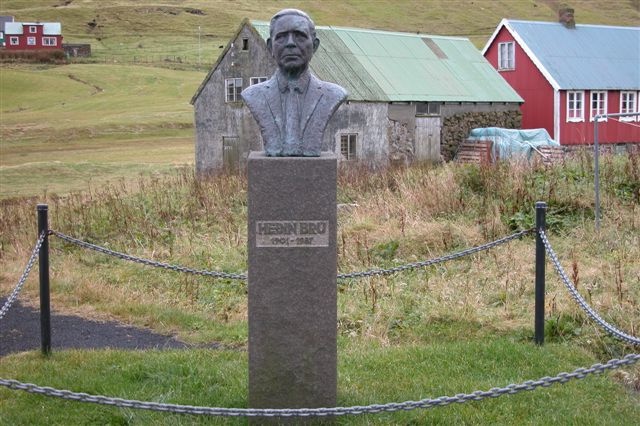
Heðin Brú
Heðin Brú (pronounced ; August 17, 1901, Skálavík – May 18, 1987, Tórshavn) was the pen-name of Hans Jacob Jacobsen, a Faroese novelist and translator. Heðin Brú is considered to be the most important Faroese writer of his generation and is known for his fresh and ironic style. His novel, ''Feðgar á ferð'' (''The Old Man and His Sons''), was chosen as the ''Book of the twentieth century'' by the Faroese. Life and Works Like many of his countrymen, Jacobsen worked as a fisherman in his early years. After two seasons, he left to study agriculture in Denmark. When he returned to the Faroes, he worked as an agricultural advisor—a job that took him to all parts of the country. The contacts he made with ordinary village people he met during this time had a lasting effect on his writing. In 1930, his first novel, ''Lognbrá'', which tells the story of a young man growing up in a Faroese village, was published. In 1935 there appeared its sequel, ''Fastatøkur'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skálavík
Skálavík ( da, Skålevig) is a village and municipality on the eastern coast of the Faroese island Sandoy. History The village's stone church was built in 1891. The famous Faroese writers Heðin Brú (born Hans Jacob Jacobsen) (1901–1987) and Kristian Osvald Viderø (1906–1988) were both born in Skálavík. In late January 2008 Skálavík was hit by a strong hurricane. The port was destroyed, along with many boats and houses. The damage was so great that emergency aid was provided from Iceland. Depilin í Skálavík - Hotel Skálavík In May 2011 a new center opened in Skálavík. It was donated by shipowner Eiler Jacobsen (1930-2010), who was born in the village. He did not live to see the opening, but he visited the building during the construction. There is a restaurant, a hotel and conference center, activities for children etc. The center was named Skeiðs- og frítíðardepilin Immanuel, but they also use the name "Depilin í Skálavík" (The Center in Skálavík). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Language
Icelandic (; is, íslenska, link=no ) is a North Germanic language The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also ... spoken by about 314,000 people, the vast majority of whom live in Iceland, where it is the national language. Due to being a West Scandinavian languages, West Scandinavian language, it is most closely related to Faroese language, Faroese, western Norwegian dialects, and the extinct language, Norn language, Norn. The language is more Linguistic conservatism, conservative than most other Germanic languages. While most of them have greatly reduced levels of inflection (particularly noun declension), Icelandic retains a four-grammatical case, case synthetic language, synthetic grammar (comparable to German cases, German, though considerably more conservative and syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroese National Library
The National Library of the Faroe Islands ( fo, Føroya Landsbókasavn) is the national library for the Faroe Islands, a self-governing country within the Kingdom of Denmark. It is both a public and a research library. The library houses the largest collection of works written in Faroese, works written by Faroese in other languages or translated by them, and works written about the Faroe Islands. History The library began in 1828, when the Danish '' Amtmaður'' (governor) Christian Ludvig Tillisch (in office 1825–30) and his ''Amtsrevisor'' Jens Davidsen began assembling books for a ''Færø Amts Bibliotek'' (Danish, 'Faroe County Library'). They were assisted by the Danish scholar Carl Christian Rafn and by private citizens, and on 5 November 1828 secured an annual grant of funds from the King. In 1831, the collection included 2,860 volumes. The library acquired its own building in 1830, and Jens Davidsen served as librarian until his death in 1878. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Seagull
''The Seagull'' ( rus, Ча́йка, r=Cháyka, links=no) is a play by Russian dramatist Anton Chekhov, written in 1895 and first produced in 1896. ''The Seagull'' is generally considered to be the first of his four major plays. It dramatises the romantic and artistic conflicts between four characters: the famous middlebrow story writer Boris Trigorin, the ingenue Nina, the fading actress Irina Arkadina, and her son the symbolist playwright Konstantin Treplev. Like Chekhov's other full-length plays, ''The Seagull'' relies upon an ensemble cast of diverse, fully developed characters. In contrast to the melodrama of mainstream 19th-century theatre, lurid actions (such as Konstantin's suicide attempts) are not shown onstage. Characters tend to speak in subtext rather than directly. The character Trigorin is considered one of Chekhov's greatest male roles. The opening night of the first production was a famous failure. Vera Komissarzhevskaya, playing Nina, was so intimidated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov (; 29 January 1860 Old Style date 17 January. – 15 July 1904 Old Style date 2 July.) was a Russian playwright and short-story writer who is considered to be one of the greatest writers of all time. His career as a playwright produced four classics, and his best short stories are held in high esteem by writers and critics."Stories ... which are among the supreme achievements in prose narrative.Vodka miniatures, belching and angry cats George Steiner's review of ''The Undiscovered Chekhov'', in ''The Observer'', 13 May 2001. Retrieved 16 February 2007. Along with Henrik Ibsen and August Strindberg, Chekhov is often referred to as one of the three seminal figures in the birth of early modernism in the theatre. Chekhov was a physician by profession. "Medicine is my lawful wife", he once said, "and literature is my mistress." Chekhov renounced the theatre after the reception of ''The Seagull'' in 1896, but the play was revived to acclaim in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Literature
World literature is used to refer to the total of the world's national literature and the circulation of works into the wider world beyond their country of origin. In the past, it primarily referred to the masterpieces of Western European literature; however, world literature today is increasingly seen in an international context. Now, readers have access to a wide range of global works in various translations. Many scholars assert that what makes a work considered world literature is its circulation beyond its country of origin. For example, Damrosch states, "A work enters into world literature by a double process: first, by being read as literature; second, by circulating out into a broader world beyond its linguistic and cultural point of origin". Likewise, the world literature scholar Venkat Mani believes that the "worlding" of literature is brought about by "information transfer" largely generated by developments in print culture. Because of the advent of the library, "Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Threepenny Review
''The Threepenny Review'' is an American literary magazine founded in 1980. It is published in Berkeley, California, by founding editor Wendy Lesser. Maintaining a quarterly schedule (March, June, September, December), it offers fiction, memoirs, poetry, essays and criticism to a readership of 10,000. Without the support of patrons or a university, the publication has an annual budget of $200,000. History The magazine was launched in 1980 after Lesser (then 27 years old with no editing experience) was a guest editor of Ron Nowicki's ''San Francisco Review of Books''. She found the experience so rewarding that she decided to create her own publication, and the first issue of ''The Threepenny Review'' appeared three months later. She chose the title for its "obvious Brechtian overtones". "The Threepenny Opera" is the title of one of Brecht's most famous works. It sometimes features an essay symposium, as described by critic Deborah Mead in reviewing issue 104 (Winter 2006): What se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rikard Long
Rikard Sigmund Long (January 23, 1889 – December 16, 1977) was a Faroese teacher, writer, and politician for the People's Party. Long was born in Tórshavn, the son of Georg Long from Copenhagen and Svanhilda Pálsson from Vágur.Long, Rikard. 1979. Kveikt og kannað. Tórshavn: Føroya skúlabókagrunnur, pp. 12–13.Jones, W. Glyn. 1992. Faroese literature. In: Sven Hakon Rossel, ed. ''A History of Danish Literature'', pp. 545–585. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, p. 558. He passed his ''examen artium'' in 1907 and his ''examen philosophicum'' in 1909. He enrolled at the University of Copenhagen in 1909, initially studying medicine and later switching to languages, but he never took any exams. He was a teacher at the Tórshavn Nautical School ( fo, Tórshavnar skiparaskúli) from 1914 to 1916 and from 1919 to 1920, and then taught at the Faroese Middle and High School ( fo, Føroya Millum- og Realskúli) from 1921 to 1954. He headed the Copenhagen Student Union from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 7th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid-to-late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not absolute, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: ''Old West Norse'' or ''Old West Nordic'' (often referred to as ''Old Norse''), ''Old East Norse'' or ''Old East Nordic'', and '' Old Gutnish''. Old West Norse and Old East Norse formed a dialect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
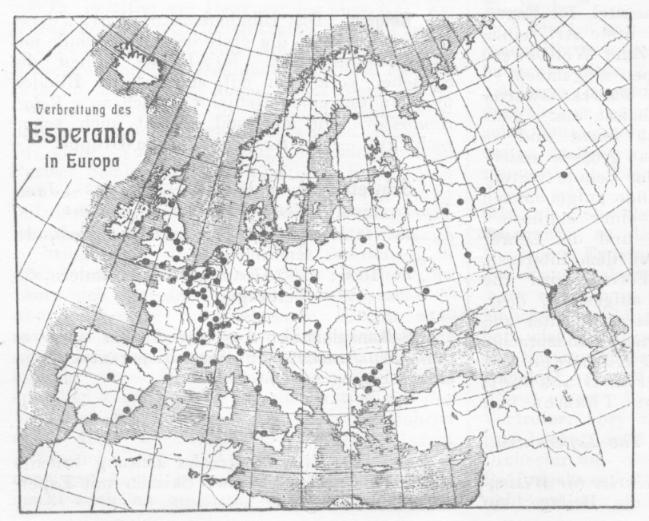
Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in ''Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena: One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ... and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |