|
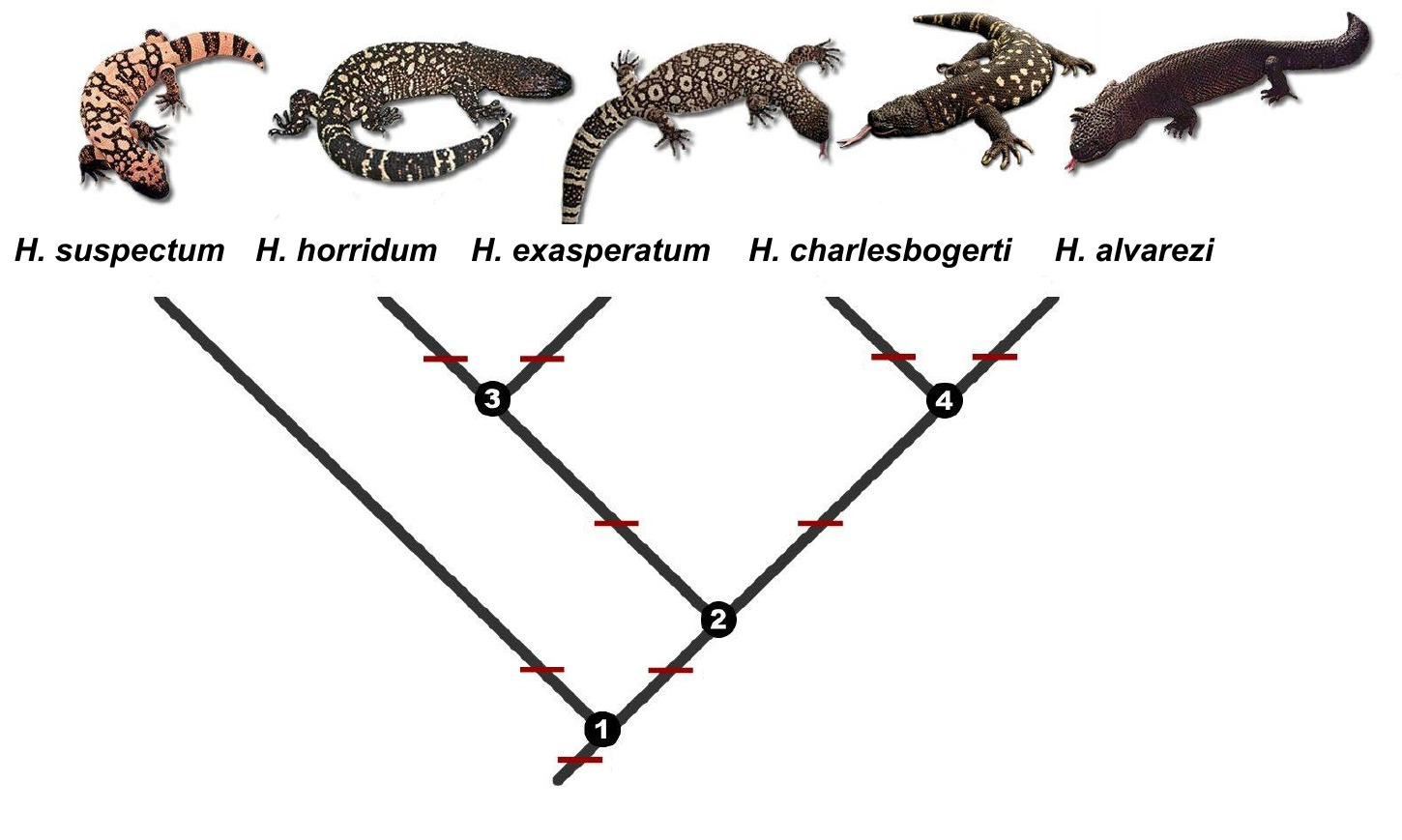
Heloderma Suspectum
The Gila monster (''Heloderma suspectum'', ) is a species of venomous lizard native to the Southwestern United States and the northwestern Mexican state of Sonora. It is a heavy, slow-moving reptile, up to long, and it is the only venomous lizard native to the United States. Its venomous close relatives, the four beaded lizards (all former subspecies of '' Heloderma horridum'') inhabit Mexico and Guatemala. The Gila monster is sluggish in nature, so it is not generally dangerous and very rarely poses a real threat to humans. However, it has a fearsome reputation and is sometimes killed despite the species being protected by state law in Arizona. History The name "Gila" refers to the Gila River Basin in the U.S. states of Arizona and New Mexico, where the Gila monster was once plentiful. ''Heloderma'' means "studded skin", from the Ancient Greek words (), "the head of a nail or stud", and (), "skin". The species epithet ''suspectum'' comes from the describer, paleontolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gila Monster
The Gila monster (''Heloderma suspectum'', ) is a species of venomous lizard native to the Southwestern United States and the northwestern Mexico, Mexican state of Sonora. It is a heavy, slow-moving reptile, up to long, and it is the only venomous lizard native to the United States. Its venomous close relatives, the four Mexican beaded lizard, beaded lizards (all former subspecies of ''Heloderma horridum'') inhabit Mexico and Guatemala. The Gila monster is sluggish in nature, so it is not generally dangerous and very rarely poses a real threat to humans. However, it has a fearsome reputation and is sometimes killed despite the species being protected by state law in Arizona. History The name "Gila" refers to the Gila River Basin in the U.S. states of Arizona and New Mexico, where the Gila monster was once plentiful. ''Heloderma'' means "studded skin", from the Ancient Greek words (), "the head of a nail or stud", and (), "skin". The species epithet ''suspectum'' comes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American International Rattlesnake Museum
The American International Rattlesnake Museum is an animal conservation museum located in Albuquerque, New Mexico in Old Town Albuquerque. The museum is devoted to snakes, particularly rattlesnakes, and is dedicated to rattlesnake education. With the staff that is a participant in regular international viper research events, the museum hosts a diverse collection of living rattlesnakes and an extensive library of study material and educational tools. The museum has the largest collection of different species of live rattlesnakes in the world, which are presented in recreated habitats, and claims to host more rattlesnake species than the Bronx Zoo, the Philadelphia Zoo, the National Zoological Park (United States), National Zoo in Washington, D.C., the Denver Zoo, the San Francisco Zoo, and the San Diego Zoo combined. In addition to rattlesnakes, the museum holds a live Gila monster, one of the few known venomous lizard species. The museum also houses a large collection of snake-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
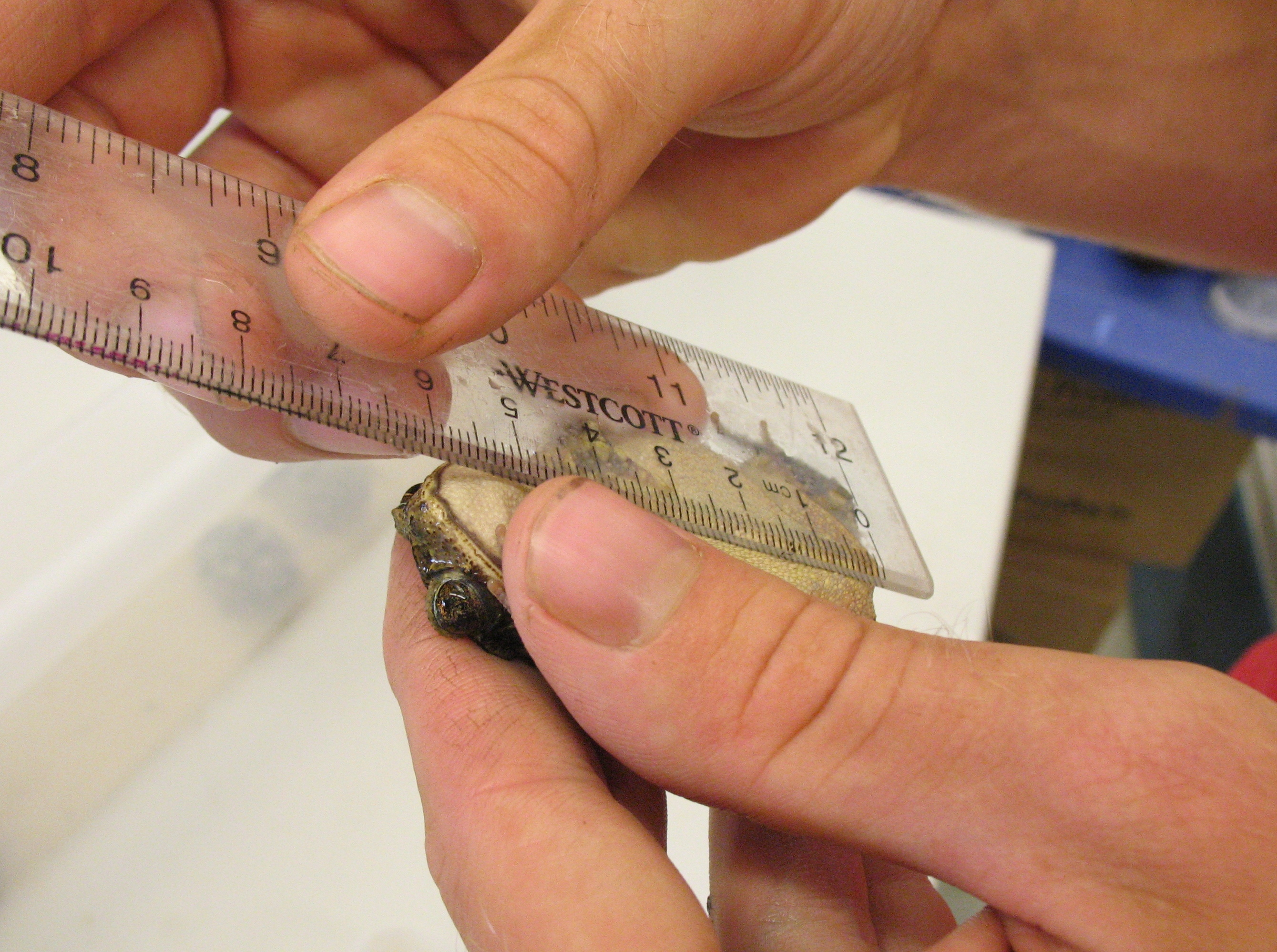
Snout–vent Length
Snout–vent length (SVL) is a morphometric measurement taken in herpetology from the tip of the snout to the most posterior opening of the cloacal slit (vent)."direct line distance from tip of snout to posterior margin of vent" It is the most common measurement taken in herpetology, being used for all amphibians, lepidosaurs, and crocodilia Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchia ...ns (for turtles, carapace length (CL) and plastral length (PL) are used instead). The SVL differs depending on whether the animal is struggling or relaxed (if alive), or various other factors if it is a preserved specimen. For fossils, an osteological correlate such as precaudal length must be used. When combined with weight and body condition, SVL can help deduce age and sex. Advantag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor Lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and West African Nile monitor, one species is also found in south America as an invasive species. About 80 species are recognized. Monitor lizards have long necks, powerful tails and claws, and well-developed limbs. The adult length of extant species ranges from in some species such as ''Dampier Peninsula monitor, Varanus sparnus'', to over in the case of the Komodo dragon, though the extinct megalania (''Varanus priscus'') may have reached lengths of more than . Most monitor species are terrestrial locomotion, terrestrial, but many are also arboreal or semiaquatic. While most monitor lizards are carnivorous, eating smaller reptiles, fish, birds, insects, small mammals, and eggs, a few species also eat fruit and vegetation. Etymology The genus, generic name ''Varanus'' is derived from the Arabic (language), Arabic word ''waral'' [St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living Fossil
A living fossil is a Deprecation, deprecated term for an extant taxon that phenotypically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade. Living fossils commonly are of species-poor lineages, but they need not be. While the body plan of a living fossil remains superficially similar, it is never the same species as the remote relatives it resembles, because genetic drift would inevitably change its chromosomal structure. Living fossils exhibit punctuated equilibrium, stasis (also called "bradytely") over geologically long time scales. Popular literature may wrongly claim that a "living fossil" has undergone no significant evolution since fossil times, with practically no molecular evolution or Morphology (biology), morphological changes. Scientific investigations have repeatedly discredited such claims. The minimal superficial changes to living foss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-largest in the Southwestern United States. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city had 641,903 residents in 2020, with a metropolitan population of 2,227,053, making it the 24th-most populous city in the United States. Las Vegas is an internationally renowned major resort city, known primarily for its gambling, shopping, fine dining, entertainment, and nightlife. Most of these venues are located in downtown Las Vegas or on the Las Vegas Strip, which is outside city limits in the unincorporated towns of Paradise and Winchester. The Las Vegas Valley serves as the leading financial, commercial, and cultural center in Nevada. Las Vegas was settled in 1905 and officially incorporated in 1911. At the close of the 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold Glacial period, glacial periods and warmer Interglacial, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans (armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes of amniotes and are an exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estesia
''Estesia'' (in honour of Richard Estes) is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous anguimorph lizard found in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia. Discovery It was discovered in June 1990 by a joint expedition made up of Mongolian and American palaeontologists, and described in 1992 by Mark Norell, Malcolm McKenna and Michael Novacek. This animal is of interest to palaeontologists, not only because it is close to the lineage of modern Gila monsters (''Heloderma''), but also because its dentition shows evidence that it was venomous. The type species is ''E. mongoliensis'', after Mongolia, where it was found. Material for ''Estesia'' has been collected in various localities in the Gobi Desert, including the Barun Goyot Formation, the Djadochta Formation and Ukhaa Tolgod. *IGM M3/14 (holotype): A well-preserved skull with mandible, from Lizard Hill, Khulsan (Barun Goyot Formation) *IGM 3/15: Partial skeleton with associated braincase, from Khermeen Tsav (Barun Goyot Formation), disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gobiderma
''Gobiderma'' is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous lizard whose fossils are known from the Gobi Desert in southern Mongolia. It was first discovered as a result of a joint Polish-Mongolian Paleontological Expedition, and formally named in 1984. In life, it probably resembled lizards of the genus ''Heloderma'' to a large degree, though its skull was more elongated than lizards of that genus. Sources * Dragons in the Dust: The Paleobiology of the Giant Monitor Lizard ''Megalania'' by Ralph E. Molnar (page 91) * In the Shadow of the Dinosaurs: Early Mesozoic Tetrapods by Nicholas C. Fraser and Hans-Dieter Sues Hans-Dieter Sues (born 1956) is a German-born American palaeontologist who is a Senior Research Geologist and Curator of Vertebrate Paleontology at the National Museum of Natural History of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC. Career ... (page 30) * The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia by Michael J. Benton, Mikhail A. Shishkin, David M. Unwin, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |