|
Ghanashyam House
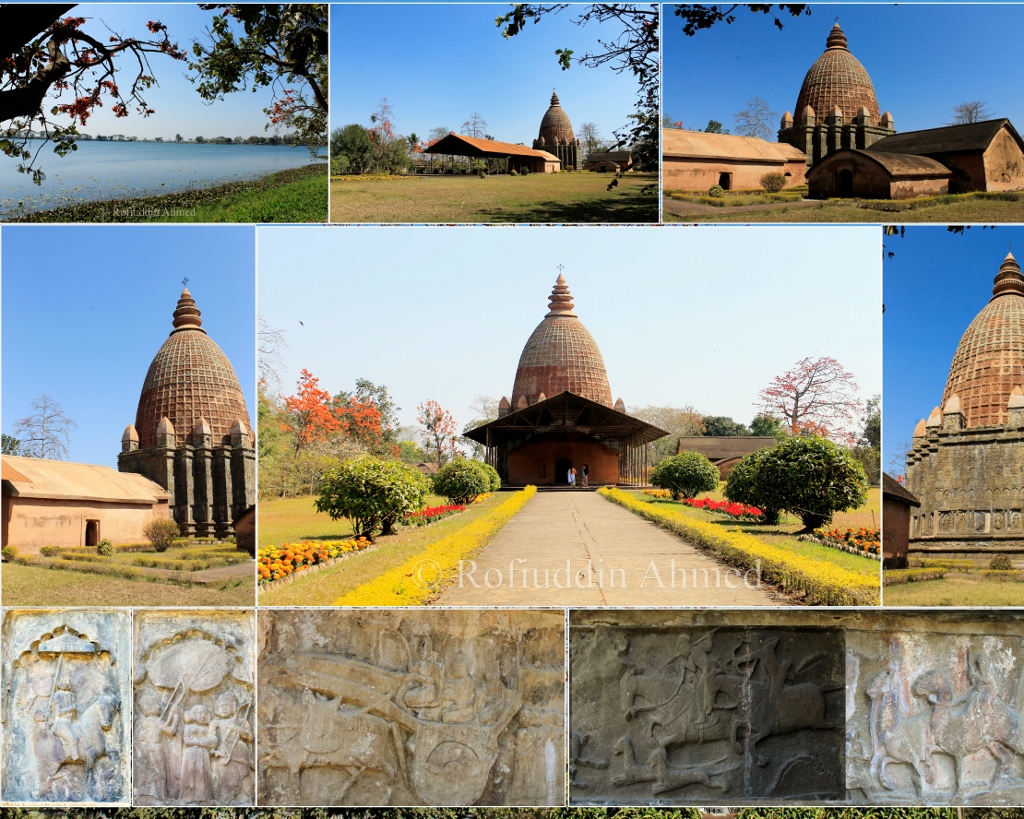
Ghanashyam House or Nati Gosain dol is an early 18th-century brick monument built during the reign of the king Rudra Singha dedicated to the architect Ghanashyam. This monument is situated on the west bank of Joysagar Tank. It is 4 km away from Sivasagar town towards west. Architecture and history It was constructed by one Ghanasyamuddin Khanikar later renamed as Ghanashyam, an architect from Bengal or Cooch Behar who was brought by king Rudra Singha, he entrusted him with the duty of designing the city of Rangpur. It is believed that Ghanashyam was earlier a Muslim who was converted to Hinduism. As a result of Ghanashyam's influence, this monument has mixture of Islamic architectural elements as well as Hindu architectural elements. The temple resembles a Bengal ekaratha structure but its cells contain a typical mihrab found in mosques. Islamic architectural influence can be heavily noticed in the architecture of this building. The temple is enriched with beautiful terracot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivasagar, Assam
{{Infobox settlement , name = Sivasagar , settlement_type = Metropolis , image_skyline = Sivasagar.jpg , image_alt = {{multiple image , border = infobox , total_width = 270 , image_style = , perrow = 1/2/2/1 , image1 = Sivasagarcitysky.jpg , caption1 = Sivasagar Aerial View , image2 = Heritage joysagar.jpg , caption2 = Heritage Joysagar , image_caption = Clockwise from top: Sivadol, Azan Faqir Dargah, Garhgaon's Kareng ghar, Rang Ghar and night view of Sivasagar tank , nickname = Ahom Kingdom , image_map = , map_alt = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = India Assam#India , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_map_alt = , pushpin_map_caption = Location in Assam, India , coordinates = {{coord, 26, 59, 04, N, 94, 38, 15, E, display=inline,title , subdivision_type = Country , subdivis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudra Singha
Swargadeo Rudra Singha (– 27 August 1714), with Tai name Sukhrungphaa, was the 30th Ahom king, reigning from 1696 to 1714 A.D . His father Gadadhar Singha freed Assam from the Mughal disturbances and internal conspiracies, thereby Rudra Singha inherited a stable state and government and had the advantage of the solid foundations laid by his father. He devoted his time to transform Assam into a first-rate power in India. He stopped the persecution of the Neo-Vaisnava sect and built temples, several public works, and patronized art, literature, and culture. Rudra Singha is also famed for being the real father of Ahom architecture. He giving up the isolationist policy of his predecessors forged diplomatic ties with various states of that time and established extensive trade with Bengal. He remodeled the administrative structure and army and carried on aggressive warfare upon the neighboring chiefdoms and countries, the Jaintias and Dimasas submitted and became vassals. Rudra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joysagar Tank
Joysagar Tank, also known as Joysagar Borpukhuri is a large tank located at Sivasagar district, Assam, India. The lake is 5 km from the center of the Sivasagar town. The lake has historical significance. History The lake was made during the reign of the renowned Ahom king, Rudra Singha. About 5 km from the Sivasagar township, three set of temples are located on the northern bank of the lake. The most renowned among these sanctuaries is the Joy dol, which is also known as the Keshavnaryan Vishu dol. As the name suggests, the sanctuary is devoted to Lord Vishnu and his numerous manifestations. This lake was formed on 1697, in just 45 days, in the memory of Joymoti Konwari, mother of Rudra Singha. The lake covers an area of 318 acres (1.28 square km). The water level of the lake is 14 feet higher from ground level. Tourism The lake attracts international tourists. The northern bank of the lake has many temples which are visited by the locals every day. Joysagar is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivasagar
{{Infobox settlement , name = Sivasagar , settlement_type = Metropolis , image_skyline = Sivasagar.jpg , image_alt = {{multiple image , border = infobox , total_width = 270 , image_style = , perrow = 1/2/2/1 , image1 = Sivasagarcitysky.jpg , caption1 = Sivasagar Aerial View , image2 = Heritage joysagar.jpg , caption2 = Heritage Joysagar , image_caption = Clockwise from top: Sivadol, Azan Faqir Dargah, Garhgaon's Kareng ghar, Rang Ghar and night view of Sivasagar tank , nickname = Ahom Kingdom , image_map = , map_alt = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = India Assam#India , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_map_alt = , pushpin_map_caption = Location in Assam, India , coordinates = {{coord, 26, 59, 04, N, 94, 38, 15, E, display=inline,title , subdivision_type = Country , sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooch Behar State
Cooch Behar, also known as Koch Bihar, was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The state was placed under the Bengal States Agency, part of the Eastern States Agency of the Bengal Presidency. It was located south of the Himalayas, Himalayan kingdom of Bhutan, in present-day West Bengal. Cooch Behar State was formed when the Kamata Kingdom under the Koch dynasty split following the death of Nara Narayan in 1586. The eastern portion, Koch Hajo, was soon absorbed by Ahom kingdom, Ahom. The western portion, Koch Bihar, formed a separate unit that came under direct challenge by the Mughal Empire. After weathering the Mughal threat, a new foe emerged in the form of an expansionist Bhutanese kingdom. After a series of wars with the Bhutanese and Tibetan people, Tibetans, the Northern threat was pushed back but not before a Bhutanese regent was installed in the royal court. The Koch Bihar court decided to invite British intervention. This came in the form of military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangpur, Assam
Rangpur (Ahom language, Tai-Ahom:Tsé-Moon; ) is the 4th capital of the Ahom kingdom, was established by Swargadeo Rudra Singha in "Meteka" in 1707 after shifting the capital from Garhgaon. It is currently a part of Sibsagar town. The place holds many monuments build by the Ahom dynasty, the most notable of which are the Talatal Ghar and the Rang Ghar. The architectural plan of Rangpur spread over almost a thousand bighas of land. Ghanasyam, an architect from Cooch Behar, Koch Bihar, was deputed by Rudra Singha to design the city. Etymology Rangpur situated near the modern day Sivasagar town, means ''City of delight'' or the ''City of Joy'' as the King here had immensely enjoyed the falconry arranged by the Borphukan and in Ahom language it is called ''Che-mun''. History Capital City The city of Rangpur was laid in C.E. 1698 by King Rudra Singha at Tengabari of Meteka area. He then excavated the famous Joysagar Tank and there after he respectively had constructed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Architecture
Islamic architecture comprises the architectural styles of buildings associated with Islam. It encompasses both Secularity, secular and religious styles from the early history of Islam to the present day. The Muslim world, Islamic world encompasses a wide geographic area historically ranging from western Africa and Europe to eastern Asia. Certain commonalities are shared by Islamic architectural styles across all these regions, but over time different regions developed their own styles according to local materials and techniques, local dynasties and patrons, different regional centers of artistic production, and sometimes Islamic schools and branches, different religious affiliations. Early Islamic architecture was influenced by Roman architecture, Roman, Byzantine architecture, Byzantine, Iranian architecture, Iranian, and Architecture of Mesopotamia, Mesopotamian architecture and all other lands which the early Muslim conquests conquered in the seventh and eighth centuries.: "As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Architecture
Hindu architecture is the traditional system of Indian architecture for structures such as temples, monasteries, statues, homes, market places, gardens and town planning as described in Hindu texts. The architectural guidelines survive in Sanskrit manuscripts and in some cases also in other regional languages. These texts include the Vastu shastras, Shilpa Shastras, the ''Brihat Samhita'', architectural portions of the Puranas and the Agamas, and regional texts such as the Manasara among others. By far the most important, characteristic and numerous surviving examples of Hindu architecture are Hindu temples, with an Hindu temple architecture, architectural tradition that has left surviving examples in stone, brick, and Indian rock-cut architecture, rock-cut architecture dating back to the Gupta Empire. These architectures had influence of Ancient Persian and Hellenistic influence on Indian art, Hellenistic architecture. Far fewer secular Hindu architecture have survived into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics of Hinduism known as the ''Itihasas'', the other being the ''Mahabharata''. The epic narrates the life of Rama, the seventh ''avatar'' of the Hindu deity Vishnu, who is a prince of Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya in the kingdom of Kosala. The epic follows Exile of Lord Rama, his fourteen-year exile to the forest urged by his father King Dasharatha, on the request of Rama's stepmother Kaikeyi; his travels across the forests in the Indian subcontinent with his wife Sita and brother Lakshmana; the kidnapping of Sita by Ravana, the king of Lanka, that resulted in bloodbath; and Rama's eventual return to Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya along with Sita to be crowned as a king amidst jubilation and celebration. Scholarly estimates for the earliest stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajeswar Singha
Suremphaa (reign 1751–1769), or Rajeswar Singha, the fourth son of Rudra Singha, became the Ahom Dynasty, king of the Ahom kingdom after the death of his brother King Pramatta Singha. Rudra Singha's third son, Mohanmala Maladev Gohain, Mohanmala Gohain, was considered ineligible for kingship as his face was pitted with smallpox marks. According to the norm established after Sulikphaa Lora Roja, an Ahom prince had to be free from any physical disability, defects or deformities to become a king. The new king was installed with the usual ceremonies. His first act was to exile his brother Mohanmala Maladev Gohain as the Raja of Namrup. During his installation as king, there was a conflict of opinion about the location of the capital between the Deodhais (Ahom priests) and the Hindu astrologers, the former recommended Taimung and the latter Rangpur (Ahom capital), Rangpur. The king took the advice of the Hindu Astrology, astrologers and built his palace at Rangpur, but afterwards, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pramatta Singha
Swargadeo Pramatta Singha () with Tai name Sunenphaa, was the king of Ahom Kingdom. He succeeded his elder brother Swargadeo Siva Singha, as the king of Ahom Kingdom. His reign of seven years was peaceful and prosperous. He constructed numerous buildings and temples. The most famous of his buildings was the Rang Ghar, which is also considered as the oldest amphitheatre in Asia. Ancestry and background Pramatta Singha was the second son of Swargadeo Rudra Singha. During the reign of his elder brother Swargadeo Siva Singha, he held the post of Charing Raja or the heir apparent to the throne. Most of the chronicles recorded that Swargadeo Rudra Singha expressed his desire at his death-bed that all his five sons Siva Singha, Pramatta Singha, Mohanmala Maladev Gohain alias Barjana Gohain, Rajeswar Singha and Lakshmi Singha successively became king, after him. Accordingly, after the death of Swargadeo Siba Singha, Chengmung Burhagohain of Pukhuriparia clan along with some other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |