|
Genomoviridae
''Genomoviridae'' is a family of single stranded DNA viruses that mainly infect fungi. The genomes of this family are small (2.2–2.4 kilobases in length). The genomes are circular single-stranded DNA and encode rolling-circle replication initiation proteins (Rep) and unique capsid proteins. In Rep-based phylogenies, genomoviruses form a sister clade to plant viruses of the family '' Geminiviridae''. Ten genera are recognized in this family. The family name is an acronym derived from ''geminivirus-like, no movement protein''. The genus name ''Gemycircularvirus'' stands for Gemini-like myco-infecting circular virus. The type species of the genus ''Gemycircularvirus'' — ''Sclerotinia gemycircularvirus 1'', reference strain Sclerotinia sclerotiorum hypovirulence associated DNA virus 1 (ssHADV-1), — was the first cultivated member of the family. The other genomoviruses are uncultivated and have been discovered using metagenomics techniques. __TOC__ Taxonomy The genera in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerotinia Sclerotiorum Hypovirulence Associated DNA Virus 1
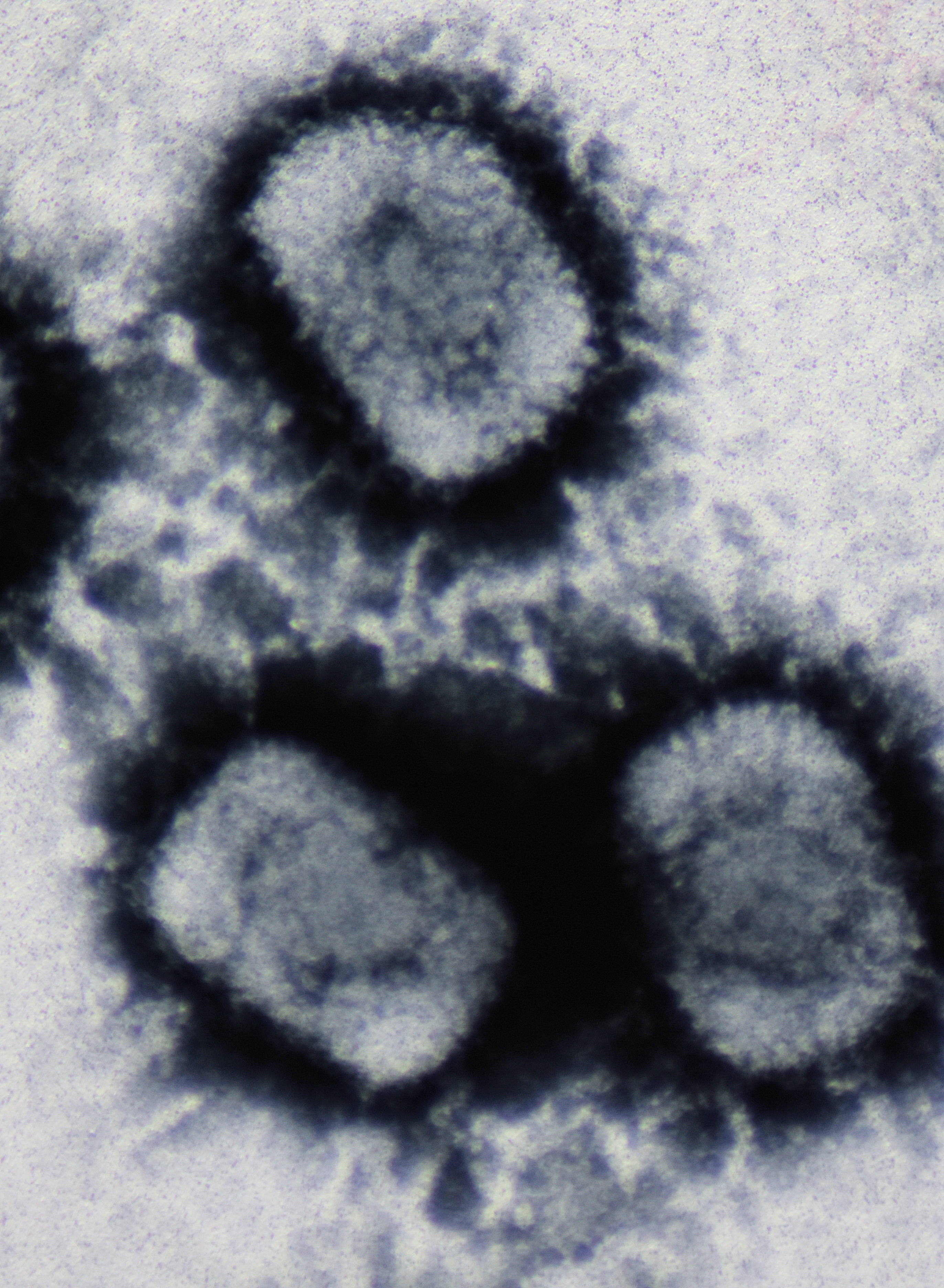
''Sclerotinia gemycircularvirus 1'' is a single stranded DNA virus with a circular genome that infects the fungus '' Sclerotinia sclerotiorum''. Infection with this virus decreases the virulence of this fungus. The mechanism of this effect is not known. Virology The virions are isometric particles, 20–22 nanometers in diameter. The capsid is composed on the viral coat protein (VCP). Genome The genome encodes only two proteins—a replicase and the coat protein. The genes are encoded on complementary strands. Taxonomy This virus appears to be related to but distinct from members of the '' Geminiviridae''. Unlike geminiviruses, this virus does not have a movement protein. It has been officially classified into the genus ''Gemycircularvirus'' within the new family ''Genomoviridae ''Genomoviridae'' is a family of single stranded DNA viruses that mainly infect fungi. The genomes of this family are small (2.2–2.4 kilobases in length). The genomes are circular single-str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom ''Pararnavirae'' in the realm ''Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |