|
Ganjin
Jianzhen (688–763), also known by his Japanese language, Japanese name Ganjin (,), was a Tang dynasty, Tang Han people, Chinese Buddhist monk, monk who helped to propagate Buddhism in Japan. In the eleven years from 743 to 754, Jianzhen attempted to visit Japan some six times, arriving in the year 753 and founding Tōshōdai-ji in Nara, Nara, Nara. When he finally succeeded on his sixth attempt, he had lost his eyesight as a result of an infection acquired during his journeys. Jianzhen's life story and voyage are described in the scroll, "The Sea Journey to the East of a Great Bonze from the Tang Dynasty." Life Jianzhen was born in Jiangyin county in Guangling Commandery, Guangling Prefecture (present day Yangzhou), China, with the surname of Chunyu (). At the age of fourteen, he became a disciple of Dayun Temple (). At twenty he travelled to Chang'an for study and returned six years later, eventually becoming abbot of Daming Temple. Besides his learning in the Tripiṭaka, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risshū (Buddhism)
, also ''Ritsu'', is one of the Nanto Rikushū, six schools of Nara Buddhism in Japan, noted for its use of the Vinaya textual framework of the Dharmaguptaka, one of the early schools of Buddhism; Risshū is the Japanese term for Vinaya. The Ritsu school was founded in Japan by the blind Chinese priest Jianzhen, better known by his Japanese name ''Ganjin''. Ganjin traveled to Japan at the request of Japanese priests, and established the Tōshōdai-ji in Nara, Nara, Nara. During the Kamakura period, the Ritsu sect was divided into schools at Tōshōdai-ji, Kaidan-in, Saidai-ji, and Sennyū-ji. However, during the Meiji period, the Ritsu sect was incorporated within the Shingon sect by decree of the Japanese government. Today only Tōshōdai-ji, which resisted the government measures, retains its identity as a Ritsu temple. History Jianzhen reached Japan in 753/4. He introduced the Four Part Vinaya Code (in Japanese, the '), a series of monastic precepts based on Chinese Buddh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tōshōdai-ji
is a Buddhist temple of the Risshū sect in the city of Nara, in Nara Prefecture, Japan. The Classic Golden Hall, also known as the '' kondō'', has a single story, hipped tiled roof with a seven bay wide facade. It is considered the archetype of "classical style". It was founded in 759 by the Tang dynasty Chinese monk Jianzhen during the Nara period. Jianzhen was hired by the newly empowered clans to travel in search of funding from private aristocrats as well. Tōshōdai-ji is one of the places in Nara that UNESCO has designated as World Heritage Site " Historic Monuments of Ancient Nara". A reflection written by Yan Wenjing on the hope for friendly Sino-Japanese relations describing the author's discovery of lotus flowers imported from China which had been planted around the portrait of Jianzhen in the Tōshōdai-ji is included as one of the oral assessment passages on the Putonghua Proficiency Test. Building list * Golden Hall – National Treasure of Japan, built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonze
A ''bhikkhu'' (, ) is an ordained male in Buddhist monasticism. Male, and female monastics (''bhikkhunī''), are members of the Sangha (Buddhist community). The lives of all Buddhist monastics are governed by a set of rules called the prātimokṣa or pātimokkha. Their lifestyles are shaped to support their spiritual practice: to live a simple and meditative life and attain nirvana. A person under the age of 20 cannot be ordained as a bhikkhu or bhikkhuni but can be ordained as a śrāmaṇera or śrāmaṇērī. Definition ''Bhikkhu'' literally means " beggar" or "one who lives by alms". The historical Buddha, Prince Siddhartha, having abandoned a life of pleasure and status, lived as an alms mendicant as part of his śramaṇa lifestyle. Those of his more serious students who renounced their lives as householders and came to study full-time under his supervision also adopted this lifestyle. These full-time student members of the sangha became the community of ordained m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagoshima
, is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 583,966 in 285,992 households, and a population density of 1100 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . Etymology While the kanji used to spell () literally mean "deer child island", or "island of the fawn", the source etymology is not clear, and may refer to "cliff" or "sailor" in the Kagoshima dialect, local dialect. Local names for the city include , , and . History Kagoshima is located in ancient Satsuma Province and was the center of the territory of the Shimazu clan from the late Kamakura period. Kagoshima City developed political and commercial port city in the Edo period (1603–1868) when it became the seat of the Shimazu's Satsuma Domain, which was one of the most powerful and wealthiest domains in the country throughout the period, and though international trade was sakoku, banned for much of this period, the city remained quite active and pros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the fifth-largest primary river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population. The Yangtze has played a major role in the history, culture, and economy of China. For thousands of years, the river has been used for water, irrigation, sanitation, transportation, industry, boundary-marking, and war. The Yangtze Delta generates as much as 20% of China's GDP, and the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze is the largest hydro-electric power station in the world. In mid-2014, the Chinese government announced it was building a multi-tier transport network, comprising railways, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiujiang
Jiujiang, formerly transliterated Kiukiang and Kew-Keang, is a prefecture-level city located on the southern shores of the Yangtze River in northwest Jiangxi Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the second-largest prefecture-level city in Jiangxi and its borders include Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lakes of China, lake in China. Jiujiang is the fourth largest port on the Yangtze River and was one of the first five cities that were opened to foreign trade along the Yangtze River following the implementation of Deng Xiaoping's Opening-Up Policy. It is Jiangxi's only international trade port city. Its population was 4,600,276 inhabitants at the 2020 Chinese census, 2020 census, 1,164,268 of whom resided in the built-up area (metro) made up of three urban districts (aka Xunyang District, Xunyang, Lianxi District, Lianxi, and Chaisang District, Chaisang). In 2007, the city was named China's top ten livable cities by the Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gan River
The Gan River (, Gan: Kōm-kong) runs north through the western part of Jiangxi before flowing into Lake Poyang and thus the Yangtze River. The Xiang-Gan uplands separate it from the Xiang River of neighboring eastern Hunan. Two similarly sized rivers, the Gong River which is the southern tributary and the Mei River from the north combine in Yudu County, Jiangxi, to form the Gan. The Gan River flows before splitting into distributaries just north of Nanchang. The longest of these, the North Branch, is several times longer than the other distributaries at . The Gan River is the major geographical feature of Jiangxi, and gives its name to the Gan variety of Chinese as well as the province's one-character abbreviation. The river feeds into Lake Poyang, which in turns connects with the Yangtze The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hainan
Hainan is an island provinces of China, province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally means "South of the Sea". The province has a land area of , of which Hainan Island is and the rest is over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos: Zhongsha Islands, Zhongsha, Xisha Islands, Xisha and Nansha Islands, Nansha. It was part of Guangdong from 1950 to 1988, after which it was made a province of its own and was designated as a special economic zones of China, special economic zone by Deng Xiaoping, as part of the Chinese economic reform program. The Han Han Chinese, Chinese population, who compose a majority of the population at 82%, speak a wide variety of languages including Standard Chinese, Hainanese, Hainam Min, Yue Chinese, Cantonese, Hakka Chinese, etc. Indigenous peoples such as the Hlai people, Hlai, a Kra–Dai l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhejiang
) , translit_lang1_type2 = , translit_lang1_info2 = ( Hangzhounese) ( Ningbonese) (Wenzhounese) , image_skyline = 玉甑峰全貌 - panoramio.jpg , image_caption = View of the Yandang Mountains , image_map = Zhejiang in China (+all claims hatched).svg , mapsize = 275px , map_caption = Location of Zhejiang in China , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = China , named_for = Old name of Qiantang River , seat_type = Capital and largest city , seat = Hangzhou , established_title = Annexation by the Qin dynasty , established_date = 222 BC , established_title2 = Jiangnandong Circuit , established_date2 = 626 , established_title3 = Liangzhe Circuit , established_date3 = 997 , established_title4 = Zhejiang Province formed , established_date4 = 1368 , established_title5 = Republican Period , established_date5 = 1 January 1912 , established_title6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
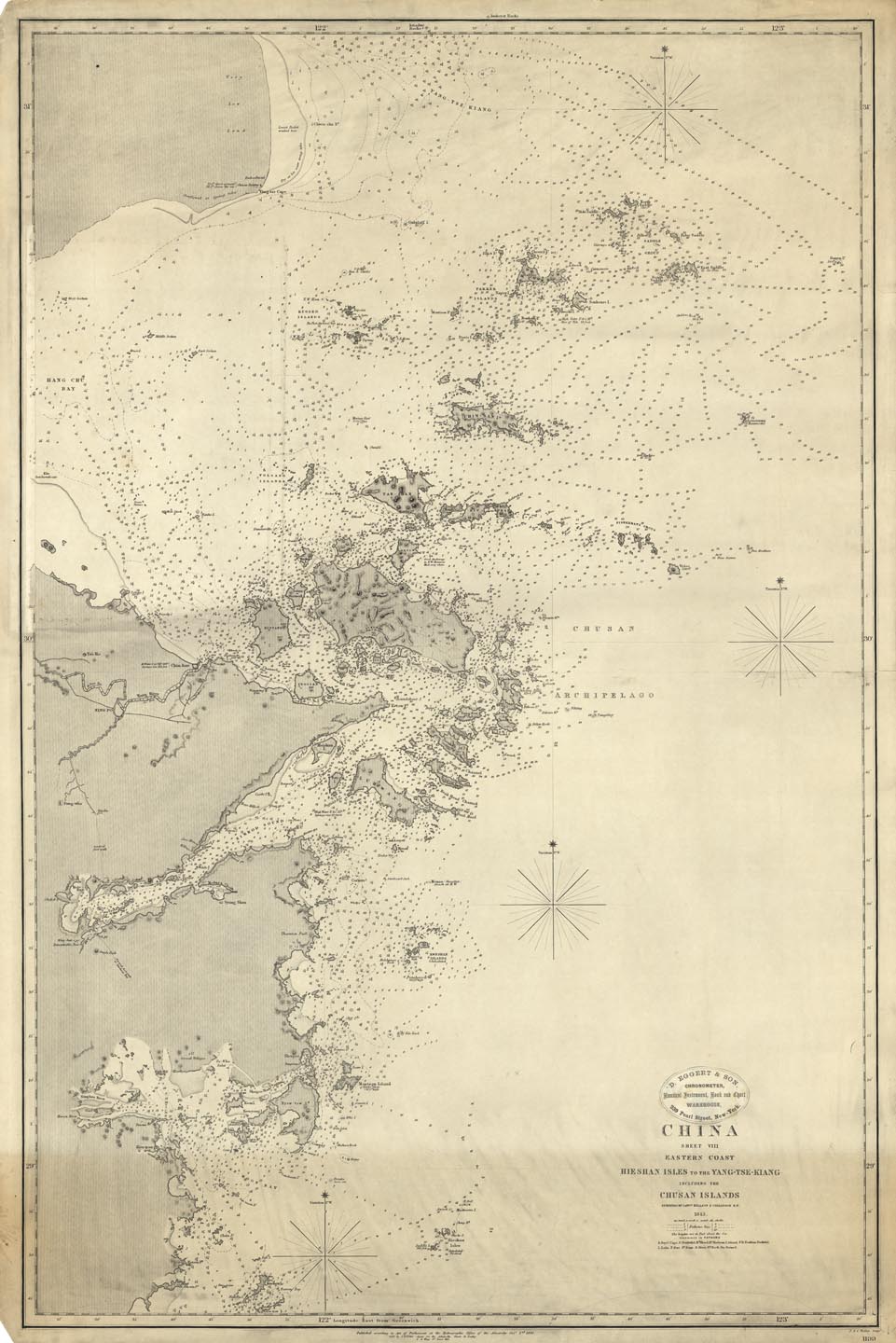
Zhoushan Archipelago
Zhoushan is an urbanized archipelago with the administrative status of a prefecture-level city in the eastern Chinese province of Zhejiang. It consists of an archipelago of islands at the southern mouth of Hangzhou Bay off the mainland city of Ningbo. The prefecture's city proper is Dinghai on Zhoushan Island, now administered as the prefecture's Dinghai District. During the 2020 census, Zhoushan Prefecture's population was 1,157,817, out of whom 882,932 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of two urban districts of Dinghai and Putuo. On 8 July 2011, the central government approved Zhoushan as Zhoushan Archipelago New Area, a state-level new area. History The archipelago was inhabited 6,000 years ago, during the Neolithic by people of the Hemudu culture. During the Spring and Autumn period, Zhoushan was called Yongdong, referring to its location east of the Yong River. At the time, it belonged to the state of Yue. The fishermen and sailors who inhabite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East China Sea
The East China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean, located directly offshore from East China. China names the body of water along its eastern coast as "East Sea" (, ) due to direction, the name of "East China Sea" is otherwise designated as a formal name by International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) and used internationally. It covers an area of roughly . The sea's northern extension between Korean Peninsula and mainland China is the Yellow Sea, separated by an imaginary line between the southwestern tip of South Korea's Jeju Island and the eastern tip of Qidong, Jiangsu, Qidong at the Yangtze River estuary. The East China Sea is bounded in the east and southeast by the middle portion of the first island chain off the eastern Eurasian continental mainland, including the Japanese island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands, and in the south by the island of Taiwan. It connects with the Sea of Japan in the northeast through the Korea Strait, the South China Sea i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripiṭaka
There are several Buddhist canons, which refers to the various scriptural collections of Buddhist sacred scriptures or the various Buddhist scriptural canons. Tipitaka Encyclopædia Britannica (2015) Some of these collections are also called ''Tipiṭaka'' () or ''Tripiṭaka'' () , meaning "Triple Basket", a traditional term for the three main divisions of some ancient canons. In ancient India, there were several Buddhist scriptural canons that were organized into three main textual divisions: Vinaya (monastic rule), (which contains teachings of the Buddha) and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |