|
Frosted Hairy Dwarf Porcupine
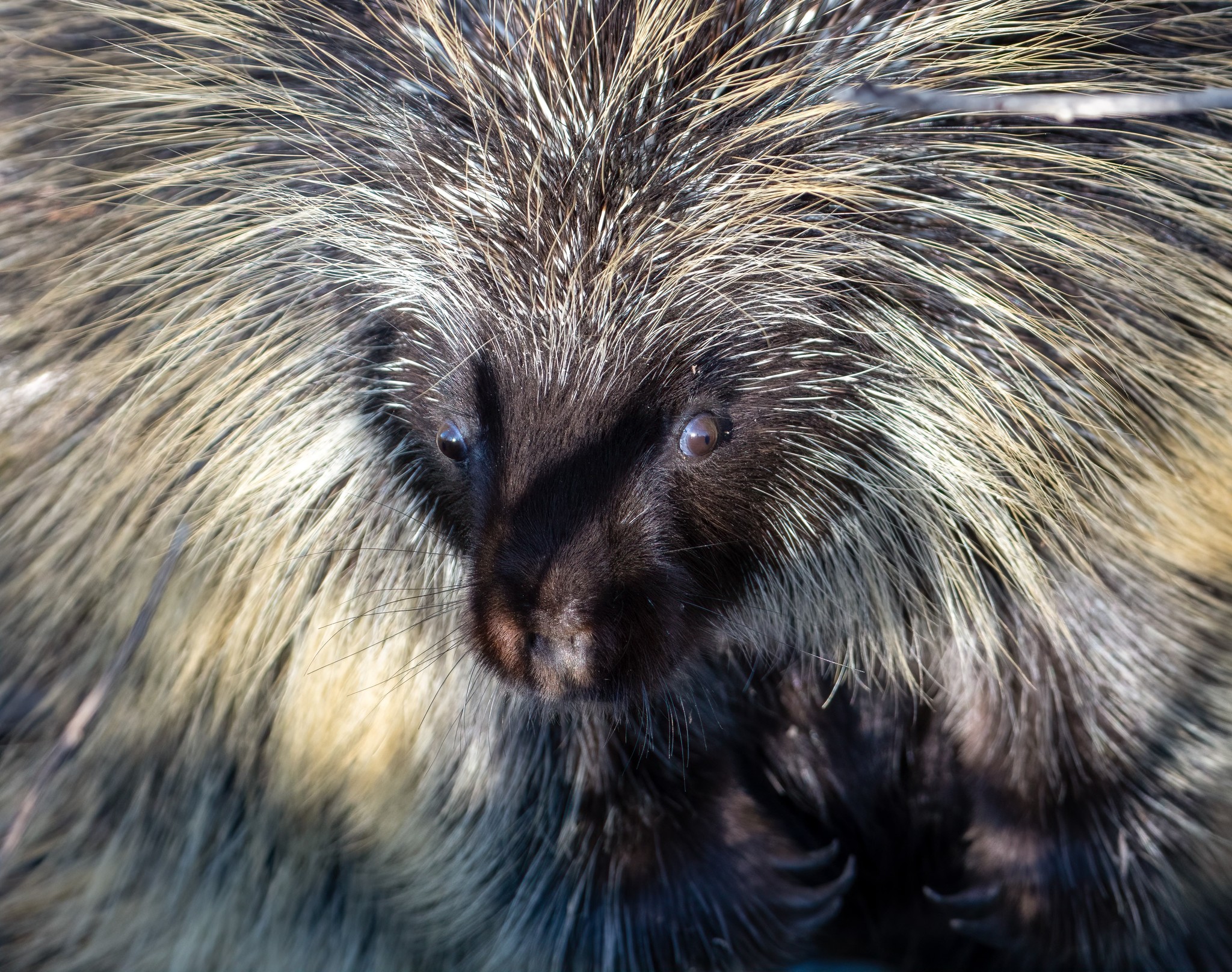
The frosted hairy dwarf porcupine (''Coendou pruinosus'') is a porcupine species in the family Erethizontidae from Colombia and northern and eastern Venezuela. It was formerly sometimes assigned to ''Sphiggurus'', a genus no longer recognized since genetic studies showed it to be polyphyletic. The species lives in lowland tropical rainforest and cloud forest at elevations from . Its karyotype A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ... has 2n = 42 and FN = 76. Its closest relative is the brown hairy dwarf porcupine (''Coendou vestitus''). References Natureserve.org Coendou Mammals described in 1905 Taxa named by Oldfield Thomas {{rodent-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldfield Thomas
Michael Rogers Oldfield Thomas (21 February 1858 – 16 June 1929) was a British zoologist. Career Thomas worked at the Natural History Museum on mammals, describing about 2,000 new species and subspecies for the first time. He was appointed to the museum secretary's office in 1876, transferring to the zoological department in 1878. In 1891, Thomas married Mary Kane, daughter of Sir Andrew Clark, heiress to a small fortune, which gave him the finances to hire mammal collectors and present their specimens to the museum. He also did field work himself in Western Europe and South America. His wife shared his interest in natural history, and accompanied him on collecting trips. In 1896, when William Henry Flower took control of the department, he hired Richard Lydekker to rearrange the exhibitions, allowing Thomas to concentrate on these new specimens. Thomas viewed his taxonomy efforts from the scope of British imperialism. "You and I in our scientific lives have seen th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethizontidae. Both families belong to the infraorder Hystricognathi within the profoundly diverse order Rodentia and display superficially similar coats of rigid or semi-rigid quills, which are modified hairs composed of keratin. Despite this, the two groups are distinct from one another and are not closely related to each other within the Hystricognathi. The largest species of porcupine is the third-largest living rodent in the world, after the capybara and beaver. The Old World porcupines (Hystricidae) live in Italy, Asia (western and southern), and most of Africa. They are large, terrestrial, and strictly nocturnal. The New World porcupines (Erethizontidae) are indigenous to North America and northern South America. They live in wooded ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World Porcupine
The New World porcupines, family Erethizontidae, are large arboreal rodents, distinguished by their spiny coverings from which they take their name. They inhabit forests and wooded regions across North America, and into northern South America. Although both the New World and Old World porcupine families belong to the Hystricognathi branch of the vast order Rodentia, they are quite different and are not closely related. Characteristics New World porcupines are stout animals, with blunt, rounded heads, fleshy, mobile snouts, and coats of thick, cylindrical or flattened spines. The "quills" are mixed with long, soft hairs. They vary in size from the relatively small prehensile-tailed porcupines, which are around long, and weigh about , to the much larger North American porcupine, which has a body length of , and weighs up to . They are distinguished from the Old World porcupines in that they have rooted molars, complete collar bones, entire upper lips, tuberculated soles, no t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi), and has a population of 52 million. Colombia's cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a Spanish colony, fusing cultural elements brought by immigration from Europe and the Middle East, with those brought by enslaved Africans, as well as with those of the various Amerindian civilizations that predate colonization. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of convergent evolution. The arrangement of the members of a polyphyletic group is called a polyphyly .. ource for pronunciation./ref> It is contrasted with monophyly and paraphyly. For example, the biological characteristic of warm-bloodedness evolved separately in the ancestors of mammals and the ancestors of birds; "warm-blooded animals" is therefore a polyphyletic grouping. Other examples of polyphyletic groups are algae, C4 photosynthetic plants, and edentates. Many taxonomists aim to avoid homoplasies in grouping taxa together, with a goal to identify and eliminate groups that are found to be polyphyletic. This is often the stimulus for major revisions of the classification schemes. Researchers concerned more with ecology than with systema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatorial evergreen rainforest''. True rainforests are typically found between 10 degrees north and south of the equator (see map); they are a sub-set of the tropical forest biome that occurs roughly within the 28-degree latitudes (in the equatorial zone between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn). Within the World Wildlife Fund's biome classification, tropical rainforests are a type of tropical moist broadleaf forest (or tropical wet forest) that also includes the more extensive seasonal tropical forests. Overview Tropical rainforests are characterized by two words: hot and wet. Mean monthly temperatures exceed during all months of the year. Average annual rainfall is no less than and can exceed although it typically lies b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Forest
A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or subtropical, evergreen, montane, moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud cover, usually at the canopy level, formally described in the '' International Cloud Atlas'' (2017) as silvagenitus. Cloud forests often exhibit an abundance of mosses covering the ground and vegetation, in which case they are also referred to as mossy forests. Mossy forests usually develop on the saddles of mountains, where moisture introduced by settling clouds is more effectively retained. Cloud forests are among the most biodiversity rich ecosystems in the world with a large amount of species directly or indirectly depending on them. Other moss forests include black spruce/ feathermoss climax forest, with a moderately dense canopy and a forest floor of feathermosses including '' Hylocomium splendens'', '' Pleurozium schreberi'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
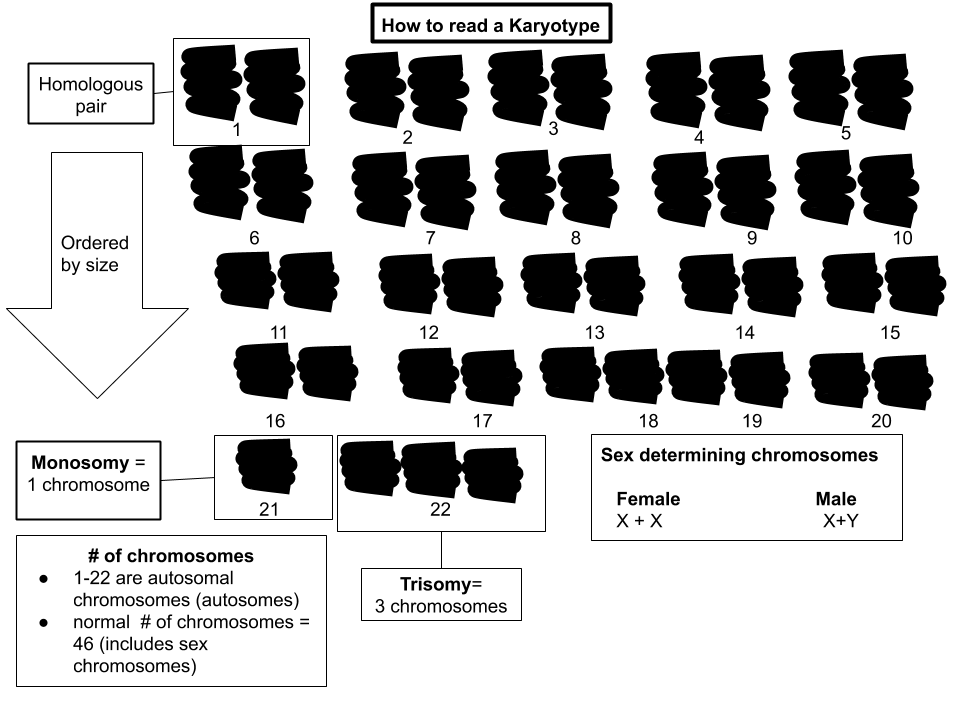
Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as one on photomicrographs as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as one on photomicrographs as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Hairy Dwarf Porcupine
The brown hairy dwarf porcupine (''Coendou vestitus'') is a species of rodent in the family Erethizontidae. Found in the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. It is not easy to study as it is only known from a few specimens and wasn't recorded from 1925 until the 2000s. The porcupine is nocturnal and arboreal, feeding on leaves, shoots, and fruits. Habitat loss severely threatens it and it may even be extinct. Formerly listed as vulnerable, it is now designated data deficient. It is not known from any protected areas or conservation measures. This species was formerly sometimes assigned to ''Sphiggurus'', a genus no longer recognized since genetic studies showed it to be polyphyletic. Its closest relative is the frosted hairy dwarf porcupine The frosted hairy dwarf porcupine (''Coendou pruinosus'') is a porcupine species in the family Erethizontidae from Colombia and northern and eastern Venezuela. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)