|
Friulan
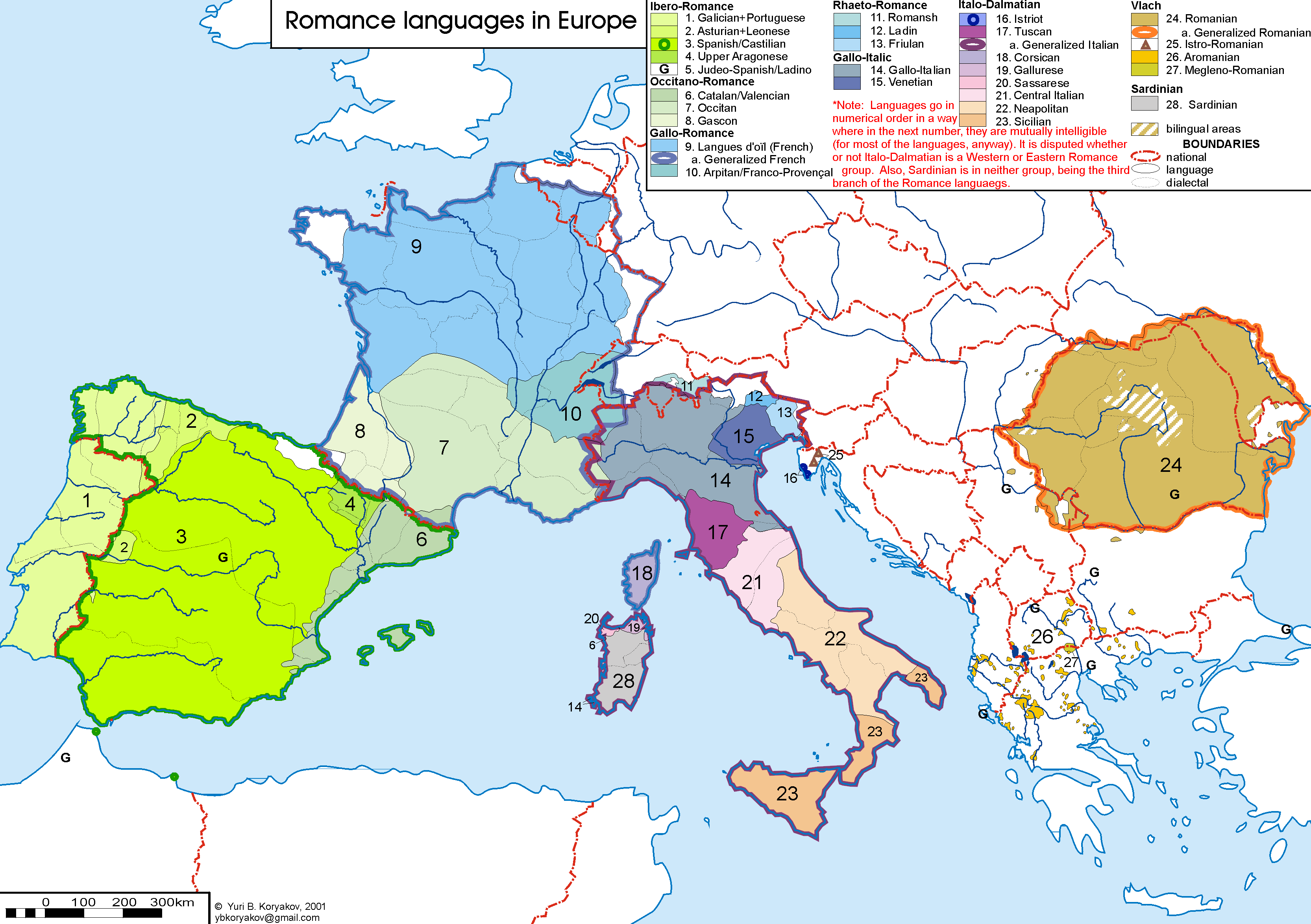
Friulian ( ) or Friulan (natively or ; ; ; ) is a Romance language belonging to the Rhaeto-Romance family. Friulian is spoken in the Friuli region of northeastern Italy and has around 600,000 speakers, the vast majority of whom also speak Italian. It is sometimes called Eastern Ladin since it shares the same roots as Ladin, but over the centuries, it has diverged under the influence of surrounding languages, including German, Italian, Venetian, and Slovene. Documents in Friulian are attested from the 11th century and poetry and literature date as far back as 1300. By the 20th century, there was a revival of interest in the language. History A question that causes many debates is the influence of the Latin spoken in Aquileia and surrounding areas. Some claim that it had peculiar features that later passed into Friulian. Epigraphs and inscriptions from that period show some variants if compared to the standard Latin language, but most of them are common to other areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, i.e. the administrative Provinces of Italy, provinces of Province of Udine, Udine, Province of Pordenone, Pordenone, and Province of Gorizia, Gorizia, excluding Province of Trieste, Trieste. Names The name originates from the ancient Roman town of ("Julius Caesar, Julius' Forum (Roman), Forum"), now Cividale del Friuli. Geography Friuli is bordered on the west by the Veneto region with the border running along the Livenza river, on the north by the crest of the Carnic Alps between Carnia and Austrian Carinthia (state), Carinthia, on the east by the Julian Alps, the border with Slovenia and the Timavo river, and on the south by the Adriatic Sea. The adjacent Slovene parts of the Soča/Isonzo valley f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friulians
Friulians, also called Friulans or Furlans (, Italian: ''Friulani''), are an ethnolinguistic minority living primarily in Italy, with a significant diaspora community. Friulians primarily inhabit the region of Friuli and speak the Rhaeto-Romantic language Friulian, which is closely related to Ladin, spoken primarily in South Tyrol/Alto Adige, and Romansh, native to the Canton of Grisons in Switzerland. Distribution About 600,000 Friulians live in the historical region of Friuli and in parts of Veneto. As the Friulian language's use has decreased, there are likely around 1 million in total, with an increasing amount speaking Italian as a first language. Some other thousands live in diaspora communities in the United States, Canada, Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, Venezuela, Australia, and Belgium. They traditionally speak Friulian language, Friulan, a distinct Rhaeto-Romance language which is the second largest recognized minority language in Italy Italy, officially the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquileia
Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river Natiso (modern Natisone), the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times. Today, the city is small (about 3,500 inhabitants), but it was large and prominent in classical antiquity as one of the world's largest cities with a population of 100,000 in the second century AD and is one of the main archaeological sites of northern Italy. In late antiquity the city was the first city in the Italian Peninsula to be sacked by Attila the Hun. It is currently a (municipality) in the Regional decentralization entity of Udine, Friuli-Venezia Giulia. History Classical Antiquity Roman Republic Aquileia was founded as a colony by the Romans in 180/181 BC along the Natiso River, on land south of the Julian Alps but about north of the lagoons. The colony served as a strategic frontier fortress at the north-east corner of transpadane Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetic
Rhaetic or Raetic (), also known as Rhaetian, was a Tyrsenian language spoken in the ancient region of Rhaetia in the eastern Alps in pre-Roman and Roman times. It is documented by around 280 texts dated from the 5th through the 1st century BC, which were found through northern Italy, southern Germany, eastern Switzerland, Slovenia and western Austria, in two variants of the Old Italic scripts. Rhaetic is largely accepted as being closely related to Etruscan. The ancient Rhaetic language is not to be confused with the modern Romance languages of the same Alpine region, known as Rhaeto-Romance. Classification The German linguist Helmut Rix proposed in 1998 that Rhaetic, along with Etruscan, was a member of a language family he called Tyrrhenian, and which was possibly influenced by neighboring Indo-European languages. Robert S. P. Beekes likewise does not consider it Indo-European. Howard Hayes Scullard (1967), on the contrary, suggested it to be an Indo-European lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortunatianus Of Aquileia
Fortunatianus of Aquileia (c.300-c.370) was an African, Christian poet, and bishop of Aquileia in the mid-fourth century, during the reign of Constantius II. The exact year of his birth is unknown, although it was around 300, and there is no recorded information concerning his early life. He is best known for his commentary on the Gospels. Writings The principal ancient source for Fortunatianus of Aquileia is a paragraph referencing him in "Famous Men" composed by Jerome, Saint Jerome in 393. Fortunatianus wrote a commentary on the Gospels which, according to its reference by Saint Jerome, is the oldest surviving Western commentary on the Gospels, though the document was lost for over a millennium. The commentary was known from only a few excerpts: two identified by French monk and scholar André Wilmart (1876-1941) from a Troyes manuscript, one from Angers identified by German philologist and paleographer Bernhard Bischoff (1906-1991), and a reference in Saint Jerome's corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christianity, Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the second century Anno domino, AD the term (, from which the English word originated as a calque) came to be used also for the books in which the message was reported. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words and deeds of Jesus, culminating in trial of Jesus, his trial and crucifixion of Jesus, death, and concluding with various reports of his Post-resurrection appearances of Jesus, post-resurrection appearances. The Gospels are commonly seen as literature that is based on oral traditions, Christian preaching, and Old Testament exegesis with the consensus being that they are a variation of Greco-Roman biography; similar to other ancient works such as Xenophon's Memorabilia (Xenophon), ''Memoirs of Socrates''. They are meant to convince people that Jesus was a charismatic miracle-working holy man, providing examples for readers to emulate. As such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as List of islands of Italy, nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the List of European countries by area, tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and List of cities in Italy, largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous List of ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetic
Venetic ( ) is an extinct Indo-European language, most commonly classified into the Italic subgroup, that was spoken by the Veneti people in ancient times in northeast Italy (Veneto and Friuli) and part of modern Slovenia, between the Po Delta and the southern fringe of the Alps, associated with the Este culture. The language is attested by over 300 short inscriptions dating from the 6th to the 1st century BCE. Its speakers are identified with the ancient people called '' Veneti'' by the Romans and ''Enetoi'' by the Greeks. It became extinct around the 1st century when the local inhabitants assimilated into the Roman sphere. Inscriptions dedicating offerings to Reitia are one of the chief sources of knowledge of the Venetic language. Linguistic classification Venetic is a centum language. The inscriptions use a variety of the Northern Italic alphabet, similar to the Etruscan alphabet. The exact relationship of Venetic to other Indo-European lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovene Language
Slovene ( or ) or Slovenian ( ; ) is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic language of the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Most of its 2.5 million speakers are the inhabitants of Slovenia, the majority of them ethnic Slovenes. As Slovenia is part of the European Union, Slovene is also one of its 24 Languages of the European Union, official and working languages. Its grammar is highly fusional languages, fusional, and it has a Dual (grammatical number), dual grammatical number, an archaic feature shared with some other Indo-European languages. Two accentual norms (one characterized by Pitch-accent language, pitch accent) are used. Its flexible word order is often adjusted for emphasis or stylistic reasons, although basically it is an subject–verb–object word order, SVO language. It has a T–V distinction: the use of the V-form demonstrates a respectful attitude towards superiors and the elderly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |