|
Edgware Road Tube Station (Bakerloo Line)
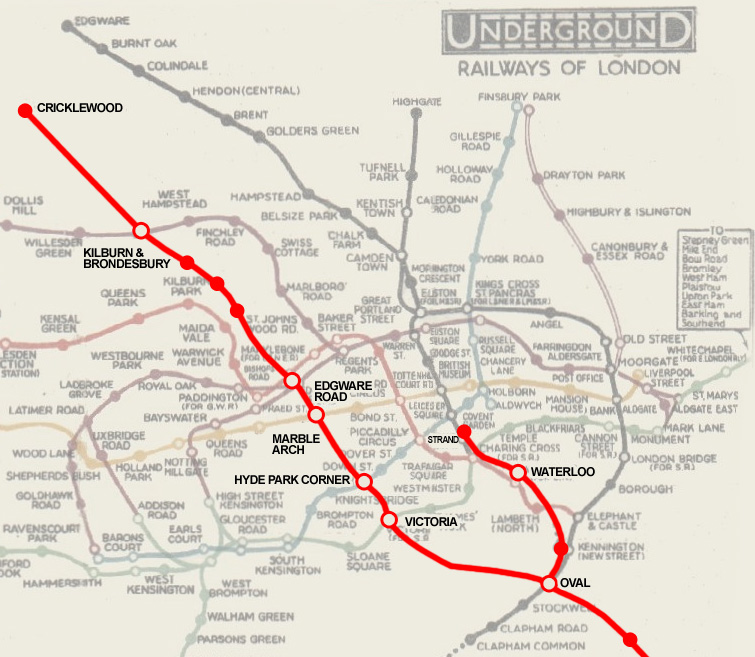
Edgware Road is a London Underground station on the Bakerloo line, located in the City of Westminster. It is between Paddington and Marylebone stations on the line and falls within Travelcard zone 1. The station is located on the north-east corner of the junction of Edgware Road, Harrow Road and Marylebone Road. It is adjacent to the Marylebone flyover. A separate station of the same name but served by the Circle, District and Hammersmith & City lines is nearby, to the south of Marylebone Road.The other station was opened by the Metropolitan Railway in 1863 as part of the world's first underground railway. History Edgware Road station was opened on 15 June 1907 by the Baker Street and Waterloo Railway (BS&WR, now the Bakerloo line) when it extended its line from the temporary northern terminus at Marylebone. In common with other early stations of the lines owned by the Underground Electric Railways Company of London, the station was designed by architect Leslie Green with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground passenger railway. Opened on 10 January 1863, it is now part of the Circle, District, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines, and in 2020/21 was used for 296 million passenger journeys, making it one of the world's busiest metro systems. The 11 lines collectively handle up to 5 million passenger journeys a day and serve 272 stations. The system's first tunnels were built just below the ground, using the cut-and-cover method; later, smaller, roughly circular tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Green
Leslie William Green (6 February 1875 – 31 August 1908) was an English architect. He is best known for his design of iconic stations constructed on the London Underground railway system in central London during the first decade of the 20th century, with distinctive oxblood red faïence blocks including pillars and semi-circular first-floor windows, and patterned tiled interiors done in the Modern Style (British Art Nouveau style). Early and private life Green was born in Maida Vale, London in 1875, the second of four children of architect and Crown Surveyor Arthur Green and his wife Emily. He spent periods studying at Dover College and South Kensington School of Art, and in Paris, between periods working as an assistant in his father's architectural practice. Green married Mildred Ethel Wildy (1879–1960) in Clapham in April 1902. In 1904, they had a daughter, Vera (1904–1995). Career Green established his own practice as an architect in 1897, working initially fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murad Qureshi
Murad Qureshi ( bn, মুরাদ কোরেশী; born 27 May 1965) is a British Labour and Co-operative Party politician, and a former Member of the London Assembly. Early life and education Qureshi was born in Greater Manchester, but he was brought up in Westminster, London, where his parents moved in July 1965. He attended Quintin Kynaston School and graduated from the University of East Anglia with a degree in Development Studies in 1987, before undertaking an MSc in Environmental Economics at University College London, which he completed in 1993. Qureshi is of Bangladeshi descent, and comes from a politically active family: his late father Mushtaq Qureshi was a Labour Party councillor in the City of Westminster and was a freedom fighter in the Bangladesh War of Liberation. His youngest sister, Papya Qureshi, was also a councillor in Westminster. Career Before becoming an Assembly Member, he worked in Housing and Regeneration for 15 years, helping establish housi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Assembly
The London Assembly is a 25-member elected body, part of the Greater London Authority, that scrutinises the activities of the Mayor of London and has the power, with a two-thirds super-majority, to amend the Mayor's annual budget and to reject the Mayor's draft statutory strategies. The London Assembly was established in 2000. It is also able to investigate other issues of importance to Londoners (most notably transport or environmental matters), publish its findings and recommendations, as well as make proposals to the Mayor. Assembly Members The Assembly comprises 25 Assembly Members elected using the additional member system of proportional representation, with 13 seats needed for a majority. Elections take place every four years, at the same time as for the Mayor. There are 14 geographical super-constituencies each electing one Member, with a further 11 members elected from a party list to make the total Assembly Members from each party proportional to the votes cast for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater London Council
The Greater London Council (GLC) was the top-tier local government administrative body for Greater London from 1965 to 1986. It replaced the earlier London County Council (LCC) which had covered a much smaller area. The GLC was dissolved in 1986 by the Local Government Act 1985 and its powers were devolved to the London boroughs and other entities. A new administrative body, known as the Greater London Authority (GLA), was established in 2000. Creation The GLC was established by the London Government Act 1963, which sought to create a new body covering more of London rather than just the inner part of the conurbation, additionally including and empowering newly created London boroughs within the overall administrative structure. In 1957 a Royal Commission on Local Government in Greater London had been set up under Sir Edwin Herbert, and this reported in 1960, recommending the creation of 52 new London boroughs as the basis for local government. It further recommended that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Railways
''Modern Railways'' is a British monthly magazine covering the rail transport industry which was published by Ian Allan until March 2012, and Key Publishing since then. It has been published since 1962. The magazine was originally based in Shepperton, Middlesex. It has always been targeted at both railway professionals and serious amateurs, an aim which derives from its origins as an amalgamation of the enthusiast magazine ''Trains Illustrated'' and the industry journal ''The Locomotive'' in the hands of its first editor Geoffrey Freeman Allen. It is currently edited by Philip Sherratt after the retirement of James Abbott. Regular contributors include Roger Ford Roger Ford may refer to: * Roger Ford (journalist) * Roger Ford (production designer) * Roger Ford (cricketer) See also * Rodger Ford, American businessman {{hndis, Ford, Roger ..., Ian Walmsley, Alan Williams and Tony Miles. The large section regularly written by Roger Ford is called ‘Informed Sources’. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Transport Executive (GLC)
The London Transport Executive was the executive agency within the Greater London Council, responsible for public transport in Greater London from 1970 to 1984. In common with all London transport authorities from 1933 to 2000, the public name and operational brand of the organisation was London Transport. Background and formation The Greater London Council came into its powers in 1965, but did not have authority over public transport. Responsibility for such provision had been removed from the London County Council and neighbouring authorities in 1933 and passed to the London Passenger Transport Board. The Transport (London) Act 1969 gave the GLC powers over the London Underground and London Buses, but not over British Rail services in Greater London. Fares policy The GLC aimed to increase usage of public transport, especially in Outer London, where car use was high. Fare setting policy was used to increase patronage on the London Underground and London Buses, partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgware Road Ticket Counters
Edgware () is a suburban town in northern Greater London, mostly in the London Borough of Barnet but with small parts falling in the London Borough of Harrow and in the London Borough of Brent. Edgware is centred north-northwest of Charing Cross and has its own commercial centre. Edgware has a generally suburban character, typical of the rural-urban fringe. It was an ancient parish in the county of Middlesex directly east of the ancient Watling Street, and gives its name to the present day Edgware Road that runs from central London towards the town. The community benefits from some elevated woodland on a high ridge marking the Hertfordshire border of gravel and sand. It includes the areas of Burnt Oak, The Hale, Edgwarebury, Canons Park, and parts of Queensbury. Edgware is principally a shopping and residential area, identified in the London Plan as one of the capital's 35 major centres, and one of the northern termini of the Northern line. It has a bus garage, a shopping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821) are published by Times Newspapers, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'', which do not share editorial staff, were founded independently and have only had common ownership since 1966. In general, the political position of ''The Times'' is considered to be centre-right. ''The Times'' is the first newspaper to have borne that name, lending it to numerous other papers around the world, such as '' The Times of India'', ''The New York Times'', and more recently, digital-first publications such as TheTimesBlog.com (Since 2017). In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as , or as , although the newspaper is of nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria (NWLR) Tube Station
Edgware Road Tube schemes covers a number of proposals to build an underground railway in London, UK at the end of the 19th century. Each scheme envisaged building some form of rail tunnel along the Edgware Road in north-west London towards London Victoria station, Victoria railway station. These proposals were made at a time of intensive railway construction, following projects such as City and South London Railway. Like several other proposals at the time, such as the City and Brixton Railway, none of the Edgware Road schemes came to fruition. Edgware Road and Victoria Railway The Edgware Road and Victoria Railway (ER&VR) was an early scheme for an underground railway under the Edgware Road. The promoters sought to raise capital of £1.2 million (£ today) to cover the estimated railway construction costs of £920,000 and the cost of constructing a dedicated power station for the railway at the Paddington Basin. The ER&VR was planned to run on a north-west-to-south-east ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble Arch (NWLR) Tube Station
Edgware Road Tube schemes covers a number of proposals to build an underground railway in London, UK at the end of the 19th century. Each scheme envisaged building some form of rail tunnel along the Edgware Road in north-west London towards Victoria railway station. These proposals were made at a time of intensive railway construction, following projects such as City and South London Railway. Like several other proposals at the time, such as the City and Brixton Railway, none of the Edgware Road schemes came to fruition. Edgware Road and Victoria Railway The Edgware Road and Victoria Railway (ER&VR) was an early scheme for an underground railway under the Edgware Road. The promoters sought to raise capital of £1.2 million (£ today) to cover the estimated railway construction costs of £920,000 and the cost of constructing a dedicated power station for the railway at the Paddington Basin. The ER&VR was planned to run on a north-west-to-south-east axis, more or less followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilburn (NWLR) Tube Station
Edgware Road Tube schemes covers a number of proposals to build an underground railway in London, UK at the end of the 19th century. Each scheme envisaged building some form of rail tunnel along the Edgware Road in north-west London towards Victoria railway station. These proposals were made at a time of intensive railway construction, following projects such as City and South London Railway. Like several other proposals at the time, such as the City and Brixton Railway, none of the Edgware Road schemes came to fruition. Edgware Road and Victoria Railway The Edgware Road and Victoria Railway (ER&VR) was an early scheme for an underground railway under the Edgware Road. The promoters sought to raise capital of £1.2 million (£ today) to cover the estimated railway construction costs of £920,000 and the cost of constructing a dedicated power station for the railway at the Paddington Basin. The ER&VR was planned to run on a north-west-to-south-east axis, more or less followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |