|
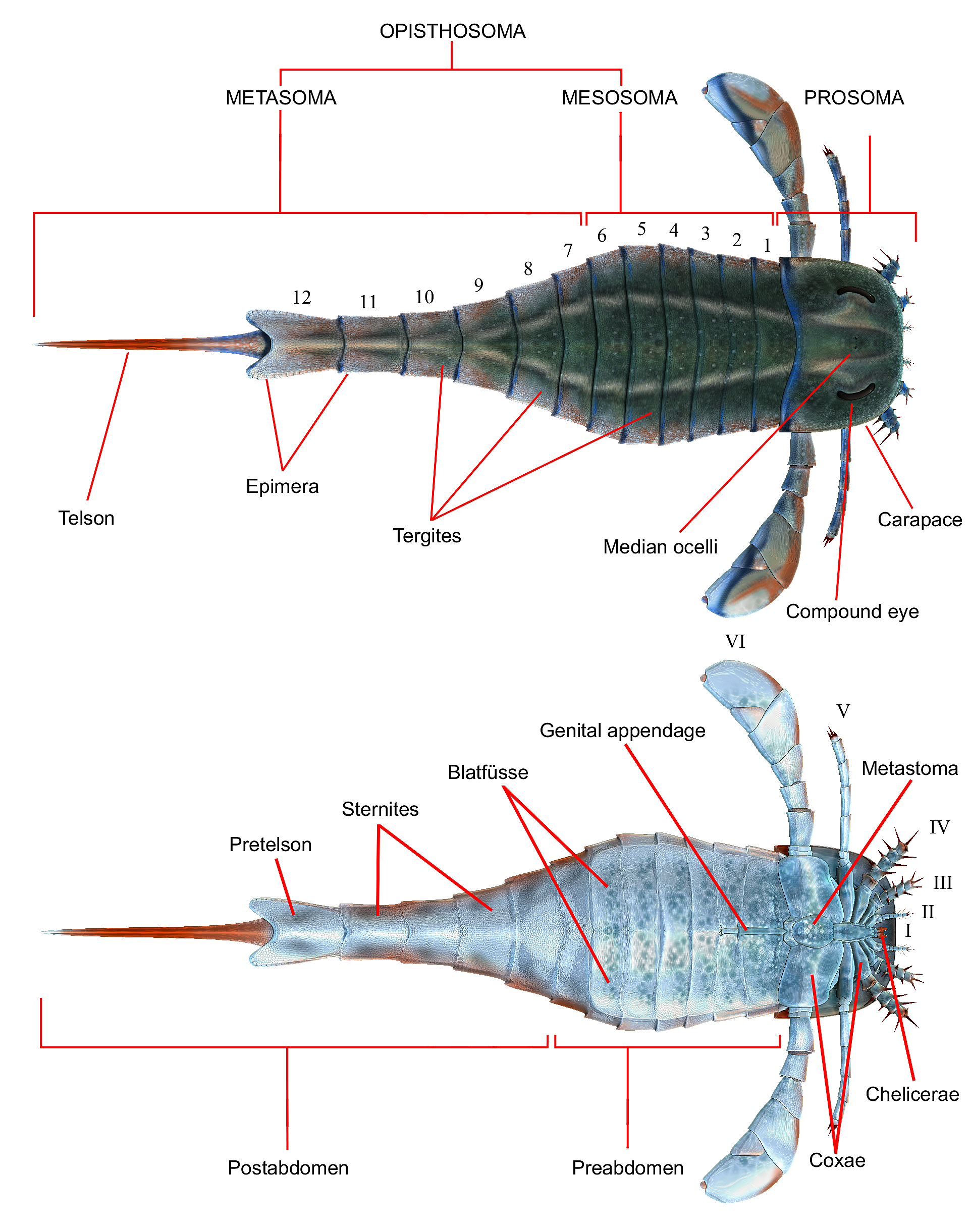
Eurypterida
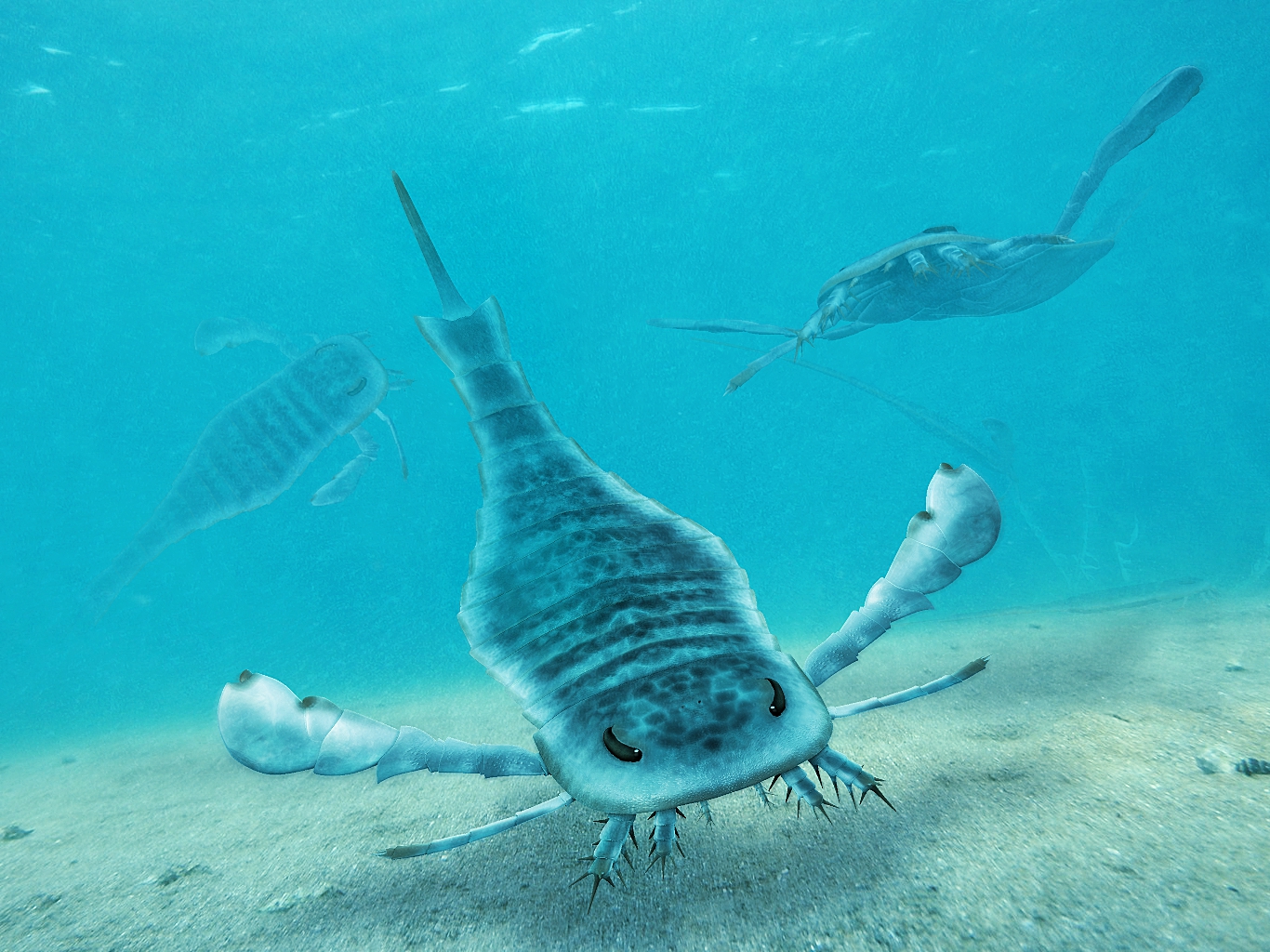
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct marine arthropods that form the order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period, 467.3 million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterus
''Eurypterus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of eurypterid, a group of organisms commonly called "sea scorpions". The genus lived during the Silurian period, from around 432 to 418 million years ago. ''Eurypterus'' is by far the most well-studied and well-known eurypterid. ''Eurypterus'' fossil specimens probably represent more than 95% of all known eurypterid specimens. There are fifteen species belonging to the genus ''Eurypterus'', the most common of which is ''E. remipes'', the first eurypterid fossil discovered and the List of U.S. state fossils, state fossil of New York (state), New York. Members of ''Eurypterus'' averaged at about in length, but the largest individual discovered was estimated to be long. They all possessed spine-bearing appendages and a large paddle they used for swimming. They were Generalist and specialist species, generalist species, equally likely to engage in predation or scavenging. Discovery The first fossil of ''Eurypterus'' was found in 1818 by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorfopterus
''Dorfopterus'' is a genus of eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Only one fossil of the single and type species, ''D. angusticollis'', has been discovered in Deposition (geology), deposits of the Early Devonian Period (geology), period (Emsian Stage (stratigraphy), stage) in the Beartooth Butte Formation in Wyoming, in the United States. The first half of the name of the genus honors the discoverer of this formation, Erling Dorf, while the second half consists in the Ancient Greek word wiktionary:πτερόν#Ancient Greek, πτερόν (''pteron''), meaning "wing". The species name ''angusticollis'' is composed by the Latin words ''wiktionary:angustus#Latin, angustus'' ("narrow") and ''wiktionary:collum#Latin, collum'' ("neck"). The only known specimen of ''Dorfopterus'' consists of an incomplete uncrushed telson (the posteriormost division of the body), which was long, narrow, styliform and with a central carina ("keel"). It had a special Biological ornament, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterina
Eurypterina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Eurypterine eurypterids are sometimes informally known as "swimming eurypterids". They are known from fossil deposits worldwide, though primarily in North America and Europe. Seventy-five percent of eurypterid species are eurypterines; this represents 99% of specimens. The superfamily Pterygotioidea is the most species-rich clade, with 56 species, followed by the Adelophthalmoidea with 43 species; as sister taxa, they comprise the most derived eurypterines. Pterygotioidea includes the pterygotids, which are the only eurypterids known to have a cosmopolitan distribution. Though more numerous both in specimens and taxa, the eurypterines have the shorter temporal range of the two eurypterid suborders. They first appeared around the same time as the Stylonurina in the Middle Ordovician. The suborder faced a slow extinction during the Middle and Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylonurina
Stylonurina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, a group of extinct arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Members of the suborder are collectively and informally known as "stylonurine eurypterids" or "stylonurines". They are known from deposits primarily in Europe and North America, but also in Siberia. Compared to the other suborder, Eurypterina, the stylonurines were comparatively rare and retained their posterior prosomal appendages for walking. Despite their rarity, the stylonurines have the longest temporal range of the two suborders. The suborder contains some of the oldest known eurypterids, such as ''Brachyopterus'', from the Middle Ordovician as well as the youngest known eurypterids, from the Late Permian. They remained rare throughout the Ordovician and Silurian, though the radiation of the mycteropoids (a group of large sweep-feeding forms) in the Late Devonian and Carboniferous is the last major radiation of the eurypterids before their extinction in the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerata
The subphylum Chelicerata (from Neo-Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. Chelicerates include the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mites, among many others), as well as a number of extinct lineages, such as the eurypterids (sea scorpions) and chasmataspidids. Chelicerata split from Mandibulata by the mid-Cambrian, as evidenced by stem-group chelicerates like Habeliida and '' Mollisonia'' present by this time. The surviving marine species include the four species of xiphosurans (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of pycnogonids (sea spiders), if the latter are indeed chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species. Like all arthropods, chelicerates have segmented bodies with jointed limbs, all covered in a cuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back Silurian, 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The Scorpion sting, venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six period (geology), geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (geologist), John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''palaiós'' (π� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupipterus
''Marsupipterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid with an uncertain classification. The genus contains one species, ''Marsupipterus sculpturatus'', from the Silurian of England England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ....Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch , version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). See also * List of eurypterids References Eurypterida Silurian eurypterids Fossils of Sweden Eurypterids of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1955 {{eurypterid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Burmeister
Karl Hermann Konrad Burmeister (also known as Carlos Germán Conrado Burmeister) (15 January 1807 – 2 May 1892) was a German Argentine zoologist, entomologist, herpetologist, botany, botanist, and coleopterologist. He served as a professor at the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg, University of Halle, headed the museum there and published the ''Handbuch der Entomologie'' (1832–1855) before moving to Argentina where he worked until his death. Career Burmeister was born in Stralsund, where his father was a customs officer. He studied medicine at University of Greifswald, Greifswald (1825–1827) and Halle (Saale), Halle (1827–1829), and in 1830 went to Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin to qualify himself to be a teacher of natural history. His dissertation was titled ''De insectorum systemate naturali'' and graduated as a doctor of medicine on November 4, 1829 and then received a doctor of philosophy on December 19 in the same year. He then joined for military ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangshanian
The Jiangshanian is the middle stage of the Furongian series. It follows the Paibian Stage and is succeeded by the still unnamed Stage 10 of the Cambrian. The base is defined as the first appearance of the trilobite '' Agnostotes orientalis'' which is estimated to be million years ago. The Jiangshanian lasted until approximately million years ago. The Jiangshanian stage was named after Jiangshan, a city in China's Zhejiang province, where its GSSP was defined. Stratigraphy The Global boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) of the Jiangshanian is the "Duibian B Section" (), west of the village of Duibian (碓边), and 10 km north of Jiangshan. The outcrop belongs to the Huayansi Formation (华严寺组). The upper boundary (the base of the Stage 10) is not formally defined by ICS, but there is a proposal to set the first appearance of an agnostoid '' Lotagnostus americanus'' as its marker. In 2012, international research group proposed the Kyrshabakty s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |