|
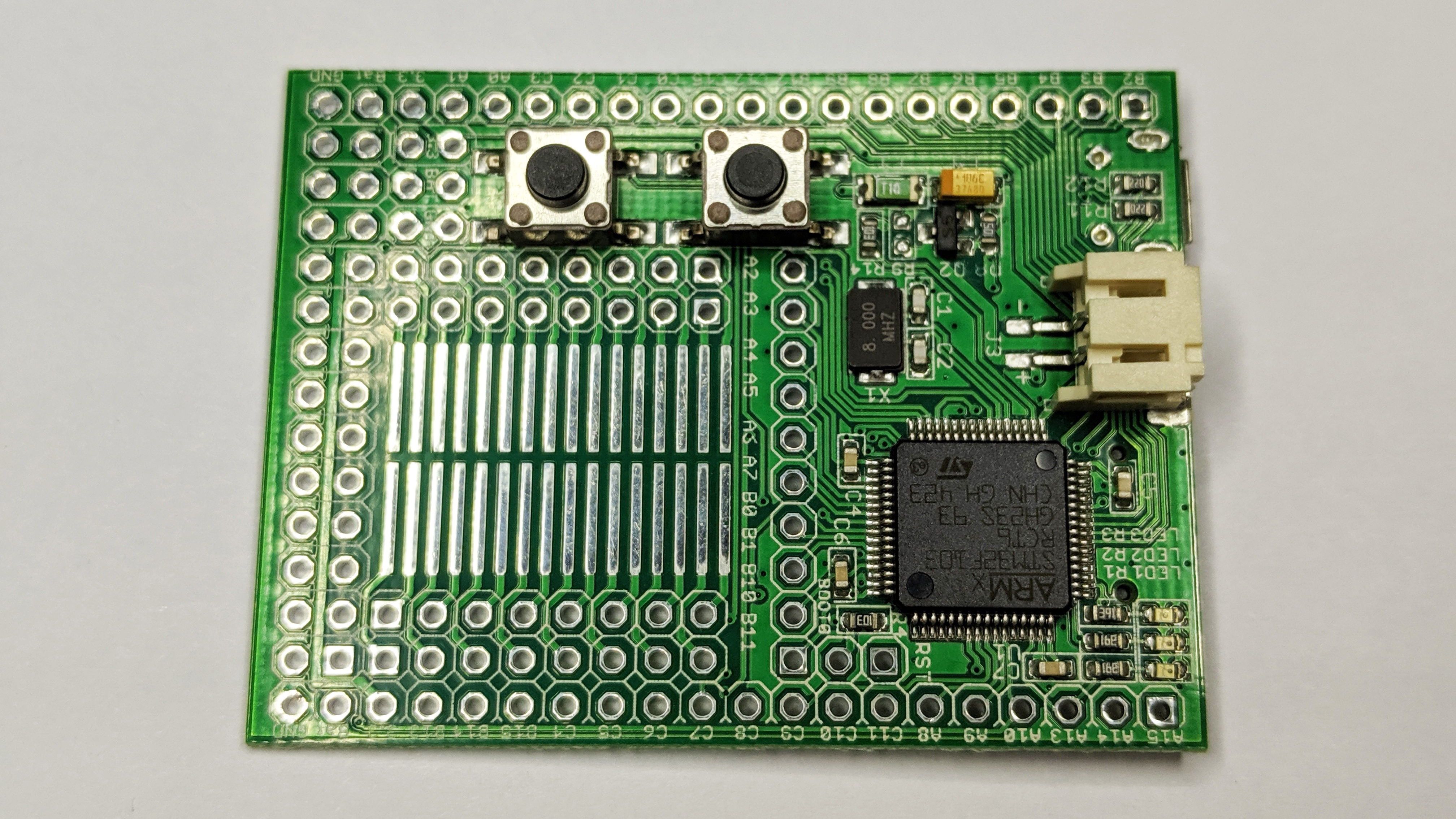
Espruino
Espruino is an open-source JavaScript interpreter for single board microcontrollers. It is designed for devices with small amounts of RAM (as low as 8kB). Overview Espruino was created by Gordon Williams in 2012 as an attempt to make microcontroller development truly multiplatform. Though initially not open-source, the Espruino firmware was offered as a free download for STM32 microcontrollers. It was made open-source in 2013 after a successful Kickstarter campaign for a development board running the software. Since the original Espruino board, there have been a number of new official development boards including the small USB thumb-drive-sized Espruino Pico, the Wifi-equipped Espruino WiFi, the Puck.js with built-in Bluetooth and the Pixl.js with a built-in LC display and Arduino shield compatibility. In addition to the official boards, Espruino runs on approximately 40 other types of development boards including the ESP8266 and BangleJS smartwatch. There is a large body of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side for Web page, webpage behavior, often incorporating third-party Library (computing), libraries. All major Web browser, web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine to execute the Source code, code on User (computing), users' devices. JavaScript is a High-level programming language, high-level, often Just-in-time compilation, just-in-time compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard. It has dynamic typing, Prototype-based programming, prototype-based object-oriented programming, object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is Programming paradigm, multi-paradigm, supporting Event-driven programming, event-driven, functional programming, functional, and imperative programming, imperative programming paradigm, programmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
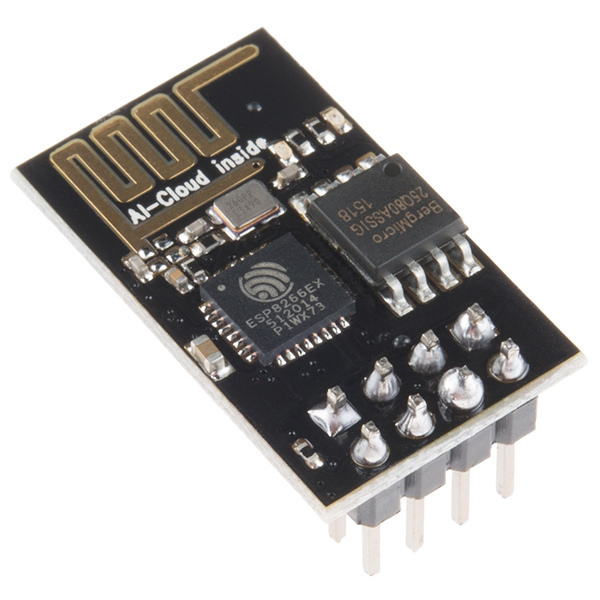
ESP8266
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontroller capability, produced by Espressif Systems in Shanghai, China. The chip was popularized in the English-speaking maker community in August 2014 via the ESP-01 module, made by a third-party manufacturer Ai-Thinker. This small module allows microcontrollers to connect to a Wi-Fi network and make simple TCP/IP connections using Hayes-style commands. However, at first, there was almost no English-language documentation on the chip and the commands it accepted. The very low price and the fact that there were very few external components on the module, which suggested that it could eventually be very inexpensive in volume, attracted many hackers to explore the module, the chip, and the software on it, as well as to translate the Chinese documentation. The ESP8285 is a similar chip with a built-in 1 MiB flash memory, allowing the design of single-chip devices capable of connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PuTTY
Putty is a material with high plasticity, similar in texture to clay or dough, typically used in domestic construction and repair as a sealant or filler. Although some types of putty (typically those using linseed oil) slowly polymerise and become stiff, many putties can be reworked indefinitely, in contrast to other types of filler which typically set solid relatively rapidly. Chemical composition Putty, or lime putty, is made from a mixture of calcium oxide (CaO) and water (H2O) in proportions of 38% and 62% by weight respectively, as result, the solution forms hydrated lime (Ca(OH)2) which takes up about a half of the weight. The other putty mixture may be a calcium carbonate (CaCO3, 750-850 parts) based with a admixtures of CaO (ash calcium, 120-180 parts), white cement (40-60 parts), and talc powders in much lower concentrations (fractions). Applications Use in construction Putty has been used extensively in glazing for fixing and sealing panes of glass into woo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcontroller Software
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips. In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). An SoC may connect the external microcontroller chips as the motherboard components, but an SoC usually integrates the advanced peripherals like graphics processing unit (GPU) and Wi-Fi interface controller as its internal microcontroller unit circuits. Microcontrollers are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creative Commons License
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work".A "work" is any creative material made by a person. A painting, a graphic, a book, a song/lyrics to a song, or a photograph of almost anything are all examples of "works". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT License
The MIT License is a permissive free software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts only very limited restriction on reuse and has, therefore, high license compatibility. Unlike copyleft software licenses, the MIT License also permits reuse within proprietary software, provided that all copies of the software or its substantial portions include a copy of the terms of the MIT License and also a copyright notice. , the MIT License was the most popular software license found in one analysis, continuing from reports in 2015 that the MIT License was the most popular software license on GitHub. Notable projects that use the MIT License include the X Window System, Ruby on Rails, Nim, Node.js, Lua, and jQuery. Notable companies using the MIT License include Microsoft ( .NET), Google ( Angular), and Meta ( React). License terms The MIT License has the identifier MIT in the SPDX License List. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozilla Public License
The Mozilla Public License (MPL) is a free and open-source weak copyleft license for most Mozilla Foundation software such as Firefox and Thunderbird The MPL license is developed and maintained by Mozilla, which seeks to balance the concerns of both open-source and proprietary developers; it is distinguished from others as a middle ground between the permissive software BSD-style licenses and the General Public License. So under the terms of the MPL, it allows the integration of MPL-licensed code into proprietary codebases, but only on condition those components remain accessible. MPL has been used by others, such as Adobe to license their Flex product line, and The Document Foundation to license LibreOffice 4.0 (also on LGPL 3+). Version 1.1 was adapted by several projects to form derivative licenses like Sun Microsystems' Common Development and Distribution License. It has undergone two revisions: the minor update 1.1, and a major update version 2.0 nearing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bytecode
Bytecode (also called portable code or p-code) is a form of instruction set designed for efficient execution by a software interpreter. Unlike human-readable source code, bytecodes are compact numeric codes, constants, and references (normally numeric addresses) that encode the result of compiler parsing and performing semantic analysis of things like type, scope, and nesting depths of program objects. The name bytecode stems from instruction sets that have one-byte opcodes followed by optional parameters. Intermediate representations such as bytecode may be output by programming language implementations to ease Interpreter (computer software), interpretation, or it may be used to reduce hardware and operating system dependence by allowing the same code to run cross-platform, on different devices. Bytecode may often be either directly executed on a virtual machine (a p-code machine, i.e., interpreter), or it may be further compiled into machine code for better performance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-board Microcontroller
A single-board microcontroller is a microcontroller built onto a single printed circuit board. This board provides all of the circuitry necessary for a useful control task: a microprocessor, I/O circuits, a clock generator, RAM, stored program memory and any necessary support ICs. The intention is that the board is immediately useful to an application developer, without requiring them to spend time and effort to develop controller hardware. As they are usually low-cost, and have an especially low capital cost for development, single-board microcontrollers have long been popular in education. They are also a popular means for developers to gain hands-on experience with a new processor family. Origins Single-board microcontrollers appeared in the late 1970s, when the appearance of early microprocessors, such as the 6502 and the Z80, made it practical to build an entire controller on a single board, as well as affordable to dedicate a computer to a relatively minor task. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Syntax Tree
In computer science, an abstract syntax tree (AST), or just syntax tree, is a tree representation of the abstract syntactic structure of text (often source code) written in a formal language. Each node of the tree denotes a construct occurring in the text. The syntax is "abstract" in the sense that it does not represent every detail appearing in the real syntax, but rather just the structural or content-related details. For instance, grouping parentheses are implicit in the tree structure, so these do not have to be represented as separate nodes. Likewise, a syntactic construct like an if-condition-then statement may be denoted by means of a single node with three branches. This distinguishes abstract syntax trees from concrete syntax trees, traditionally designated parse trees. Parse trees are typically built by a parser during the source code translation and compiling process. Once built, additional information is added to the AST by means of subsequent processing, e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |