|
Dravidian Studies
Dravidian studies (also Dravidology, Dravidiology) is the academic field devoted to the Dravidian languages, literature, and culture. It is a superset of Tamil studies and a subset of Indology. Early missionaries The 16th to 18th century missionaries who wrote Tamil grammars or lexica include Henrique Henriques, Bartholomaeus Ziegenbalg and Constantino Giuseppe Beschi. Dravidian language hypothesis The recognition that the Dravidian languages were a phylogenetic unit separate from Indo-European dates to 1816, and was presented by F. W. Ellis, Collector of Madras, at the College of Fort St. George. Nineteenth-century experts The 19th century contributors to the field of Dravidology were: Twentieth-century experts The noted Dravidologists from the twentieth century are: Contemporary programs The Dravidian University at Kuppam, Andhra Pradesh has created Chairs in the names of Western and Dravidian scholars to encourage research in individual Dravidian languages as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
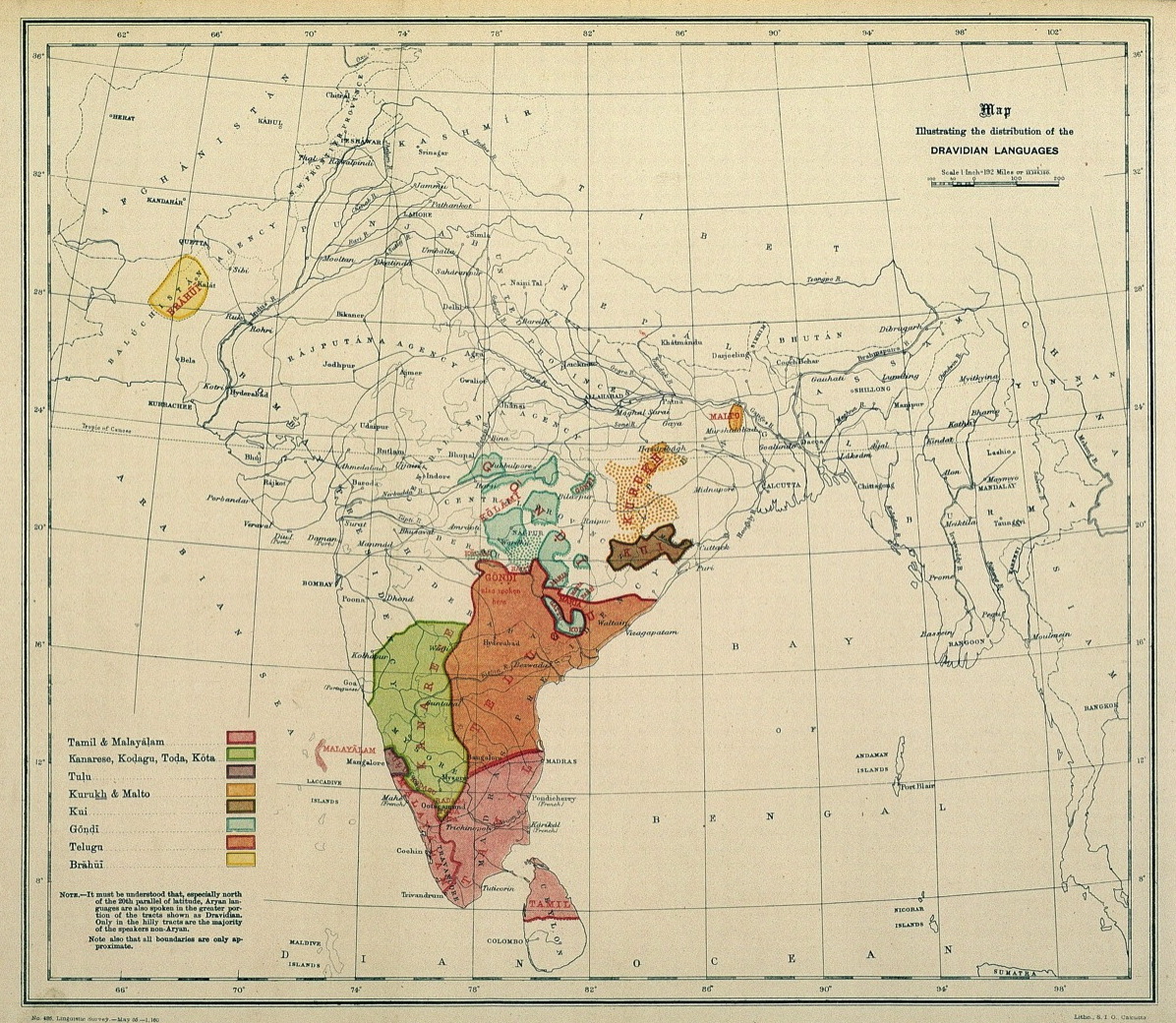
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thembavani
''Thembavani'' (; ) is a Tamil classic poetical work by Veeramamunivar ( Costanzo Joseph Beschi) (Tamil : வீரமாமுனிவர்) on the life of Saint Joseph, the legal father of Jesus of Nazareth. It is divided into thirty-six ''cantos'', containing 3,615 stanzas. Story The poem begins with the birth of Joseph, called Valan. He becomes a staunch ascetic who later marries Mary, a resolute virgin. Through divine intervention, Mary gives birth to a son. The following episodes describe the family's lives. The work ends with Valan's coronation by the Triune God in heavenly glory. Finally, kings from the Holy Roman Empire (England, Ireland, Spain, Gaul, Prussia, Norway, Lusitania, Genoa, Etruria, Parthia, Cyprus, and Paeonia) came to Vienna at the invitation of Leopold I to install the statue of the hero of the epic. ''Thembavani'' has over 100 references to events and teachings in the Bible. It has an abundance of historical, biblical and fictional characters, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Kittel
Ferdinand Kittel (7 April 1832 – 18 December 1903) was a Lutheran priest and indologist with the Basel Mission in south India and worked in Mangalore, Madikeri and Dharwad in Karnataka. He is most famous for his studies of the Kannada language and for producing a Kannada-English dictionary of about 70,000 words in 1894. He also composed numerous Kannada poems.Journal of the Karnatak University: Humanities: Volume 19 Karnatak University - 1975 "He was also involved in the work of the revision of the Kannada Bible. But his magnum opus was the school dictionary English- Kannada Shala Nighantu, which saw the light of the day in 1876. Though William Reeve (missionary) compiled and published ..." Early life Kittel was born 7 April 1832 in Resterhafe, East Frisia, off the northwestern coast of Germany. His father, Gottfried Christian Kittel, was a priest. His mother was Helen Hubert. Kittel was the eldest of five children. His education was praised by the headmaster as "Never Less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Gundert
Hermann Gundert (Stuttgart, 4 February 1814 – 25 April 1893) was a German missionary, scholar, and linguist, as well as the maternal grandfather of German novelist and Nobel laureate Hermann Hesse. Gundert is chiefly known for his contributions as an Indologist, and compiled a Malayalam grammar book, ''Malayalabhaasha Vyakaranam'' (1859), in which he developed and constricted the grammar spoken by the Malayalis, nowadays; a Malayalam-English dictionary (1872), and contributed to work on Bible translations into Malayalam. He worked primarily at Tellicherry on the Malabar coast, in present day Kerala, India. Gundert also contributed to the fields of history, geography and astronomy. Gundert gave the famous epithet "God's own country" to Kerala seeing the beauty of the land while he traveled from Kunnamkulam to Mangalore on a boat. Early years Hermann Gundert was born to Ludwig Gundert and Christiana Enslin, and was the couple's third child. His father was the secretary of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Caldwell
Robert Caldwell (7 May 1814 – 28 August 1891) was a British missionary and linguist. A missionary for the London Missionary Society, he arrived in Company Raj, British India at age 24, and studied the local language to spread the word of the Bible in a vernacular language, studies that led him to author a text on comparative grammar of the South Indian languages. In his book, Caldwell proposed that there are Dravidian languages, Dravidian words in the Hebrew of the Old Testament, the archaic Greek language, and the places named by Ptolemy. Caldwell married Eliza Mault, the daughter of another missionary Rev. Charles Mault posted in India. He served as assistant bishop of Tirunelveli from 1877. The Government of Tamil Nadu has created a memorial in his honor and a postage stamp has been issued in his name. A statue of Caldwell was erected in 1967 near to Marina Beach, Chennai, as a gift of the Church of South India. Early life Robert Caldwell was born at Clady, County Tyrone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Whyte Ellis
Francis Whyte Ellis (1777–1819) was a British civil servant in the Madras Presidency and a scholar of Tamil and Sanskrit. Biography Ellis became a writer in the East India Company's service at Madras in 1796. He was promoted to the offices of assistant-under secretary, deputy-secretary, and secretary to the board of revenue in 1798, 1801, and 1802 respectively. In 1806 he was appointed judge of the zillah of Machilipatnam, in 1809 collector of land customs in the Madras presidency, and in 1810 collector of Madras. He died at Ramnad of cholera on 10 March 1819. Dravidian language hypothesis Ellis is the first scholar who classified the Dravidian languages as a separate language family. Robert Caldwell, who is often credited as the first scholar to propose a separate language family for South Indian languages, acknowledges Ellis's contribution in his preface to the first edition of ''A Comparative Grammar of the Dravidian or South Indian Family of Languages'': The first to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as Sacred Scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of 27 Christianity, Christian texts written in Koine Greek by various authors, forming the second major division of the Christian Bible. It includes four Gospel, gospels, the Acts of the Apostles, epistles attributed to Paul the Apostle, Paul and other authors, and the Book of Revelation. The Development of the New Testament canon, New Testament canon developed gradually over the first few centuries of Christianity through a complex process of debate, rejection of Heresy, heretical texts, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in Koine Greek. The Old Testament consists of many distinct books by various authors produced over a period of centuries. Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections: the first five books or Pentateuch (which corresponds to the Jewish Torah); the history books telling the history of the Israelites, from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon; the poetic and wisdom literature, which explore themes of human experience, morality, and divine justice; and the books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God. The Old Testament canon differs among Christian denominations. The Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranquebar
Tharangambadi (), formerly Tranquebar (, ), is a town in the Mayiladuthurai district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu on the Coromandel Coast. It lies north of Karaikal, near the mouth of a distributary named Uppanar of the Kaveri River. It was established on 19 November 1620 as the first Danish trading post in India. King Christian IV had sent his envoy Ove Gjedde who established contact with Raghunatha Nayak of Thanjavur. An annual tribute was paid by the Danes to the Rajah of Tanjore until the colony was sold to the British East India Company in 1845. Tharangambadi is the headquarters of Tharangambadi taluk. Its name means "place of the singing waves"; the old designation ''Trankebar'' remains current in modern Danish. Tharangambadi is located at the distance of 285 km from Chennai. The nearest airport is Tiruchirappalli International Airport, 172 km away and the nearest port is at Karaikal at 26 km. It is served by Tharangambadi railway station. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietist
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christianity, Christian life. Although the movement is aligned with Lutheranism, it has had a tremendous impact on Protestantism worldwide, particularly in North America and Europe. Pietism originated in modern Germany in the late 17th century with the work of Philipp Spener, a Lutheran theologian whose emphasis on personal transformation through spiritual rebirth and renewal, individual devotion, and piety laid the foundations for the movement. Although Spener did not directly advocate the Quietism (Christian contemplation), quietistic, legalistic, and semi-separatist practices of Pietism, they were more or less involved in the positions he assumed or the practices which he encouraged. Pietism spread from Germany to Switzerland, the rest of German-speaking Europe, and to Scandinavia and the Balt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |