|
Dios Y Federación
''Dios y Federación'' () is considered the traditional Motto, state motto of Venezuela. It was first used as the rallying cry of the rebel forces during the Federal War, and it was subsequently incorporated into the country's Coat of arms of Venezuela, coat of arms after the conflict ended in 1863. History According to an account by historian José Gil Fortoul, two France, French adventurers who had joined the forces of General Ezequiel Zamora near Barinas State, Barinas initially suggested that the customary ''...your humble servant'' valediction in written communications be replaced with ''Liberté, égalité, fraternité'', which was finally modified to ''Dios y Federación''. The phrase subsequently became emblematic of the rebel movement. After the signing of the Treaty of Coche in April 1863 and the establishment of the new government by the victorious rebels, General Juan Crisóstomo Falcón modified the official seal from 1836, replacing the word ''Liberty'' in the cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Venezuela (1871)
The current coat of arms of Venezuela was primarily approved by the Congress on April 18, 1836, undergoing small modifications through history, reaching the present version. The coat of arms was established in the Law of the National Flag, Shield and Anthem (''Ley de Bandera, Escudo e Himno Nacionales''), passed on February 17, 1954, by the military governor of Venezuela, Marcos Pérez Jiménez. The shield is divided in the colors of the national flag. In the dexter chief, on a red field, wheat represents the union of the 24 states of the Republic existing at the time and the wealth of the nation. In sinister chief, on a yellow field, weapons (a sword, a sabre and three lances) and two national flags are tied by a branch of laurel, as a symbol of triumph in war. In base, on a deep blue field, a wild white horse (representing Simón Bolívar's white horse ''Palomo'') runs free, an emblem of independence and freedom. Above the shield are two crossed cornucopias (horns of plenty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberté, égalité, Fraternité
(; French for , ), is the national motto of France and the Republic of Haiti, and is an example of a tripartite motto. Although it finds its origins in the French Revolution, it was then only one motto among others and was not institutionalized until the Third Republic at the end of the 19th century. (abridged translation, ''Realms of Memory'', Columbia University Press, 1996–98). Debates concerning the compatibility and order of the three terms began at the same time as the Revolution. It is also the motto of the Grand Orient and the Grande Loge de France. Origins during the French Revolution Some claim that Camille Desmoulins invented the phrase, in number 35 of ''Révolutions de France et de Brabant'', published on 26 July 1790. However, it is not confirmed as this is only the first official mention of the phrase. Speaking of the July 1790 Fête de la Fédération festival, he described "the citizen-soldiers rushing into each other's arms, promising each other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Mottos
This article lists state and national mottos for the world's nations. The mottos for some List of unrecognized countries, states lacking general international recognition, List of extinct states, extinct states, non-sovereign nations, regions, and territories are listed, but their names are not bolded. A state motto is used to describe the intent or motivation of the state in a short phrase. For example, it can be included on a country's flag, coat of arms, or currency. Some countries do not have a national motto. Current sovereign countries *: ''Shahada, There is no other god other than Allah (God); Muhammad is the messenger of God.'' (; ) *: ''You, Albania, give me honour, give me the name Albanian'' () *: ''By the people and for the people'' (; ). *: ''Strength united is stronger'' (). *: ''Virtue is stronger when united'' () *: ''Each endeavouring, all achieving'' *: No official motto. Unofficial motto: ''In Union and Liberty'' (). *: ''One Nation, One Culture'' (; ). *: No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Venezuela
The history of Venezuela reflects events in areas of the Americas colonized by Spain starting 1502; amid resistance from indigenous peoples, led by Native caciques, such as Guaicaipuro and Tamanaco. However, in the Andean region of western Venezuela, complex Andean civilization of the Timoto-Cuica people flourished before European contact. After the first contacts between Europeans, specifically Portuguese and Spanish conquerors, there were no significant events between 1515 and 1528. The biggest event that happened after 1528 was the German Colonization of Venezuela. This event occurred because of a business between Charles V and the banking family of the Augsburg. Charles V, gave the family of the Augsburg most of the territory of the Province of Venezuela, which after the concession was called by the Germans "Klein-Venedig" which means "Little Venice". The Germans in Venezuela were mostly conquistadores or explorers, which their mission was to find El Dorado. At the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
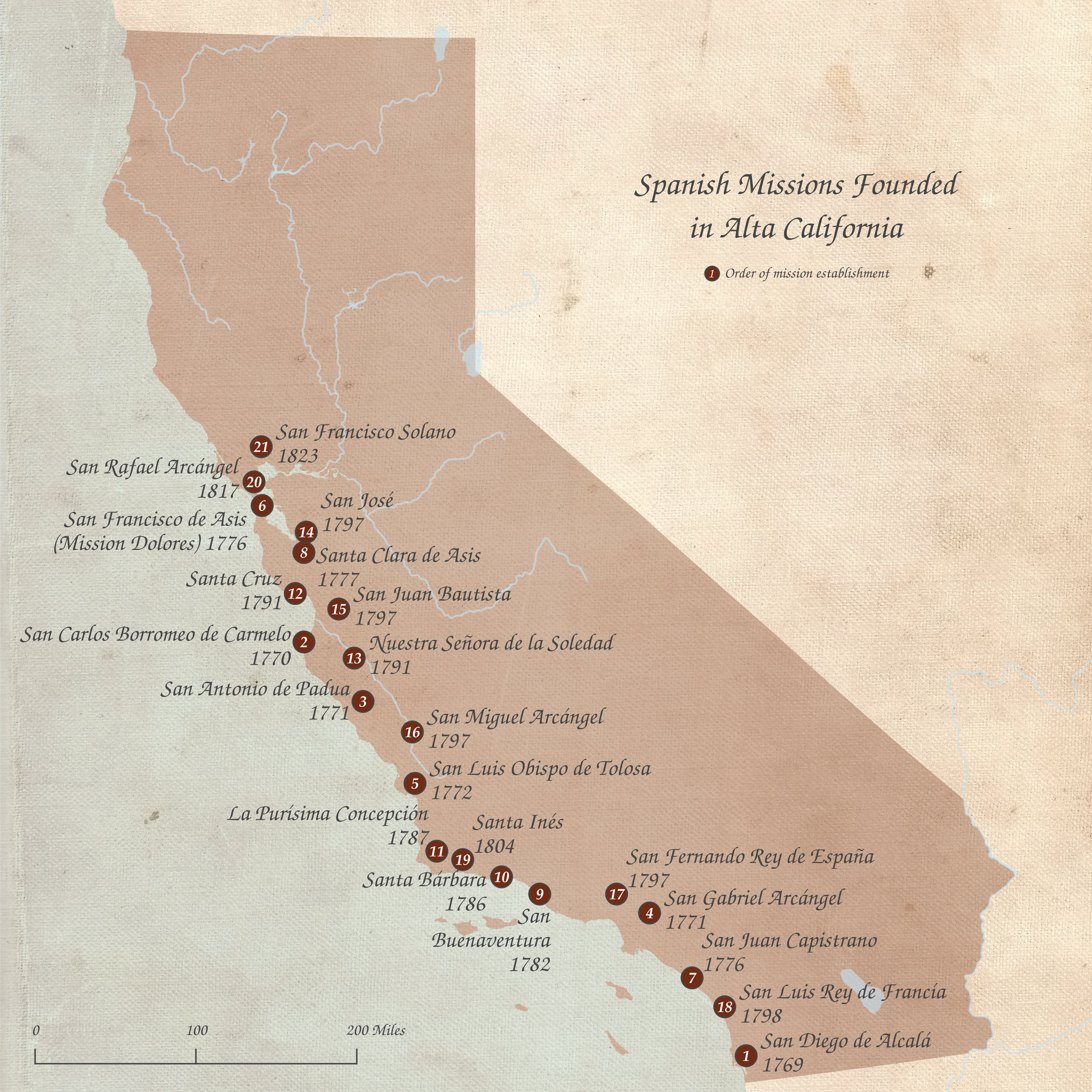
Alta California
Alta California (, ), also known as Nueva California () among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was made a separate province in 1804 (named ). Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of First Mexican Empire, Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed in 1824. The territory included all of the present-day U.S. states of California, Nevada, and Utah, and parts of Arizona, Wyoming, and Colorado. The territory was with Baja California Territory, Baja California (as a single ) in Mexico's 1836 ''Siete Leyes'' (Seven Laws) constitutional reform, granting it more autonomy. That change was undone in 1846, but rendered moot by the outcome of the Mexican–American War in 1848, when most of the areas formerly comprising Alta California Mexican Cession, were ceded to the U.S. in Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, the treaty which ended the war. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcón
Falcón State (, ) is one of the 23 States of Venezuela, states of Venezuela. The state capital is Coro, Venezuela, Coro. The state was named after Juan Crisóstomo Falcón. History Early history Present day Falcón State was first explored in 1499 by Juan de la Cosa and Américo Vespucio, as part of an expedition supervised by Alonso de Ojeda. In 1527, the city of Coro was founded by Juan Martínez de Ampiés, Juan Ampíes, who named it "Coro, Venezuela, Santa Ana de Coro". In 1811, when Venezuela declared its independence from Spain, Coro remained faithful to the Spanish Crown and was merged with the Maracaibo Province (Venezuela), Province of Maracaibo. In 1815, King Ferdinand VII of Spain, Fernando VII created the Coro Province, Province of Coro. In 1821, the province was liberated from Spain by Josefa Camejo during the Venezuelan War of Independence. The area then became a province of the department of Zulia of the Republic of Gran Colombia. In 1830, with the separation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Republic Of Venezuela
The First Republic of Venezuela () was the first independent government of Venezuela, lasting from 5 July 1811, to 25 July 1812. The period of the First Republic began with the overthrow of the Spanish colonial authorities and the establishment of the Junta Suprema de Caracas on 19 April 1810, initiating the Venezuelan War of Independence, and ended with the surrender of the republican forces to the Spanish Captain Domingo de Monteverde. The congress of Venezuela declared the nation's independence on 5 July 1811, and later wrote a constitution for it. In doing so, Venezuela is notable for being the first Spanish American colony to declare its independence. History Antecedents Several European events set the stage for Venezuela's declaration of independence. The Napoleonic Wars in Europe not only weakened Spain's imperial power, but also put Britain unofficially on the side of the independence movement. In May 1808, Napoleon asked for and received the abdication of Ferdinan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Crisóstomo Falcón
Juan Crisóstomo Falcón Zavarce (27 January 1820 – 29 April 1870) was the president of Venezuela from 1863 to 1868.Biography (Spanish) Biography Falcón was a member of the Liberal Venezuelan Federalist Party, and had been exiled to Curaçao after the Conservative March Revolution of 1858. At the outbreak of the , he returned to Venezuela as the supreme chief of the rebel movement in August 1859. When his military leader Ezequiel Zamora, was kill ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Coche
The Treaty of Coche was an agreement that formally established the end of the Federal War in Venezuela. The name of the treaty originates from the fact that it was made at the estate of Coche, in that period very close to Caracas, and today part of the Parish of Coche in Caracas. The agreement was initially made on 23 April 1863, between, on the one hand for the Conservatives, Pedro José Rojas, Secretary General of the Supreme Chief of the Republic: José Antonio Páez, and on the other hand for the Liberals, Antonio Guzmán Blanco, Secretary General of the Provisional President of the Federation: Juan Crisóstomo Falcón, and later confirmed by both Páez and Falcón on 25 May 1863. History In 1863, after the four-year-long Federal War The Federal War () — also known as the Great War or the 5 Year War — was a civil war in Venezuela between the Conservative Party and the Liberal Party over the monopoly the Conservatives held over government positions and land ownersh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valediction
A valediction (Derivation (linguistics), derivation from Latin ''vale dicere'', "to say farewell"), parting phrase, or complimentary close in American English, is an expression used to say farewell, especially a word or phrase used to end a letter or message,Valediction – Definition from American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. (2011). as cited by The Free Dictionary. or a speech made at a farewell. Valediction's counterpart is a greeting called a salutation. Oral valedictions Parting phrases are used to acknowledge the parting of individuals or groups of people from each other. They are an element of parting traditions. Parting phrases are specific to culture and situation, and vary based on the social status and relationship of the persons involved. Religiou ...
|
Motto
A motto (derived from the Latin language, Latin , 'mutter', by way of Italian language, Italian , 'word' or 'sentence') is a Sentence (linguistics), sentence or phrase expressing a belief or purpose, or the general motivation or intention of an individual, family, social group, or organization. Mottos (or mottoes) are usually found predominantly in written form (unlike slogans, which may also be expressed orally), and may stem from long traditions of social foundations, or from significant events, such as a civil war or a revolution. One's motto may be in any language, but Latin language, Latin has been widely used, especially in the Western world. Language Latin language, Latin has been very common for mottos in the Western World, but for nation states, their official national language is generally chosen. Examples of using other historical languages in motto language include: *Counties of England, County of Somerset in England: (All the men of Somerset), Old English language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barinas State
Barinas State (, ) is one of the 23 States of Venezuela, states of Venezuela. The state capital is Barinas, Barinas, Barinas. Barinas State covers a total surface area of and had an estimated population of 970,689 in 2015. Toponymy The toponym "Barinas" is a variant of "varinas" (the name of an indigenous ethnic group that inhabited the Piedemonte before the arrival of the Spaniards); this may have a relationship with the name "Barima", given by the tunebos to the Santo Domingo River, Santo Domingo river in the Aya myth. The meaning is unknown, but according to popular belief, it means a 'strong wind that comes from the valleys of the Santo Domingo river', referring to the Barinese wind, which blows in the Llanos Altos. According to Virgilio Tosta, the place name was first used before 1628 as an alternative name for Altamira (other), Altamira; in contrast, according to Betancourt Martínez, it was in the foundations of Barinitas such as Nueva Trujillo de Barinas (1628 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |