|
Colo Colo (mythology)
The Colo Colo or Colocolo is an evil rat-like creature from Mapuche mythology. The marsupial monito del monte is sometimes called "colocolo" due to its similarity with the mythical beast. Description The appearance of the Colo Colo varies depending on the region where the myth is told. Sometimes it is described as a feathered rat, sometimes as a snake or lizard with a rat's head, and occasionally it is just depicted as a huge rat. The Colo Colo falls under the mythical category of "Pillians". Legend The Colo Colo hatches from an egg laid by a snake, and incubated by a rooster. After hatching, the Colo Colo will hide in a house, where it will feed on the saliva of the residents. If the Colo Colo feeds from a person, that individual will feel exhausted; if the Colo Colo is not stopped, the victim may even die. It is also said that this creature can provoke several serious diseases. The Colo Colo can be detected if someone of the house is feeling tired for no reason, or because of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their habitat once extended from Aconcagua Valley to Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of extended families, under the direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monito Del Monte
The monito del monte or colocolo opossum, ''Dromiciops gliroides'', also called ''chumaihuén'' in Mapudungun, is a diminutive marsupial native only to southwestern South America (Argentina and Chile). It is the only extant species in the ancient order Microbiotheria, and the sole New World representative of the superorder Australidelphia (all other New World marsupials are members of the paraphyletic Ameridelphia). The species is nocturnal and arboreal, and lives in thickets of South American mountain bamboo in the Valdivian temperate rain forests of the southern Andes, aided by its partially prehensile tail. It eats primarily insects and other small invertebrates, supplemented with fruit. Taxonomy and etymology ''Dromiciops gliroides'' is the sole extant member of the order Microbiotheria. It was first described by British zoologist Oldfield Thomas in 1894. The generic name ''Dromiciops'' is based on the resemblance of the monito del monte to the eastern pygmy possum (''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lipase and amylase), antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes). The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay. Saliva also performs a lubricating function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the oral mucosa from drying out. Various animal species have special uses for saliva that go beyond predigestion. Some swifts use their gummy saliva to build nests. '' Aerodramus'' nests form the basis of bird's nest soup. Cobras, vipers, and certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
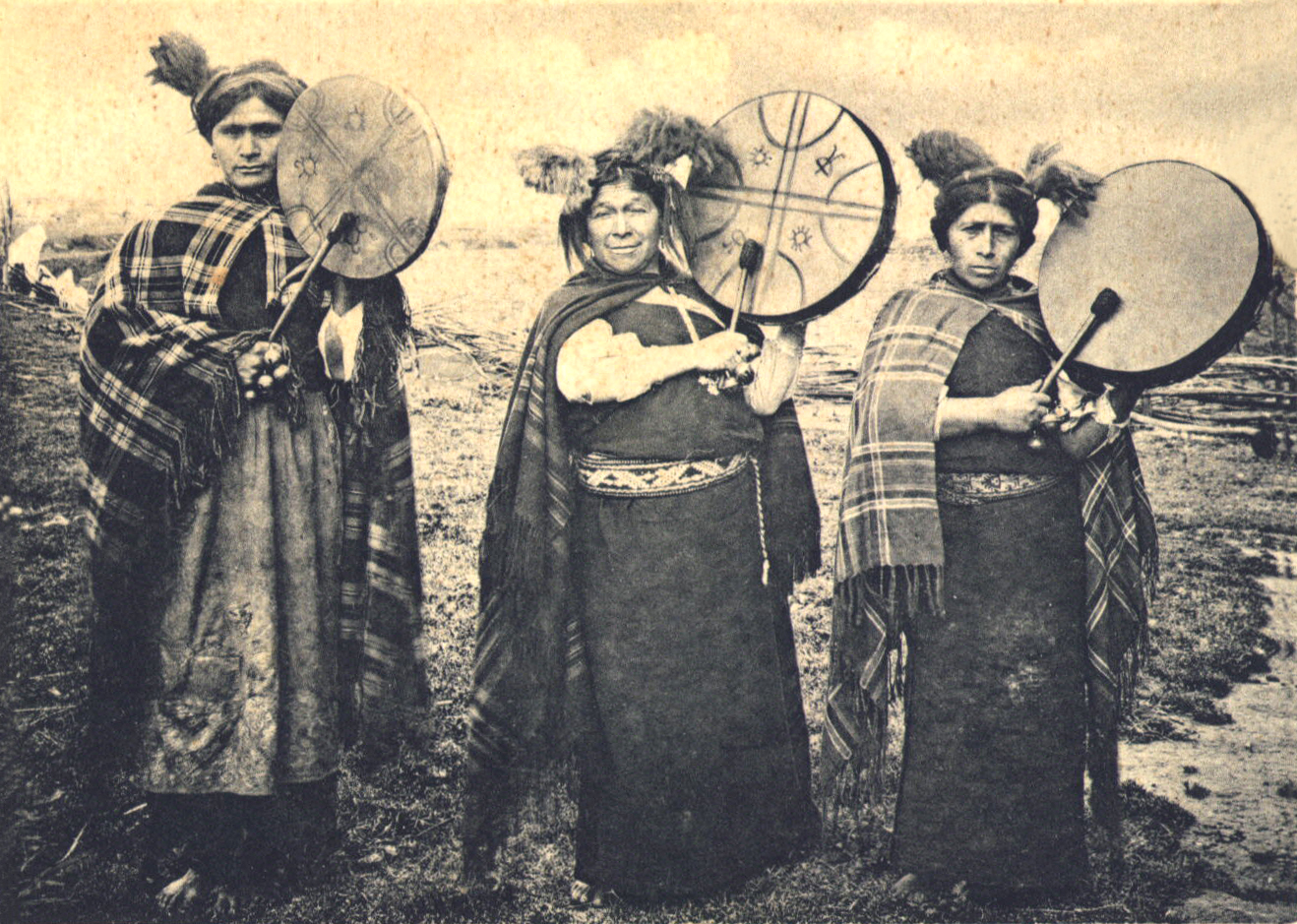
Machi (shaman)
A machi is a traditional healer and religious leader in the Mapuche culture of Chile and Argentina. Machis play significant roles in Mapuche religion. In contemporary Mapuche culture, women are more commonly machis than men but it is not a rule. Description As a religious authority, a machi leads healing ceremonies, called Machitun. During the machitun, the machi communicates with the spirit world. Machies also serve as advisors, and oracles for their community. In the past, they advised on peace and warfare. The term is sometimes interchangeable with the word ''kalku'', however, ''kalku'' has a usually evil connotation whereas ''machi'' is usually considered good; this, however, is not always true since in common use the terms may be interchanged. The Mapuches live in southern South America mostly in central Chile ( Araucanía and Los Lagos) and the adjacent areas of Argentina. To become a machi, a Mapuche person has to demonstrate character, willpower, and courage, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche Religion
The mythology and religion of the indigenous Mapuche people of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina is an extensive and ancient belief system. A series of unique legends and myths are common to the various groups that make up the Mapuche people. These myths tell of the creation of the world and the various deities and spirits that reside in it. Overview In order to describe the beliefs of the Mapuche people, it is important to note that there are no written records about their ancient legends and myths from before the Spanish arrival, since their religious beliefs were passed down orally. Their beliefs are not necessarily homogenous; among different ethnic groups, and the families, villages, and territorial groups within those ethnic groups, there are variations and differences and discrepancies in these beliefs. Likewise, it is important to understand that many of the Mapuche beliefs have been integrated into the myths and legends of Chilean folklore, and to a les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous South American Legendary Creatures
Indigenous may refer to: *Indigenous peoples *Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention *Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band *Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse * ''Indigenous'' (film), Australian, 2016 See also *Disappeared indigenous women *Indigenous Australians *Indigenous language *Indigenous religion *Indigenous peoples in Canada In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and '' Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider th ... * Native (other) * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche Legendary Creatures
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their habitat once extended from Aconcagua Valley to Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of extended families, under the direction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |