|
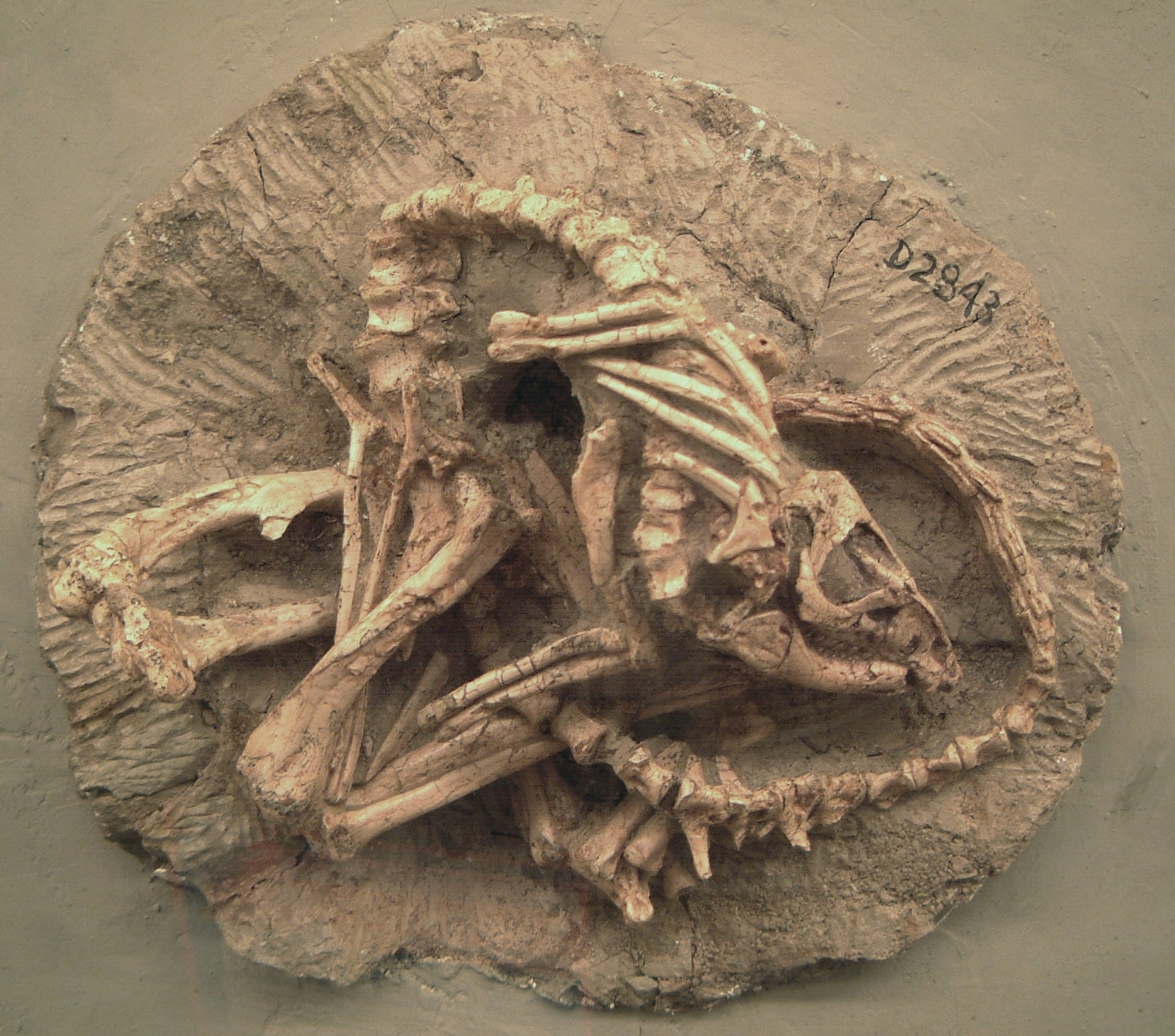
Changchunsaurus
''Changchunsaurus'' (meaning "Changchun lizard") is an extinct genus of small herbivorous dinosaur from Early Cretaceous deposits of Gongzhuling, Jilin, China. It is the first named dinosaur genus from Jilin. Description ''Changchunsaurus'' was first named by Zan Shu-Qin, Chen Jun, Jin Li-Yong and Li Tao in 2005. The type and only known species is ''C. parvus'' ("parvus" meaning "petite"), named for its small size. It is known from a skull and skeleton and additional skull fragments. All specimens of ''Changchunsaurus'' were collected from the Quantou Formation of the Songliao Basin, dating to the Aptian– Cenomanian stages. ''Changchunsaurus'' is based on the holotype JLUM L0403-j–Zn2, a skeleton and skull, with a premaxilla (upper beak) and partial lower jaw also known. Only the skull was figured and described in the official description. According to Zan ''et al.'' 2005, who described it, the animal shows a combination of features like those of derived ornithopods (redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeholosaurus
''Jeholosaurus'' is a genus of neornithischian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Period. It is thought to have been a herbivorous small ornithopod. History of discovery The first two ''Jeholosaurus'' specimens were found in 2000 at Lujiatun near Beipiao City, Liaoning Province, China, and named and described the same year by Xu Xing, Wang Xioalin and You Hailu. The type and only known species is ''Jeholosaurus shangyuanensis''. The generic name ''Jeholosaurus'' means "lizard from Jehol"; Jehol is the name of a historical province situated in western Liaoning and northern Hebei. The specific name refers to the geographical area of Shangyuan where the fossil site is located. The type specimen of ''Jeholosaurus'', on which the genus is based, is IVPP V 12529. It was found in a layer of the early Yixian Formation, dating from the early Aptian, about 126-125 million years old. The layers consist of fluvial sandstone interspersed with tuff and it is thought that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2005 In Paleontology
Protozoans Diatoms Plants Conifers Angiosperms Fungi Arthropoda Arachnids Insects Xiphosurans * Fossils of ''Lunataspis'', the earliest known xiphosuran, are discovered in Canada. It was not given a formal description until 2008, however. Plesiosaurs New taxa Archosauromorphs Newly named Non-Avian dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Newly named pterosaurs Synapsids Non-mammalian Footnotes Complete author list As science becomes more collaborative, papers with large numbers of authors are becoming more common. To prevent the deformation of the tables, these footnotes list the contributors to papers that erect new genera and have many authors. References {{DEFAULTSORT:2005 In Paleontology 2000s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantou Formation
The Quantou Formation is a Cretaceous Period (Mesozoic Era) geologic formation in China. It is primarily Albian in age. It has been explored for its potential as a tight oil reservoir. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. Vertebrate paleofauna *''Changchunsaurus'' *''Helioceratops'' *''Jiutaisaurus'' See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils have been documented. Containing body fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with few ... Footnotes Bibliography * Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp. . Geologic formations of China Cretaceous System of Asia Cretaceous China Albian Stage Aptia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further divided by locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postcrania
Postcrania (postcranium, adjective: postcranial) in zoology and vertebrate paleontology is all or part of the skeleton apart from the skull. Frequently, fossil remains, e.g. of dinosaurs or other extinct tetrapods, consist of partial or isolated skeletal elements; these are referred to as ''postcrania''. There is some disagreement over whether the skull and skeleton belong to the same or different animals. One example is the case of a Cretaceous sauropod Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their bo ... skull of '' Nemegtosaurus'' found in association with the postcranial skeleton '' Opisthocoelicaudia''. In paleoanthropological studies, reconstruction of relationship between various species/remains is considered to be better supported by cranial characters rather than postcrania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
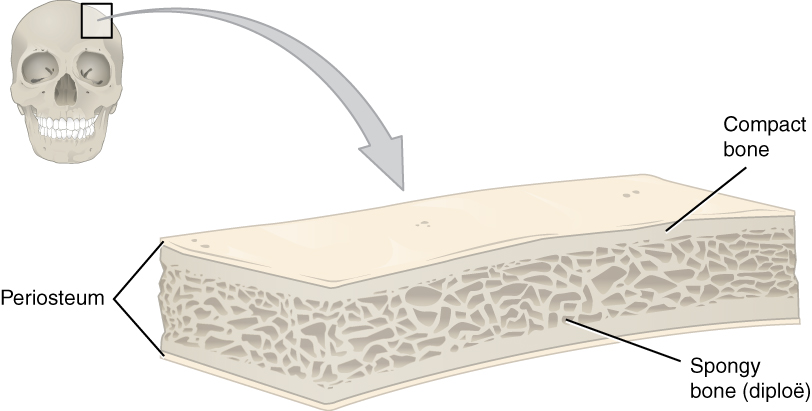
Cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistics
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies'')'' that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms ''worms'' or ''fishes'' were used within a ''strict'' cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a ' grade', which are fruitless to precisely delineate, especially when including extinct species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incertae Sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty at specific taxonomic levels is indicated by ' (of uncertain family), ' (of uncertain suborder), ' (of uncertain order) and similar terms. Examples *The fossil plant '' Paradinandra suecica'' could not be assigned to any family, but was placed ''incertae sedis'' within the order Ericales when described in 2001. * The fossil '' Gluteus minimus'', described in 1975, could not be assigned to any known animal phylum. The genus is therefore ''incertae sedis'' within the kingdom Animalia. * While it was unclear to which order the New World vultures (family Cathartidae) should be assigned, they were placed in Aves ''incertae sedis''. It was later agreed to place them in a separate order, Cathartiformes. * Bocage's longbill, ''Motacilla boc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Specimen
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species. Anatomy The jugal bone is located on either side of the skull in the circumorbital region. It is the origin of several masticatory muscles in the skull. The jugal and lacrimal bones are the only two remaining from the ancestral circumorbital series: the prefrontal, postfrontal, postorbital, jugal, and lacrimal bones. During development, the jugal bone originates from dermal bone. In dinosaurs This bone is considered key in the determination of general traits in cases in which the entire skull has not been found intact (for instance, as with dinosaurs in paleontology). In some dinosaur genera the jugal also forms part of the lower margin of either the antorbital fenestra or the infratemporal fenestra, or both. Most commonly, this bone ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Fenestrae
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the fronta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
.jpg)