|
Central Product Classification
The Central Product Classification (CPC) is a product classification for goods and services promulgated by the United Nations Statistical Commission. It is intended to be an international standard for organizing and analyzing data on industrial production, national accounts, trade, prices and so on. The European Union's ''Classification of Products by Activity'' (CPA) is based on CPC. See also *Classification of Types of Construction The Classification of types of construction (CC), is a nomenclature for the classification of constructions (i.e. buildings) according to their type. It is based on the CPC that was published by the United Nations in 1991. Its final version was app ... References * Central Product Classification (CPC) Version 2.1 (August 2015* Central Product Classification, CPC Version 2 (Dec 2008Parent page [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Classification
Product classification or product taxonomy is a type of economic taxonomy which organizes products for a variety of purposes. However, not only products can be referred to in a standardized way but also sales practices in form of the “Incoterms” and industries can be classified into categories. Some standard product classifications include: * CPA — Classification of Products by Activity, a product nomenclature that was used in the European Economic Community and now in use in the EU, a European version of the CPC ** CPA 1996 ** CPA 2002 ** CPA 2008 ** CPA 2.1 * CPC — Central Product Classification, a United Nations standard classification for products * ETIM, the ETIM Technical Information Model * Global Classification and Harmonized Schedule Numbers for customs classification * HS — Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System * SITC — Standard International Trade Classification * Trade in Services * UNSPSC, the United Nations Standard Products and Services C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Statistical Commission
The United Nations Statistical Commission (StatCom) is a Functional Commission of the United Nations Economic and Social Council, established in 1947. The Statistical Commission oversees the work of the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD). Its 24 member states are elected by the Economic and Social Council on the basis of the following geographical distribution: African states (5), Asian States (4), Eastern European States (4), Latin American and Caribbean States (4), Western European and other States (7). Since July 1999 the Commission meets every year. As set forth by the Economic and Social Council, in the terms of reference, the Commission shall assist the Council: :*"In promoting the development of national statistics and the improvement of their comparability;" :*"In the coordination of the statistical work of specialized agencies;" :*"In the development of the central statistical services of the Secretariat;" :*"In advising the organs of the United Nations on general qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Standard
international standard is a technical standard developed by one or more international standards organization, standards organizations. International standards are available for consideration and use worldwide. The most prominent such organization is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Other prominent international standards organizations including the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Together, these three organizations have formed the World Standards Cooperation alliance. Purpose International standards may be used either by direct application or by a process of modifying an international standard to suit local conditions. Adopting international standards results in creating national standards that are equivalent, or substantially the same as international standards in technical content, but may have (i) editorial differences as to appearance, use of symbols and measurement units, substitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Production
Industrial production is a measure of output of the industrial sector of the economy. The industrial sector includes manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Although these sectors contribute only a small portion of gross domestic product (GDP), they are highly sensitive to interest rates and consumer demand. This makes industrial production an important tool for forecasting future GDP and economic performance. Industrial production figures are also used by central banks to measure inflation, as high levels of industrial production can lead to uncontrolled levels of consumption and rapid inflation . See also *Index of industrial production The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is an index for India which details out the growth of various sectors in an economy such as mineral mining, electricity and manufacturing. The all India IIP is a composite indicator that measures the short- ... * Industrial Production Index References Economic data Secondary sector of the econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Accounts
National accounts or national account systems (NAS) are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that rely on double-entry accounting. By design, such accounting makes the totals on both sides of an account equal even though they each measure different characteristics, for example production and the income from it. As a method, the subject is termed national accounting or, more generally, social accounting.Nancy D. Ruggles, 1987. "social accounting," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 4, pp. 377–82. Stated otherwise, national accounts as ''systems'' may be distinguished from the economic data associated with those systems. While sharing many common principles with business accounting, national accounts are based on economic concepts. One conceptual construct for representing flows of all economic transactions that take place in an econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market. An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exchange of goods and services for other goods and services, i.e. trading things without the use of money. Modern traders generally negotiate through a medium of exchange, such as money. As a result, buying can be separated from selling, or earning. The invention of money (and letter of credit, paper money, and non-physical money) greatly simplified and promoted trade. Trade between two traders is called bilateral trade, while trade involving more than two traders is called multilateral trade. In one modern view, trade exists due to specialization and the division of labour, a predominant form of economic activity in which individuals and groups concentrate on a small aspect of production, but use their output in trades for other produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
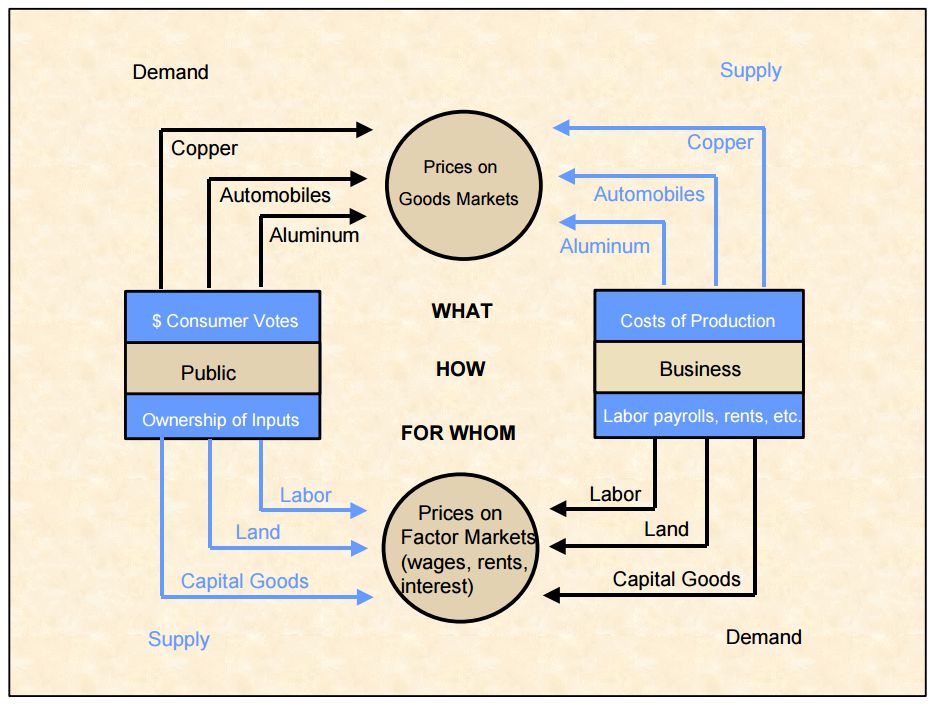
Price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the commercial exchange, the payment for this product will likely be called its "price". However, if the product is "service", there will be other possible names for this product's name. For example, the graph on the bottom will show some situations A good's price is influenced by production costs, supply of the desired item, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted to currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Products By Activity
Product classification or product taxonomy is a type of economic taxonomy which organizes products for a variety of purposes. However, not only products can be referred to in a standardized way but also sales practices in form of the “Incoterms” and industries can be classified into categories. Some standard product classifications include: * CPA — Classification of Products by Activity, a product nomenclature that was used in the European Economic Community and now in use in the EU, a European version of the CPC ** CPA 1996 ** CPA 2002 ** CPA 2008 ** CPA 2.1 * CPC — Central Product Classification, a United Nations standard classification for products * ETIM, the ETIM Technical Information Model * Global Classification and Harmonized Schedule Numbers for customs classification * HS — Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System * SITC — Standard International Trade Classification * Trade in Services * UNSPSC, the United Nations Standard Products and Servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Types Of Construction
The Classification of types of construction (CC), is a nomenclature for the classification of constructions (i.e. buildings) according to their type. It is based on the CPC that was published by the United Nations in 1991. Its final version was approved in 1997. The decimal system classification - each type is qualified by a four-digit number - comprises: #2 Sections (1-digit) - Buildings, Civil engineering works #6 Divisions (2-digit) #20 Groups (3-digit) #46 Classes (4-digit) The CC is a "standard that must be taken into account in recording, collecting, processing, analysing, transmitting and disseminating data on construction works for statistical and record-keeping purposes" in various European countries and Eurostat. The classification of types of construction should not be confused with the 16 Divisions or 50 Divisions 50 Divisions refers to the 50 divisions of construction information, as defined by the Construction Specifications Institute (CSI)'s MasterFormat beginni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |