|
Cassegrain (crater)
Cassegrain is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, beyond the southeastern limb. It lies to the southeast of the larger crater Lebedev, and to the northeast of the comparably-sized Priestley. It is named after the inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, who was later identified as most likely Laurent Cassegrain Laurent Cassegrain (; – 1 September 1693) was a Catholic priest who is notable as the probable inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, a folded two-mirror reflecting telescope design. Biography Laurent Cassegrain was born in the region of Char .... The interior of this crater has a relatively dark-hued floor, a feature it has in common with other craters to the west and northwest that form part of the Mare Australe. The floor is level and mostly featureless, except for some deposits in the northwest corner. The rim is more heavily worn in the northwest corner than elsewhere, and the remaining inner wall displays a slumped shelf below th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions to the Moon. Its detailed mapping program is identifying safe landing sites, locating potential resources on the Moon, characterizing the radiation environment, and demonstrating new technologies. Launched on June 18, 2009, in conjunction with the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), as the vanguard of NASA's Lunar Precursor Robotic Program, LRO was the first United States mission to the Moon in over ten years. LRO and LCROSS were launched as part of the United States's Vision for Space Exploration program. The probe has made a 3-D map of the Moon's surface at 100-meter resolution and 98.2% coverage (excluding polar areas in deep shadow), including 0.5-meter resolution images of Apollo landing sites. The first images f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurent Cassegrain
Laurent Cassegrain (; – 1 September 1693) was a Catholic priest who is notable as the probable inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, a folded two-mirror reflecting telescope design. Biography Laurent Cassegrain was born in the region of Chartres around 1629 and was the son of Mathurin Cassegrain and Jehanne Marquet. It is unknown what his education was but he was a priest and professor by 1654. He may have been interested in acoustics, optics and mechanics. At the time of his death he was working as a teacher giving science classes at the Collège de Chartres, a French lycée, i.e., a high-school like institution. He died at Chaudon ( Eure-et-Loir) on 1 September 1693. Connection with the Cassegrain reflector The Cassegrain reflector is a reflecting telescope design that solved the problem of viewing an image without obstructing the primary mirror by using a convex secondary mirror on the optical axis to bounce the light back through a hole in the primary mirror thus perm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Craters
Lunar craters are impact craters on Earth's Moon. The Moon's surface has many craters, all of which were formed by impacts. The International Astronomical Union currently recognizes 9,137 craters, of which 1,675 have been dated. History The word ''crater'' was adopted from the Greek word for "vessel" (, a Greek vessel used to mix wine and water). Galileo built his first telescope in late 1609, and turned it to the Moon for the first time on November 30, 1609. He discovered that, contrary to general opinion at that time, the Moon was not a perfect sphere, but had both mountains and cup-like depressions. These were named craters by Johann Hieronymus Schröter (1791), extending its previous use with volcanoes. Robert Hooke in '' Micrographia'' (1665) proposed two hypotheses for lunar crater formation: one, that the craters were caused by projectile bombardment from space, the other, that they were the products of subterranean lunar volcanism. Scientific opinion as to the ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury, Callisto, Ganymede and most small moons and asteroids. On other planets and moons that experience more active surface geological processes, such as Earth, Venus, Europa, Io and Titan, visible impact craters are less common because they become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far Side (Moon)
The far side of the Moon is the lunar hemisphere that always faces away from Earth, opposite to the near side, because of synchronous rotation in the Moon's orbit. Compared to the near side, the far side's terrain is rugged, with a multitude of impact craters and relatively few flat and dark lunar maria ("seas"), giving it an appearance closer to other barren places in the Solar System such as Mercury and Callisto. It has one of the largest craters in the Solar System, the South Pole–Aitken basin. The hemisphere is sometimes called the "dark side of the Moon", where "dark" means "unknown" instead of "lacking sunlight" each side of the Moon experiences two weeks of sunlight while the opposite side experiences two weeks of night. About 18 percent of the far side is occasionally visible from Earth due to libration. The remaining 82 percent remained unobserved until 1959, when it was photographed by the Soviet Luna 3 space probe. The Soviet Academy of Sciences publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebedev (crater)
Lebedev is a crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located at the eastern edge of the irregular feature known as Mare Australe. The crater lies to the southeast of the larger, flooded Lamb, and to the east-northeast of Anuchin. To the southeast of Lebedev lies the smaller crater Cassegrain. This is a worn and eroded crater formation with an uneven outer rim, although no significant impacts overlay the rim edge. There are a few small craterlets along the inner wall, with a pair along the southeast and another to the southwest. The most distinctive feature about this crater, however, is the dark, lava Lava is molten or partially molten rock ( magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...-flooded interior. This surface is pitted with many tiny craterlets and has a low ridge in the southern half, but is otherwise lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priestley (lunar Crater)
Priestley is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon from the Earth, in the low southern latitudes. It lies to the southeast of the flooded crater Kugler. This is a worn crater with a rim and inner wall that have been softened and have lost the sharp features of a young crater. The satellite crater Priestley X lies across the northern rim and part of the inner wall. There is a small, relatively fresh crater on the inner wall to the south-southwest. An old crater-like feature is attached to the southwestern outer rim, and shares part of its rim with Priestley. The inner wall is narrower in the southeast than elsewhere. Within the interior is a level, featureless floor. A depression in the surface to the south of Priestley has been flooded with lava, leaving a level plain with a low albedo Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
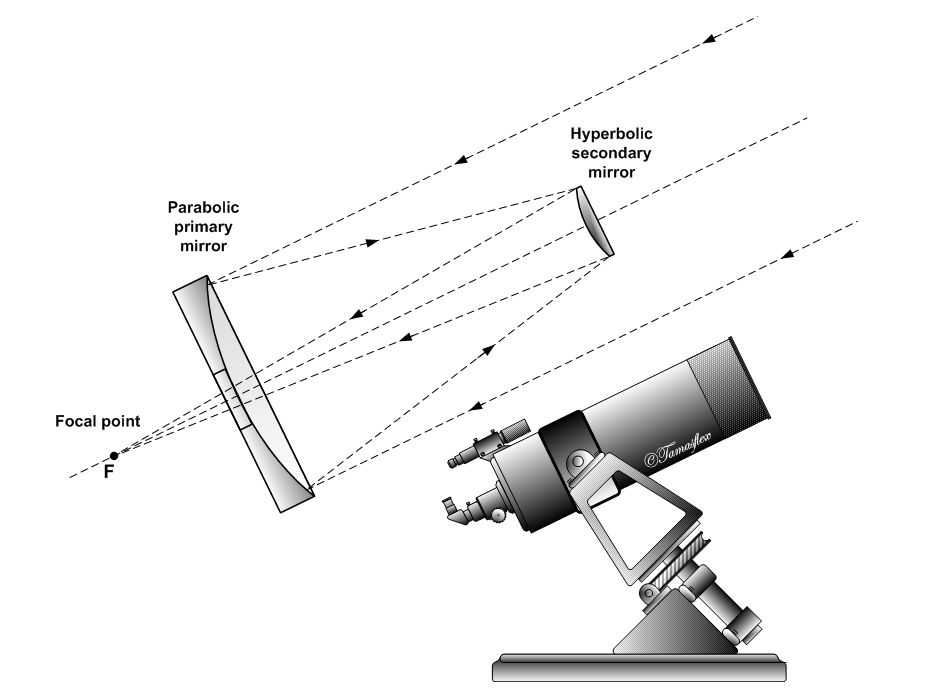
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mare Australe
Mare Australe (Latin ''austrāle'' the "Southern Sea") is a lunar mare located in the southeastern hemisphere of the Moon. It is 997 kilometers in diameter, overlapping the near and far sides of the Moon. Smooth, dark volcanic basalt lines the bottom of the mare. The Australe basin was formed in the Pre-Nectarian epoch, while the mare material inside formed in the Upper Imbrian epoch. The basin was almost completely destroyed by impacts prior to the appearance of the mare. Unlike most of the lunar maria, Mare Australe has an uneven surface that is marked by a number of crater impacts. Examples of these include the craters Jenner and Lamb, which are flooded with basaltic lava much like many of the other crater features in this mare. The selenographic coordinates of this mare are 38.9° S, 93.0° E. The eastern half of the mare lies on the far side of the Moon, although it can be viewed in its entirety during periods of favorable libration. Gallery File:Mare Australe AS15-M-250 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_launches_with_LRO_and_LCROSS.jpg)