|
CFexpress
CFexpress is a standard for removable media memory card, cards by the CompactFlash Association (CFA). The standard uses the NVM Express protocol over a PCI Express, PCIe interface. 3 different form factors are available, with 1 to 4 PCI-E lanes available. History On 7 September 2016, the CompactFlash Association announced the CFexpress standard, with specifications based on the PCI Express interface and NVM Express protocol. On 18 April 2017 the CompactFlash Association published the CFexpress 1.0 specification. Version 1.0 will use the XQD card, XQD form-factor (38.5 mm × 29.8 mm × 3.8 mm) with two PCIe 3.0 lanes for speeds up to 2 GB/s. NVMe 1.2 is used for low-latency access, low overhead and highly parallel access. On 13 June 2017, Delkin introduced the first CFexpress cards based on the CFexpress 1.0 specification. The CFexpress 2.0 standard was announced on 28 February 2019. It features two new card formats - a more compact Type A with one lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFast
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994. CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the early memory card formats, surpassing Miniature Card and SmartMedia. Subsequent formats, such as MMC/ SD, various Memory Stick formats, and xD-Picture Card offered stiff competition. Most of these cards are smaller than CompactFlash while offering comparable capacity and speed. Proprietary memory card formats for use in professional audio and video, such as P2 and SxS, are faster, but physically larger and more costly. CompactFlash's popularity is declining as CFexpress is taking over. As of 2022, both Canon and Nikon's newest high end cameras, e.g. the Canon EOS R5, Canon EOS R3, and Nikon Z 9 use CFexpress cards for the higher performance required to record 8K video. Traditional CompactFlash cards use the Parallel ATA interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XQD Card
The XQD card is a memory card format primarily developed for flash memory cards. It uses PCI Express as a data transfer interface. The format is targeted at high-definition camcorders and high-resolution digital cameras. It offers target read and write speeds from 1 Gbit/s to about 5 Gbit/s and storage capabilities beyond 2 TiB. The cards are not backward compatible with CompactFlash or CFast cards, and despite the name similarity, has no connection with the xD-Picture Card. XQD and CFast were both designed as a replacement of the 1994 CompactFlash standard. The format was first announced in November 2010 by SanDisk, Sony and Nikon, and was immediately picked up by the CompactFlash Association for development. The final specification was announced in December 2011. XQD version 2.0 was announced in June 2012, featuring support for PCI Express 3.0 with transfer rates up to 8 Gbit/s (1 GB/s). On 7 September 2016 the CFA announced the successor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Card
A memory card is an electronic data storage device used for storing digital information, typically using flash memory. These are commonly used in digital portable electronic devices, such as digital cameras as well as in many early games consoles such as the Neo Geo. They allow adding memory to such devices using a card in a socket instead of protruding USB flash drives. Common types of flash memory card include SD cards (including microSD), Sony's Memory Stick and CompactFlash. , SD cards are the most common type of memory cards. History The basis for memory card technology is flash memory. It was invented by Fujio Masuoka at Toshiba in 1980 and commercialized by Toshiba in 1987. The development of memory cards was driven in the 1980s by the need for an alternative to floppy disk drives that had lower power consumption, had less weight and occupied less volume in laptops. Some were also marketed as a lower cost alternative to ROM cartridges. Several competing and inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
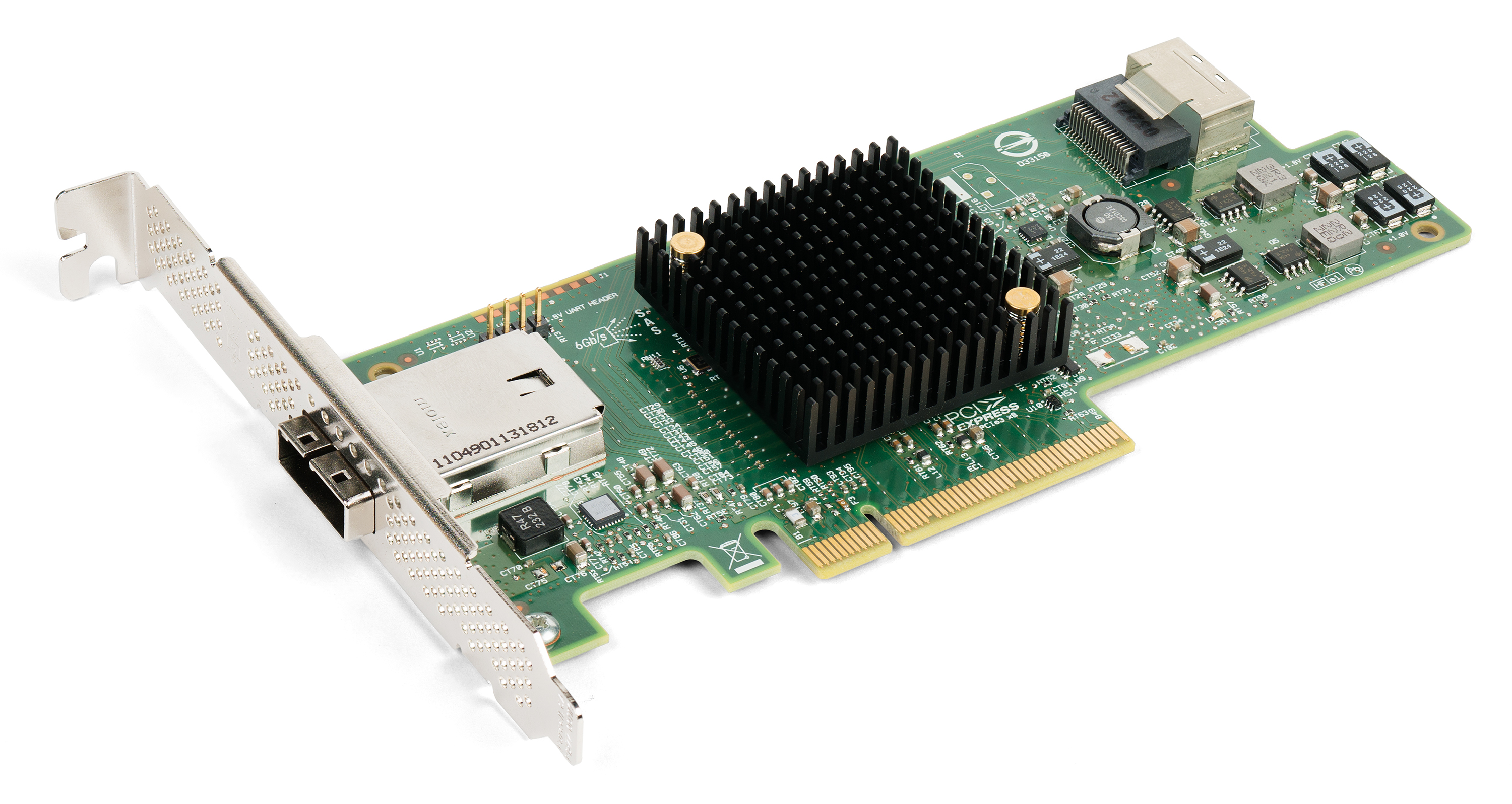
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon Z8
The Nikon Z8 is a high-end full-frame mirrorless camera produced by Nikon. The camera was announced on May 10, 2023. It is the tenth Z-mount camera body and the seventh full-frame Z-mount body. Features The Z8 has the same 45.7 MP stacked CMOS sensor as the Z9, with identical autofocus and video capabilities to the Z9, but in an around 30% smaller body, comparable to that of the D850, but approximately 100 grams lighter. Aircraft (civilian and military) were added to the subject detection autofocus. The camera utilizes an electronic shutter with speeds up to 1/32000 sec and includes 5-axis in-body image stabilization. The battery is the same EN-EL15 series used in the Z5/6/7 and various DSLRs; the much larger EN-EL18 batteries for the Z9 and D4/5/6 DSLRs cannot be used. HEIF was added as a recording format. The magnesium alloy and a new material developed by Teijin give it the same dust and water resistance as the D850. Firmware version 2.0 introduced Auto Capture (automati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NVM Express
NVM Express (NVMe) or Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification (NVMHCIS) is an open, logical-device interface functional specification, specification for accessing a computer's non-volatile storage media usually attached via the PCI Express bus. The initial ''NVM'' stands for ''non-volatile memory'', which is often NAND flash memory that comes in several physical form factors, including solid-state drives (SSDs), PCIe add-in cards, and M.2 cards, the successor to mSATA cards. NVM Express, as a logical-device interface, has been designed to capitalize on the low Hard disk drive performance characteristics#Access time, latency and internal parallelism of solid-state storage devices. Architecturally, the logic for NVMe is physically stored within and executed by the NVMe controller chip that is physically co-located with the storage media, usually an SSD. Version changes for NVMe, e.g., 1.3 to 1.4, are incorporated within the storage media, and do not affect PCIe-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SD Card
Secure Digital (SD) is a proprietary, non-volatile, flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA). Owing to their compact size, SD cards have been widely adopted in a variety of portable consumer electronics, including digital cameras, camcorders, video game consoles, mobile phones, action cameras, and camera drones. The SD format was introduced in August 1999 by SanDisk, Panasonic (then known as Matsushita), and Kioxia (then part of Toshiba). It was designed as a successor to the MultiMediaCard (MMC) format, introducing several improvements aimed at enhancing usability, durability, and performance, which contributed to its rapid emergence as an industry standard. To manage the licensing and intellectual property rights related to the format, the three companies established SD-3C, LLC. In January 2000, they also founded the SDA, a non-profit organization dedicated to developing and promoting SD card standards. As of 2023, the SDA includes approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Flash Storage
Universal Flash Storage (UFS) is a flash storage specification for digital cameras, mobile phones and consumer electronic devices. It was designed to bring higher data transfer speed and increased reliability to flash memory storage, while reducing market confusion and removing the need for different adapters for different types of cards. The standard encompasses both packages permanently embedded (via ball grid array package) within a device (), and removable UFS memory cards. Overview UFS uses NAND flash. It may use multiple stacked 3D TLC NAND flash dies (integrated circuits) with an integrated controller. The proposed flash memory specification is supported by consumer electronics companies such as Nokia, Sony Ericsson, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Samsung, Micron, and SK Hynix. UFS is positioned as a replacement for and SD cards. The electrical interface for UFS uses the M-PHY, developed by the MIPI Alliance, a high-speed serial interface targeting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |