|
Annulenes
Annulenes are cyclic compound, monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds ('wikt:mancude, mancude'). They have the general formula C''n''H''n'' (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd number). The IUPAC nomenclature, IUPAC accepts the use of 'annulene nomenclature' in naming carbocyclic ring systems with 7 or more carbon atoms, using the name '[''n'']annulene' for the mancude hydrocarbon with ''n'' carbon atoms in its ring, though in certain contexts (e.g., discussions of aromaticity for different ring sizes), smaller rings (''n'' = 3 to 6) can also be informally referred to as annulenes. Using this form of nomenclature 1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene is [8]annulene and benzene is [6]annulene (and occasionally referred to as just 'annulene'). The discovery that [18]annulene possesses a number of key properties associated with other aromatic molecules was an important development in the understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclodocosahendecaene
Annulenes are monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds (' mancude'). They have the general formula C''n''H''n'' (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd number). The IUPAC accepts the use of 'annulene nomenclature' in naming carbocyclic ring systems with 7 or more carbon atoms, using the name ' 'n''nnulene' for the mancude hydrocarbon with ''n'' carbon atoms in its ring, though in certain contexts (e.g., discussions of aromaticity for different ring sizes), smaller rings (''n'' = 3 to 6) can also be informally referred to as annulenes. Using this form of nomenclature 1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene is nnulene and benzene is nnulene (and occasionally referred to as just 'annulene'). The discovery that 8nnulene possesses a number of key properties associated with other aromatic molecules was an important development in the understanding of aromaticity as a chemical concept. In the related annul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclododecahexaene
Cyclododecahexaene or [12]annulene () is a member of the series of annulenes with some interest in organic chemistry with regard to the study of aromaticity. Cyclododecahexaene is non-aromatic due to the lack of planarity of the structure. On the other hand the dianion with 14 electrons is a Hückel's rule, aromatic by Hückel's rules and more stable. According to in silico experiments the tri-trans isomer is expected to be the most stable, followed by the 1,7-ditrans and the all cis-isomers (+1 kcal/mol) and by the 1,5-ditrans isomer (+5 kcal/mol). The first [12]annulene with sym-tri-trans configuration was synthesized in 1970 from a tricyclic precursor by photolysis at low temperatures. On heating the compound rearranges to a bicyclic [6.4.0] isomer. Organic reduction, Reducing the compound at low temperatures allowed analysis of the dianion by proton NMR with the inner protons resonating at −4.5 ppm relative to TMS, evidence of an aromatic diamagnetic ring current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclodecapentaene
Cyclodecapentaene or 0nnulene is an annulene with molecular formula C10H10. This organic compound is a conjugated 10 pi electron cyclic system and according to Huckel's rule it should display aromaticity. It is not aromatic, however, because various types of ring strain destabilize an all-planar geometry. Conformation, strain, and non-aromaticity Although not aromatic itself, 0nnulene can transition between different conformational isomers through aromatic or quasiaromatic excited states, such that its conformational isomerism is fixed only at extreme cryogenic temperatures. Understanding the composition and reactivity of these mixtures computationally has proven difficult, because a large number of conformations all minimize the energy locally. The all- ''cis'' isomer ( 1), a fully convex decagon, would have bond angles of 144°, which creates large amounts of angle strain relative t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
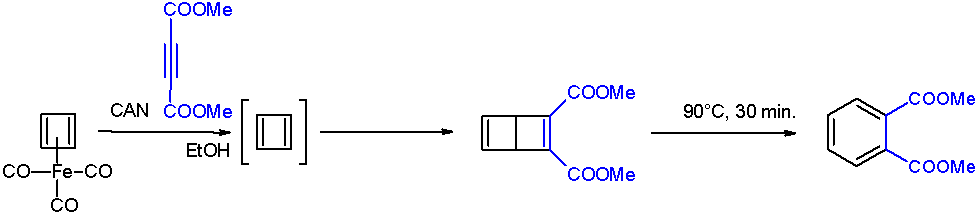
Cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene is an organic compound with the formula . It is very reactive owing to its tendency to dimerize. Although the parent compound has not been isolated, some substituted derivatives are robust and a single molecule of cyclobutadiene is quite stable. Since the compound degrades by a bimolecular process, the species can be observed by matrix isolation techniques at temperatures below 35 K. It is thought to adopt a rectangular structure. Structure and reactivity The compound is the prototypical antiaromatic hydrocarbon with 4 pi electrons (or π electrons). It is the smallest 'n''annulene ( annulene). Its rectangular structure is the result of a pseudo- (or second order) Jahn–Teller effect, which distorts the molecule and lowers its symmetry, converting the triplet to a singlet ground state. The electronic states of cyclobutadiene have been explored with a variety of computational methods. The rectangular structure is consistent with the existence of two different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulyne
In organic chemistry, annulynes or dehydroannulenes are conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds in addition to at least one triple bond. They are related to annulenes, which only have alternating single and double bonds. The smallest member of this class is nnulyne but is never observed because the molecule carries too much angle strain. The next member is nnulyne or benzyne which is a reactive intermediate well known in organic chemistry. nnulyne is known to exist but quickly dimerizes or trimerizes; the compound has been trapped as its radical anion and observed by EPR spectroscopy. 0nnulyne, like nnulyne, only exists in theory. 2nnulyne has been observed in 2005 by Stevenson et al. in solution by NMR spectroscopy at room temperature. Reaction of 1,5-hexadiyne and potassium tert-butoxide was reported to yield two isomers 5,9-di-''trans''- 2annulyne and 3,11-di-''trans''- 2nnulyne in a 1:1 ratio. The proposed reaction sequence in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctadecanonaene
Cyclooctadecanonaene or 8nnulene is an organic compound with chemical formula . It belongs to the class of highly conjugated compounds known as annulenes and is aromatic. The usual isomer that 8nnulene refers to is the most stable one, containing six interior hydrogens and twelve exterior ones, with the nine formal double bonds in the ''cis'',''trans'',''trans'',''cis'',''trans'',''trans'',''cis'',''trans'',''trans'' configuration. It is reported to be a red-brown crystalline solid. Aromaticity Notably, 8nnulene is the first annulene after benzene ( nnulene) to be fully aromatic: its π-system contains 4''n'' + 2 electrons (''n'' = 4), and it is large enough to comfortably accommodate six hydrogen atoms in its interior, allowing it to adopt a planar shape, thus satisfying Hückel's rule. The discovery of aromatic stabilization for 8nnulene is historically significant for confirming earlier theoretical predictions based on molecular orbital theory, since simple versions of vale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotetradecaheptaene
Cyclotetradecaheptaene, often referred to as 4nnulene, is a hydrocarbon with molecular formula C14H14, which played an important role in the development of criteria (Hückel's rule) for aromaticity, a stabilizing property of central importance in physical organic chemistry Physical organic chemistry, a term coined by Louis Hammett in 1940, refers to a discipline of organic chemistry that focuses on the relationship between chemical structures and chemical reaction, reactivity, in particular, applying experimental to .... It forms dark-red needle-like crystals. Structure and aromaticity Although the conjugated ring of 4 nnulene contains 4''n''+2 electrons, it only exhibits limited evidence for being aromatic. It does not fully conform to Hückel's rule because none of its ''cis''/''trans'' isomers can adopt a completely planar conformation due to crowding of the interior hydrogens. There is evidence that it has two isomeric forms of comparable stability (''trans'', ''cis'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulyne
In organic chemistry, annulynes or dehydroannulenes are conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds in addition to at least one triple bond. They are related to annulenes, which only have alternating single and double bonds. The smallest member of this class is nnulyne but is never observed because the molecule carries too much angle strain. The next member is nnulyne or benzyne which is a reactive intermediate well known in organic chemistry. nnulyne is known to exist but quickly dimerizes or trimerizes; the compound has been trapped as its radical anion and observed by EPR spectroscopy. 0nnulyne, like nnulyne, only exists in theory. 2nnulyne has been observed in 2005 by Stevenson et al. in solution by NMR spectroscopy at room temperature. Reaction of 1,5-hexadiyne and potassium tert-butoxide was reported to yield two isomers 5,9-di-''trans''- 2annulyne and 3,11-di-''trans''- 2nnulyne in a 1:1 ratio. The proposed reaction sequence in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as nnulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of its stoichiometric relationship to benzene, COT has been the subject of much research and some controversy. Unlike benzene, C6H6, cyclooctatetraene, C8H8, is not aromatic, although its dianion, ( cyclooctatetraenide), is. Its reactivity is characteristic of an ordinary polyene, i.e. it undergoes addition reactions. Benzene, by contrast, characteristically undergoes substitution reactions, not additions. History 1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene was initially synthesized by Richard Willstätter in Munich in 1905 using pseudopelletierine as the starting material and the Hofmann elimination as the key transformation: : Willstätter noted that the compound did not exhibit the expected aromaticity. Between 1939 and 1943, chemists throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
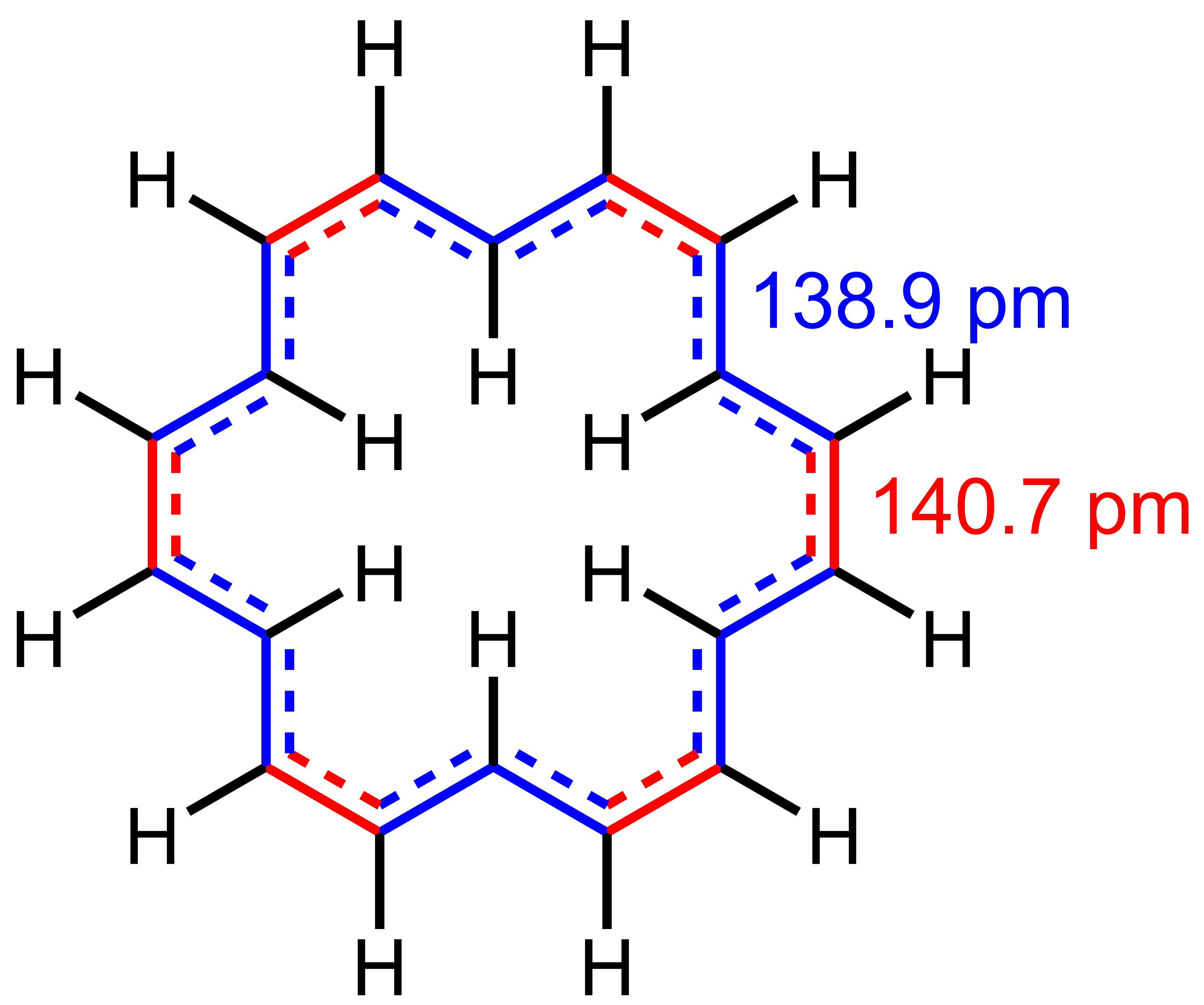
Benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly Combustibility and flammability, flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structures, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major Chemical industry, industrial che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulvenes
Fulvenes are the class of hydrocarbon obtained by formally cross-conjugation, cross-conjugating one Cycloalkane, ring and methylidene through a common exocyclic alkene, double bond. The name is derived from fulvene, which has one pentagonal ring. Other examples include methylenecyclopropene (triafulvene) and heptafulvene. Fulvenes are generally named based on the number of ring atoms. Thus methylenecyclopropene is "triafulvene", methylenecyclopentadiene is "pentafulvene", etc. Preparation Fulvenes are readily prepared by the condensation of cyclopentadiene and aldehydes and ketones: :C5H6 + R2C=O → C4H4C=CR2 + H2O Johannes Thiele (chemist), Johannes Thiele is credited with discovering this reaction. Modern synthesis of fulvenes employ buffer systems. Properties The cross-conjugation generally destabilizes the exocyclic double bond, as (per Hückel's rules) polarization of the π electrons would lead to an aromatic ring ion. Consequently, fulvenes add nucleo- and electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |