Cyclobutadiene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cyclobutadiene is an
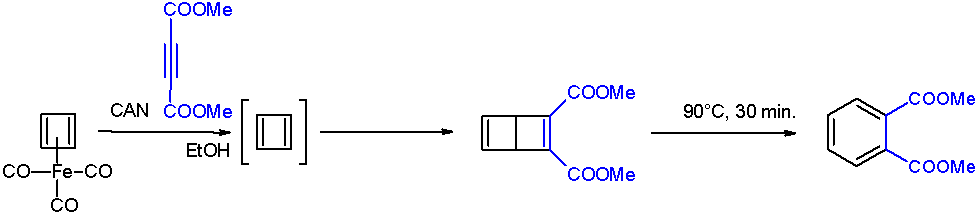 The Dewar benzene converts to dimethyl phthalate on heating at 90 °C.
One cyclobutadiene derivative is also accessible through a +2 ycloaddition of a di-
The Dewar benzene converts to dimethyl phthalate on heating at 90 °C.
One cyclobutadiene derivative is also accessible through a +2 ycloaddition of a di-
organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
with the formula . It is very reactive owing to its tendency to dimerize
In chemistry, dimerization is the process of joining two identical or similar Molecular entity, molecular entities by Chemical bond, bonds. The resulting bonds can be either strong or weak. Many symmetrical chemical species are described as dim ...
. Although the parent compound has not been isolated, some substituted derivatives are robust and a single molecule of cyclobutadiene is quite stable. Since the compound degrades by a bimolecular
In chemistry, molecularity is the number of molecules that come together to react in an elementary reaction, elementary (single-step) reactionAtkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry. Oxford University Press, 2014 and is equal to the sum of Sto ...
process, the species can be observed by matrix isolation techniques at temperatures below 35 K. It is thought to adopt a rectangular structure.
Structure and reactivity
The compound is the prototypical antiaromatic hydrocarbon with 4pi electron
In chemistry, pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent chemical bonds, in each of which two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom, and in which this overlap occurs laterally. Each of these atomic orbitals ...
s (or π electrons). It is the smallest 'n''annulene
Annulenes are monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds (' mancude'). They have the general formula C''n''H''n'' (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd num ...
( annulene). Its rectangular structure is the result of a pseudo- (or second order) Jahn–Teller effect, which distorts the molecule and lowers its symmetry, converting the triplet to a singlet ground state. The electronic states of cyclobutadiene have been explored with a variety of computational methods. The rectangular structure is consistent with the existence of two different 1,2-dideutero-1,3-cyclobutadiene valence isomers. This distortion indicates that the pi electrons are localized, in agreement with Hückel's rule
In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule predicts that a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties if it has 4''n'' + 2 π-electrons, where ''n'' is a non-negative integer. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was f ...
which predicts that a π-system of 4 electrons is not aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugati ...
.
In principle, another situation is possible. Namely, cyclobutadiene could assume an undistorted square geometry, ''if it'' ''adopts a triplet spin state''. In this case the molecule will be aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugati ...
in agreement with Baird's rule
In organic chemistry, Baird's rule estimates whether the lowest triplet state of planar, cyclic structures will have aromatic properties or not. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist N. Colin ...
. While a theoretical possibility, the triplet form of the parent cyclobutadiene and its substituted derivatives remained elusive for decades. However, in 2017, the square triplet excited state of 1,2,3,4-tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)-1,3-cyclobutadiene was observed spectroscopically, and a singlet-triplet gap of ''E''ST = 13.9 kcal/mol (or 0.6 eV per molecule) was measured for this compound.
Synthesis
Several cyclobutadiene derivatives have been isolated with steric bulky substituents. Orange tetrakis ( ''tert''-butyl)cyclobutadiene arises by thermolysis of its isomer tetra-''tert''-butyl tetrahedrane. Although the cyclobutadiene derivative is stable (with respect to dimerization), it decomposes upon contact with .Trapping
Samples of cyclobutadiene are unstable since the compound dimerizes at temperatures above 35 K by a Diels-Alder reaction. By suppressing bimolecular decomposition pathways, cyclobutadiene is well-behaved. Thus it has been generated in a hemicarceplex. Theinclusion compound
Inclusion or Include may refer to:
Sociology
* Social inclusion, action taken to support people of different backgrounds sharing life together.
** Inclusion (disability rights), promotion of people with disabilities sharing various aspects of li ...
is generated by photodecarboxylation of bicyclopyran-2-one. When released from the host–guest complex, cyclobutadiene dimerizes and then converts to cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as nnulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of ...
.
After numerous attempts, cyclobutadiene was first generated by oxidative degradation of cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl
Cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl is an organoiron compound with the formula Fe(C4H4)(CO)3. It is a yellow oil that is soluble in organic solvents. It has been used in organic chemistry as a precursor for cyclobutadiene, which is an elusive species i ...
with ammonium cerium(IV) nitrate. When liberated from the iron complex, cyclobutadiene reacts with electron-deficient alkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and n ...
s to form a Dewar benzene:
: The Dewar benzene converts to dimethyl phthalate on heating at 90 °C.
One cyclobutadiene derivative is also accessible through a +2 ycloaddition of a di-
The Dewar benzene converts to dimethyl phthalate on heating at 90 °C.
One cyclobutadiene derivative is also accessible through a +2 ycloaddition of a di-alkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and n ...
. In this particular reaction, the trapping reagent is ''2,3,4,5-tetraphenylcyclopenta-2,4-dienone'' and one of the final products (after expulsion of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
) is a cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as nnulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of ...
:
:
See also
*Butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two ...
* Cyclobutene
References
Further reading
* {{Annulenes Annulenes Antiaromatic compounds Four-membered rings