|
Burgenland Croats
Burgenland Croats (, , , ) is the name for ethnic Croats in the Austrian state of Burgenland, along with Croats in neighboring Hungary and Slovakia. Around 320,000 residents of Austria identify as of Croat heritage; 56,785 have, as sole or multiple nationality, Croatian citizenship as at 2017. Between 87,000 and 130,000 of them are Burgenland Croats Since 1993, Croatian organizations have appointed their representatives to the Council for National Minorities of the Austrian government. History The to-be Burgenland Croats began to emigrate from Lika, Krbava, Kordun, Banovina, Moslavina and Western Bosnia. These areas were occupied by the Turks (Ottomans) during the Turkish wars (1533–1584). The refugee Croats were given land and independent ecclesiastical rights by the Austrian King Ferdinand I, because many of their villages had been pillaged by the Turks. This gave the Croats a safe place to live while providing Austria with a buffer zone between Vienna and the Ott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgenland In Austria
Burgenland (; hu, Őrvidék; hr, Gradišće; Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland;'' Slovene: ''Gradiščanska'') is the easternmost and least populous state of Austria. It consists of two statutory cities and seven rural districts, with a total of 171 municipalities. It is long from north to south but much narrower from west to east ( wide at Sieggraben). The region is part of the Centrope Project. Geography Burgenland is the third-smallest of Austria's nine states, or ''Bundesländer'', at . The highest point in the province is exactly on the border with Hungary, on the Geschriebenstein, above sea level. The highest point entirely within Burgenland is 879 metres above sea level; the lowest point (which is also the lowest point of Austria) at , is in the municipal area of Apetlon. Burgenland borders the Austrian state of Styria to the southwest, and the state of Lower Austria to the northwest. To the east it borders Hungary ( Vas County and Győr-Moson-Sopron County). In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
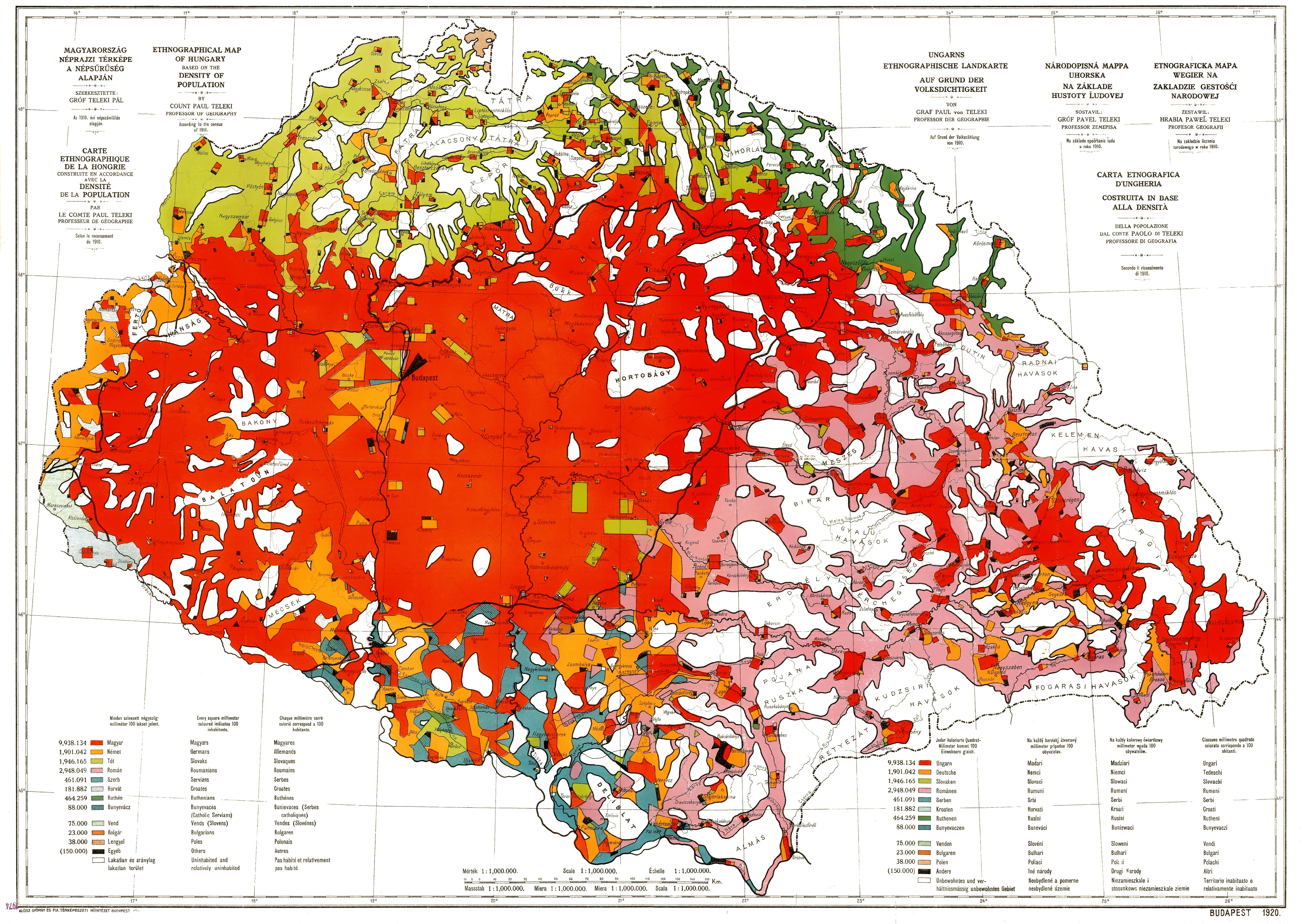
Magyarization
Magyarization ( , also ''Hungarization'', ''Hungarianization''; hu, magyarosítás), after "Magyar"—the Hungarian autonym—was an assimilation or acculturation process by which non-Hungarian nationals living in Austro-Hungarian Transleithania adopted the Hungarian national identity and language in the period between the Compromise of 1867 and Austria-Hungary's dissolution in 1918. Magyarization occurred both voluntarily and as a result of social pressure, and was mandated in certain respects by specific government policies. Before the World War I, only three European countries declared ethnic minority rights, and enacted minority-protecting laws: the first was Hungary (1849 and 1868), the second was Austria (1867), and the third was Belgium (1898). In contrast, the legal systems of other pre-WW1 era European countries did not allow the use of European minority languages in primary schools, in cultural institutions, in offices of public administration and at the legal cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine ( Subcarpathia), central and western Romania ( Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to the Ugric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Monarchy
Dual monarchy occurs when two separate kingdoms are ruled by the same monarch, follow the same foreign policy, exist in a customs union with each other, and have a combined military but are otherwise self-governing. The term is typically used to refer to Austria-Hungary, a dual monarchy that existed from 1867 to 1918 that spanned across parts of Central and Eastern Europe, but applies to other dual monarchies such as the Kingdom of Nejd and Hejaz. Dual monarchy is a fairly rare form of government, and has been practiced few times in history, although many of the world's most powerful countries have been or are dual monarchies. In the 1870s, using the Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary as a model, the Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII) and William Ewart Gladstone proposed that Ireland and Great Britain form a dual monarchy. Their efforts were unsuccessful, but the idea was later used in 1904 by Arthur Griffith in his seminal work, ''The Resurrection of Hungary''. Griffit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) and largely ended with the conclusion of the European wars of religion in 1648. Initiated to address the effects of the Protestant Reformation, the Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort composed of apologetic and polemical documents and ecclesiastical configuration as decreed by the Council of Trent. The last of these included the efforts of Imperial Diets of the Holy Roman Empire, heresy trials and the Inquisition, anti-corruption efforts, spiritual movements, and the founding of new religious orders. Such policies had long-lasting effects in European history with exiles of Protestants continuing until the 1781 Patent of Toleration, although smaller expulsions took place in the 19th century. Such reforms included the found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molise Croats
Molise Croats ( hr, Moliški Hrvati) or Molise Slavs ( it, Slavo-molisani, Slavi del Molise) are a Croat community in the Molise province of Campobasso of Italy, which constitutes the majority in the three villages of Acquaviva Collecroce (''Kruč''), San Felice del Molise (''Štifilić'') and Montemitro (''Mundimitar''). There are about 1,000 active and 2,000 passive speakers of the Slavomolisano dialect. The community originated from Dalmatian refugees fleeing from the Ottoman conquests in the late 15th and 16th centuries. Identity and status The community does not have an ethnonym of their own, but are traditionally accustomed to the term ''Zlava'' and ''Škjavuna'' ("Slavs"). Since 1999 the governments of Italy and Croatia recognize the community as a Croatian minority in Italy. However, the people consider themselves to be Italo-Slavs or Croatian-speaking Italians, and the term "Molise Croat" is a recent exonym rather than their own name for themselves, dating to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro, and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains more than 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of . The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja, Požega-Slavonia, Virovitica-Podravina, and Vukovar-Syrmia, although the territory of the counties includes Baranya, and the definition of the western extent of Slavonia as a region varies. The counties cover or 22.2% of Croatia, inhabited by 806,192—18.8% of Croatia's population. The largest city in the region is Osijek, followed by Slavonski Brod and Vinkovci. Slavonia is located in the Pannonian Basin, largely bordered by the Danube, Drava, and Sava rivers. In the west, the region consists of the Sava and Drava valleys and the mountains surrounding the Požega Valley, and plains in the east. Slavonia enjoys a moderate continental climate with relatively low precipitation. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velika Kapela
The Velika Kapela (; lit. ''Great Chapel'') is a large mountain range in the east of Gorski Kotar, Croatia. The highest peak is Bjelolasica-Kula at 1533 m.a.s.l. It overlooks Velebit, Plješivica, islands Krk, Cres, Lošinj, and the Kvarner Gulf. Velika Kapela belongs to the Dinaric Alps, and it stretches from the Gorski Kotar region in the west, to the Mala Kapela and Lika in the east, from the Ogulin-Plaški valley in the north, to the Vinodol coastline in the south. The area is narrowest mountain prague between continental Pannonia and the coastal Mediterranean. Velika Kapela is mainly composed of karst — limestone rocks. On the Velika Kapela there are many protected areas and landscapes. The famous are White cliffs and Samarske cliffs ( hr, Bijele i Samarske stijene), and Klek above Frankopan town of Ogulin Ogulin () is a town in north-western Croatia, in Karlovac County. It has a population of 7,389 (2021) (it was 8,216 in 2011), and a total municipal populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kupa
The Kupa () or Kolpa ( or ; from la, Colapis in Roman times; hu, Kulpa) river, a right tributary of the Sava, forms a natural border between north-west Croatia and southeast Slovenia. It is long, with its border part having a length of and the rest located in Croatia. Name The name ''Colapis'', recorded in antiquity, is presumed to come from the Proto-Indo-European roots ''*quel-'' 'turn, meander' and ''*ap-'' 'water', meaning 'meandering water'. An alternative interpretation is ''*(s)kel-''/''*skul-'' 'shiny, bright', meaning 'clear river'. Course The Kupa originates in Croatia in the mountainous region of Gorski Kotar, northeast of Rijeka, in the area of Risnjak National Park. It flows a few kilometers eastwards, receives the small Čabranka River from the left, before reaching the Slovenian border. It then continues eastwards between the White Carniola region in the north and Central Croatia in the south. The Kupa receives influx from the river Lahinja from the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |