|
Bodo (genus)
''Bodo'' () is a genus of microscopic kinetoplastids, flagellate excavates first described in 1831 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. Ehrenberg was an evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scient ....Ehrenberg C.G. 1831. Über die Entwicklung und Lebensdauer der Infusionsthiere nebst ferneren Beiträgen zu einer Vergleichung ihrer organischen Systemen. Physikalische Abhandlungen der Königlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin 1-154. The genus is small, as it has recently been redefined to include only four species.Cavalier-Smith, T. 2016. Higher classification and phylogeny of Euglenozoa. European Journal of Protistology 56, 250–276. ''Bodo'' includes free-living, phagotrophic organisms that can be found in many marine and freshwater environments as well as some terrestrial environments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic forms, and also includes some important parasites of humans, including ''Giardia'' and ''Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now obsolete Protista kingdom. They are classified based on their flagellar structures, and they are considered to be the most basal flagellate lineage. Phylogenomic analyses split the members of Excavata into three different and not all closely related groups: Discobids, Metamonads and Malawimonads. Except for Euglenozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic. Characteristics Most excavates are unicellular, heterotrophic flagellates. Only the Euglenozoa are photosynthetic. In some (particularly anaerobic intestinal parasites), the mitochondria have been greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglenozoa
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by three major clades, i.e., Kinetoplastea, Diplonema and Symbiontida. Euglenozoa are unicellular, mostly around in size, although some euglenids get up to long. Structure Most euglenozoa have two flagella, which are inserted parallel to one another in an apical or subapical pocket. In some these are associated with a cytostome or mouth, used to ingest bacteria or other small organisms. This is supported by one of three sets of microtubules that arise from the flagellar bases; the other two support the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the cell. Some other euglenozoa feed through absorption, and many euglenids possess chloroplasts, the only eukaryotes outside Diaphoretickes to do so without performing kleptoplasty, and so obtain energy through photosynthesis. These chloroplasts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetoplastida
Kinetoplastida (or Kinetoplastea, as a class) is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa, and characterised by the presence of an organelle with a large massed DNA called kinetoplast (hence the name). The organisms are commonly referred to as "kinetoplastids" or "kinetoplasts" The group includes a number of parasites responsible for serious diseases in humans and other animals, as well as various forms found in soil and aquatic environments. Their distinguishing feature, the presence of a kinetoplast, is an unusual DNA-containing granule located within the single mitochondrion associated with the base of the cell's flagellum (the basal body). The kinetoplast contains many copies of the mitochondrial genome. The kinetoplastids were first defined by Bronislaw M. Honigberg in 1963 as the members of the flagellated protozoans. They are traditionally divided into the biflagellate Bodonidae and uniflagellate Trypanosomatidae; the former appears to be paraph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodonida
Bodonida is an order of kinetoplastid flagellate excavates. It contains the genera ''Bodo Bodo may refer to: Ethnicity * Boro people, an ethno-linguistic group mainly from Northwest Assam, India * Bodo-Kachari people, an umbrella group from Nepal, India and Bangladesh that includes the Bodo people Culture and language * Boro cu ...'' and '' Rhynchomonas'', relatives to the parasitic trypanosomes. This order also contains the colonial genus '' Cephalothamnium''. Taxonomy Bodonida contains the following suborders and families: * Eubodonina * Neobodonina ** Bodonidae Bütschli, 1887 ** Neobodonidae ** Rhynchomonadidae * Parabodonina ** Cryptobiidae Vickerman ** Parabodonidae Cavalier-Smith References Kinetoplastids Excavata orders {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German Natural history, naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopy, microscopist. Ehrenberg was an Evangelicalism, evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin and became a friend of the famous List of explorers, explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile, Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
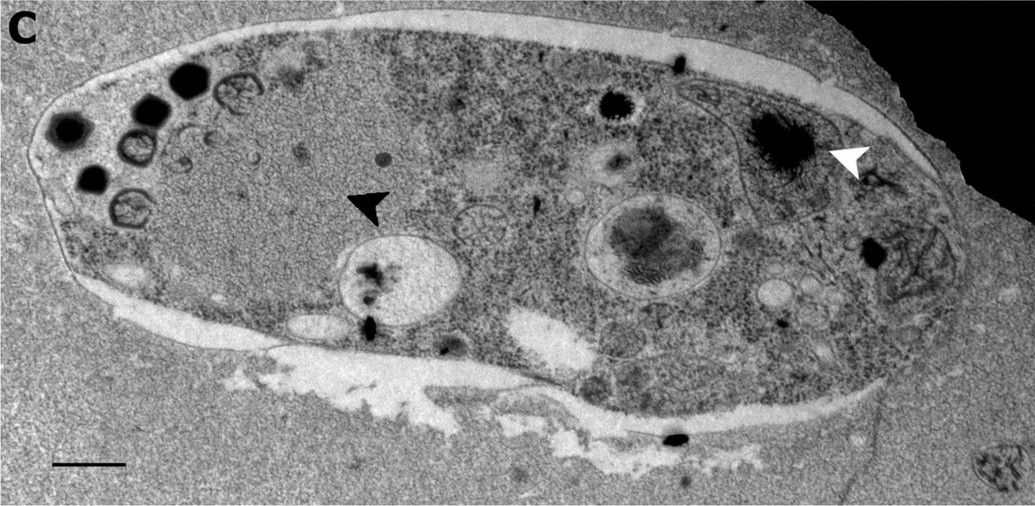
Bodo Saltans
''Bodo saltans'' (alternatively known as ''Pleuromonas jaculans'') is a free-living nonparasitic species of kinetoplastid flagellated phagotrophic protozoa that feed on bacteria. ''Bodo saltans'' cells have been reported in freshwater and marine environments. ''Bodo saltans'' is a single-celled bean-shaped organism 4 to 5 micrometers in length. It has two flagella: a short anterior projecting flagellum and a longer posterior-projecting flagellum without hairs (acronematic) that extends beyond the length of the cell. ''B. saltans'' secures itself to the substrate of its aquatic habitat by the tip of a posterior flagellum. Flexing of the posterior flagellum results in a twitching, jumping movement that is characteristic of this species. This type of movement appears similar to the undulating membrane of the sexually-transmitted pathogen ''Trichomonas vaginalis'' and can result in a false-positive diagnosis in cases where ''B. saltans'' is a contaminant in test samples, especially if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Virus
A giant virus, sometimes referred to as a girus, is a very large virus, some of which are larger than typical bacteria. All known giant viruses belong to the phylum '' Nucleocytoviricota''. Description While the exact criteria as defined in the scientific literature vary, giant viruses are generally described as viruses having large, pseudo- icosahedral capsids (200 to 400 nanometers in diameter) that may be surrounded by a thick (approximately 100 nm) layer of filamentous protein fibers. The viruses have large, double-stranded DNA genomes (300 to >1000 kilobasepairs) that encode a large contingent of genes (of the order of 1000 genes). The best characterized giant viruses are the phylogenetically related mimivirus and megavirus, which belong to the family ''Mimiviridae'' (aka ''Megaviridae''), and are distinguished by their large capsid diameters. Giant viruses from the deep ocean, terrestrial sources, and human patients contain genes encoding cytochrome P450 (CYP; P450) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
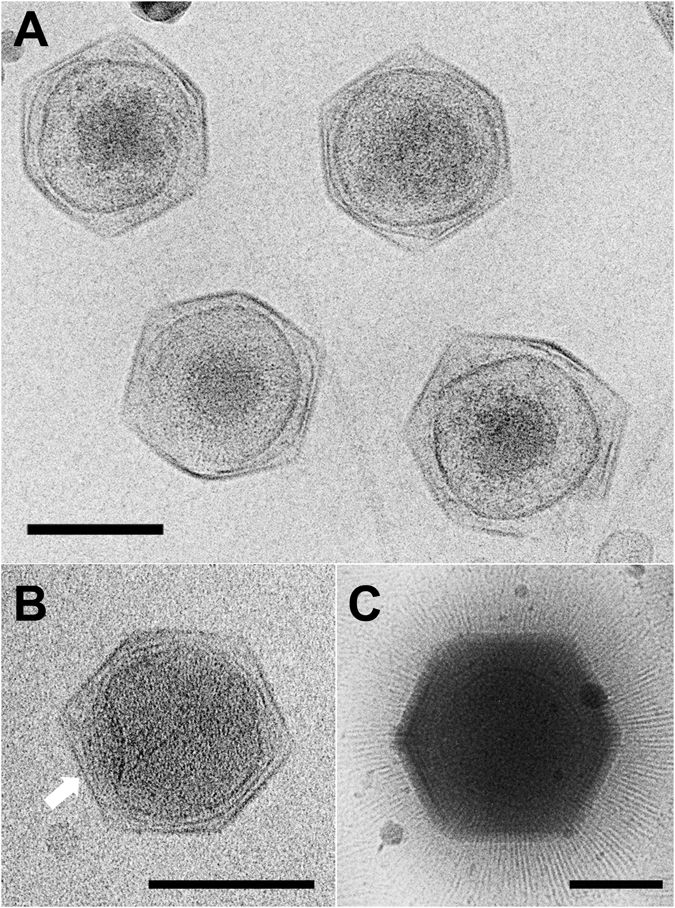
Bodo Saltans Virus
The Bodo saltans virus is a giant virus of the ''Mimiviridae'' family that infects the protozoa ''Bodo saltans''. It has a genome of 1.39 megabases A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DN ..., one of the largest known viral genomes. References Mimiviridae {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigoneme
Mastigonemes are lateral "hairs" that attach to protistan flagella. Flimsy hairs attach to the flagella of euglenid flagellates, while stiff hairs occur in stramenopile and cryptophyte protists.Hoek, C. van den, Mann, D. G. and Jahns, H. M. (1995). Algae : An introduction to phycology', Cambridge University Press, UK. Stramenopile hairs are approximately 15 nm in diameter, and usually consist of flexible basal part that inserts into the cell membrane, a tubular shaft that itself terminates in smaller "hairs". They reverse the thrust caused when a flagellum beats. The consequence is that the cell is drawn into the water and particles of food are drawn to the surface of heterotrophic species. Typology of flagella with hairs: *whiplash flagella (= smooth, acronematic flagella): without hairs but may have extensions , e.g., in Opisthokonta *hairy flagella (= tinsel, flimmer, pleuronematic flagella): with hairs (= mastigonemes ''sensu lato''), divided in: **with fine hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |