|
Bighorn Basin Paleontological Institute
The Elevation Science Institute (ESI), formerly known as the Bighorn Basin Paleontological Institute, is a non-profit 501(c)(3) organization dedicated to paleontology and earth science research, education, and outreach. The organization conducts paleontological field work in the Bighorn Basin of Montana and Wyoming, largely focusing on Vertebrate, vertebrates from the Mesozoic. During the off-season, the ESI is primarily based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, where they work to provide free outreach and education programs in the natural sciences to the public. The ESI is the official scientific and educational partner of Field Station: Dinosaurs. The ESI also operates the Fossil Preparation Lab at the Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University, which serves as the ESI's base of operations for fossil preparation and research. The ESI also works very closely with the Academy to develop and implement educational programming. The Cincinnati Museum Center at Union Terminal, Cincinna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bighorn Basin
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Pryor Mountains on the north, the Bighorn Mountains on the east, and the Owl Creek Mountains and Bridger Mountains on the south. It is drained to the north by tributaries of the Bighorn River, which enters the basin from the south, through a gap between the Owl Creek and Bridger Mountains, as the Wind River, and becomes the Bighorn as it enters the basin. The region is semi-arid, receiving only 6–10 in (15–25 cm) of rain annually. The largest cities in the basin include the Wyoming towns of Cody, Thermopolis, Worland, and Powell. Sugar beets, pinto beans, sunflowers, barley, oats, corn and alfalfa hay are grown on irrigated farms in the region. History The basin was explored by John Colter in 1807. Just west of Cody, he discovered geothermal features that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willwood Formation
The Willwood Formation is a sedimentary sequence deposited during the late Paleocene to early Eocene, or Clarkforkian, Wasatchian and Bridgerian in the NALMA classification.Willwood Formation at .orgNeasham & Vondra, 1972 Description It consists of fine grained clastic rocks ( mudstone and shale) interbedded with medium grained clastic rocks ( sand ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
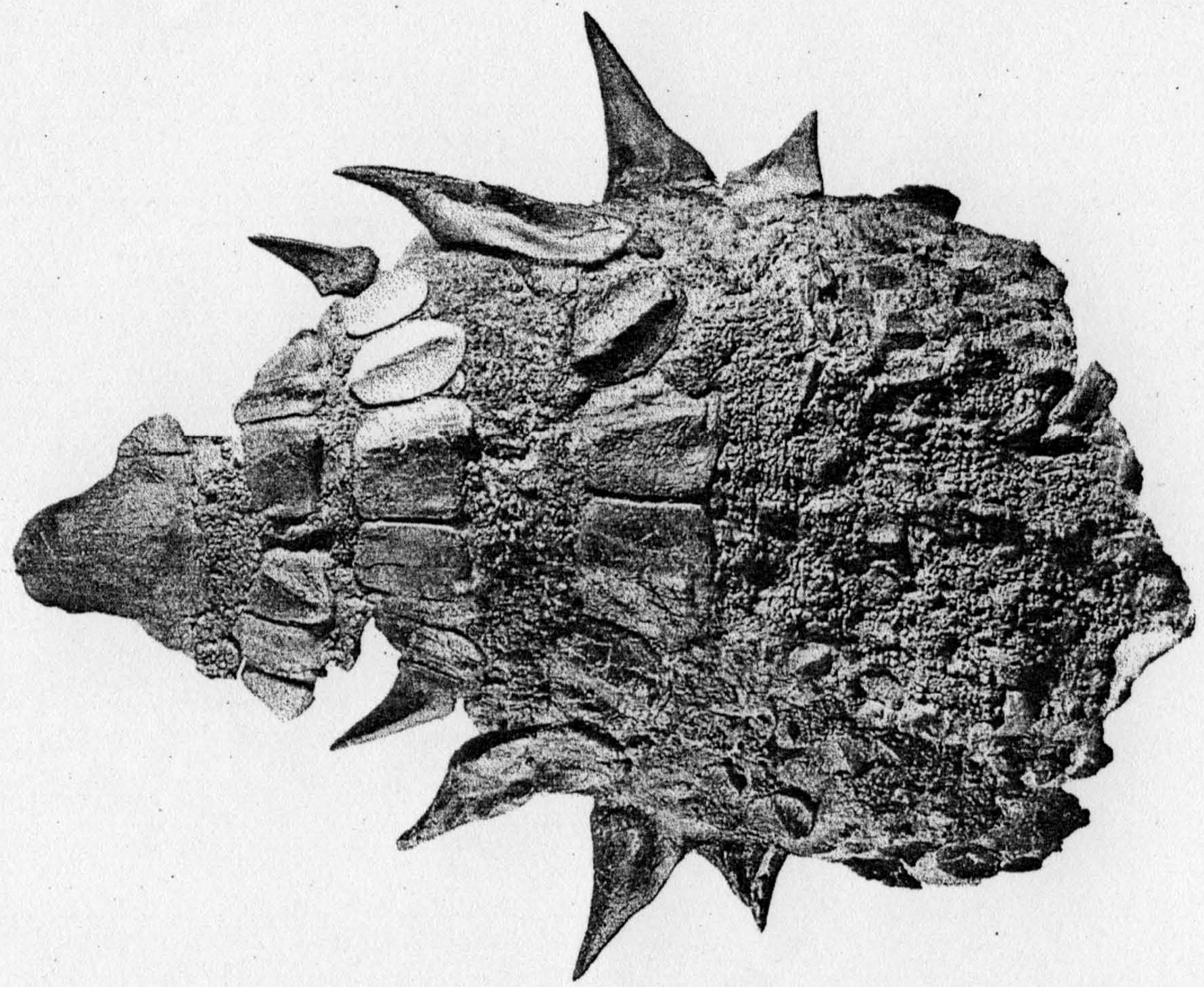
Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Cretaceous Period. The two main families of Ankylosaurs, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae are primarily known from the Northern Hemisphere, but the more basal Parankylosauria are known from southern Gondwana during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group Thyreophora, which also includes the stegosaurs, armored dinosaurs known for their combination of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmontosaurus
''Edmontosaurus'' ( ) (meaning "lizard from Edmonton") is a genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. It contains two known species: ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' and '' Edmontosaurus annectens''. Fossils of ''E. regalis'' have been found in rocks of western North America that date from the late Campanian stage of the Cretaceous Period 73 million years ago, while those of ''E. annectens'' were found in the same geographic region but in rocks dated to the end of the Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous, 66 million years ago. ''Edmontosaurus'' was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs, and lived alongside dinosaurs like ''Triceratops'', ''Tyrannosaurus'', ''Ankylosaurus'', and '' Pachycephalosaurus'' shortly before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. ''Edmontosaurus'' included some of the largest hadrosaurid species, with ''E. annectens'' measuring up to in length and weighing around in average asymptotic body mass, although some individuals would have been larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suuwassea
''Suuwassea'' is a genus of Dicraeosauridae, dicraeosaurid sauropod dinosaur found in the Upper Jurassic strata of the Morrison Formation, located in southern Carbon County, Montana, Carbon County, Montana, United States. The fossil remains were recovered in a series of expeditions during a period spanning the years 1999 and 2000 and were described by J.D. Harris and Peter Dodson in 2004. They consist of a disarticulated but associated partial skeleton, including partial vertebral series and limb bones. Etymology Since the fossil was found in an ancestral territory of the Native Americans in the United States, Native American Crow Nation, Crow tribe, the etymology of the generic name is derived from a term in Crow language, their language, ''suuwassa'', “the first thunder heard in spring”. The root ''suu'', meaning “thunder” and ''wassa'', “ancient”, are a nod to the “thunder lizard” moniker often applied to sauropods. The specific descriptor honours the deceased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptoceratops
''Leptoceratops'' (meaning 'Thin-horned face' and derived from Greek ''lepto-/λεπτο-'' meaning 'small', 'insignificant', 'slender', 'meagre' or 'lean', ''kerat-/κερατ-'' meaning 'horn' and ''-ops/ωψ'' meaning face), is a genus of leptoceratopsid ceratopsian dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous Period (late Maastrichtian age, 68.8-66 Ma ago) of what is now Western North America. Their skulls have been found in Alberta, Canada and Wyoming. Description ''Leptoceratops'' could probably stand and run on their hind legs: analysis of forelimb function indicates that even though they could not pronate their hands, they could walk on four legs. Paul proposed that ''Leptoceratops'' was around long and could have weighed , but Tereschenko proposed a maximum length of . Discovery and species The first small ceratopsian named ''Leptoceratops'' was discovered in 1910 by Barnum Brown in the Red Deer Valley in Alberta, Canada. He described it four years later. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivorous chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one of the last-known non-avian dinosaur genera, and became extinct in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The name ''Triceratops'', which literally means 'three-horned face', is derived from the Greek words () meaning 'three', () meaning 'horn', and () meaning 'face'. Bearing a large bony frill, three horns on the skull, and a large four-legged body, exhibiting convergent evolution with rhinoceroses and bovines, ''Triceratops'' is one of the most recognizable of all dinosaurs and the most well-known ceratopsid. It was also one of the largest, up to long and in body mass. It shared the landscape with and was most likely preyed upon by ''Tyrannosaurus'', though it is less certain that two adults did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' () is a genus of large carnosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic epoch ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian). The name "''Allosaurus''" means "different lizard" alluding to its unique (at the time of its discovery) concave vertebrae. It is derived from the Greek (') ("different, other") and (') ("lizard / generic reptile"). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to this genus were described in 1877 by paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh. As one of the first well-known theropod dinosaurs, it has long attracted attention outside of paleontological circles. ''Allosaurus'' was a large bipedal predator. Its skull was light, robust and equipped with dozens of sharp, serrated teeth. It averaged in length for ''A. fragilis'', with the largest specimens estimated as being long. Relative to the large and powerful hindlimbs, its three-fingered forelimbs were small, and the body was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' is a genus of large theropoda, theropod dinosaur. The species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' (''rex'' meaning "king" in Latin), often called ''T. rex'' or colloquially ''T-Rex'', is one of the best represented theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. ''Tyrannosaurus'' had a much wider range than other Tyrannosauridae, tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of geologic formation, rock formations dating to the Maastrichtian Age (geology), age of the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), period, 68 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids and among the last non-aves, avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Like other tyrannosaurids, ''Tyrannosaurus'' was a bipedal carnivore with a massive skull balanced by a long, heavy tail. Relative to its large and powerful hind limbs, the foreli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplodocus
''Diplodocus'' (, , or ) was a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs, whose fossils were first discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878, is a neo-Latin term derived from Greek διπλός (''diplos'') "double" and δοκός (''dokos'') "beam", in reference to the double-beamed chevron bones located in the underside of the tail, which were then considered unique. The genus of dinosaurs lived in what is now mid-western North America, at the end of the Jurassic period. It is one of the more common dinosaur fossils found in the middle to upper Morrison Formation, between about 154 and 152 million years ago, during the late Kimmeridgian Age. The Morrison Formation records an environment and time dominated by gigantic sauropod dinosaurs, such as ''Apatosaurus'', ''Barosaurus'', '' Brachiosaurus'', '' Brontosaurus'', and '' Camarasaurus''. Its great size may have been a deterrent to the predators '' Allosaurus'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mother's Day Quarry
The Mother's Day Quarry (MDQ) is a Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) fossil site in the Morrison Formation that is located at the base of the Pryor Mountains in Carbon County, Montana. The site was first discovered by the Museum of the Rockies in 1994 and has produced over 2,500 elements since its discovery. Apart from approximately 12 theropod teeth, stegosaur limb material, and two conchostracans found at the site, these elements almost exclusively belong to specimens of the sauropod dinosaur ''Diplodocus'' sp. This deposit of fossils is thought to be the result of an age-segregated herd of these dinosaurs congregating at a limited water source and eventually succumbing to drought conditions. Some debate has arisen regarding the age of the individuals found at the site. Originally the diplodocid specimens from the MDQ were thought to consist solely of juveniles and sub-adults based on the small size of the fossils and the low levels of ossification encountered in these elements. Mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Union Formation
The Fort Union Formation is a geologic unit containing sandstones, shales, and coal beds in Wyoming, Montana, and parts of adjacent states. In the Powder River Basin, it contains important economic deposits of coal, uranium, and coalbed methane. Description The Fort Union is mostly of Paleocene age and represents a time of extensive swamps as well as fluvial and lacustrine conditions. The rocks are more sandy in southwestern Wyoming and more coal-bearing in northeast Wyoming and southeast Montana, reflecting a general change from rivers and lakes in the west to swamps in the east, but all three environments were present at various times in most locations. Coal in the Fort Union in the Powder River Basin occurs mainly in the Tongue River Member, where as many as 32 coal seams total more than 300 feet in thickness. One such bed, the Wyodak Coal near Gillette, Wyoming, is as much as thick. Most of the coals in the Fort Union Formation are ranked subbituminous.''Cretaceous and Ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |