|
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe is a landscape park in Kassel, Germany. The area of the park is , making it the largest European hillside park, and second largest park on a hill slope in the world. Construction of the ''Bergpark'', or "mountain park", began in 1689 at the behest of the Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel and took about 150 years. The park is open to the public today. Since 2013, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its monumental Baroque architecture and its unique fountains and water features. Geography Location , a ''Stadtteil'' of Kassel in northern Hesse, is situated west of the city centre at the foot of the Habichtswald hill range. It is also known for Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe station on the Hanover–Würzburg high-speed railway line. Description The park comprises an area of about , stretching from Kassel up to the Karlsberg mountain at . At the summit of the park stands the Hercules monument, a 40-meter high pyramid with a 8.5-meter bronze statue of Hercul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules Monument (Kassel)
The Hercules monument is a landmark in the German city of Kassel. It is located in the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe (Wilhelmshöhe Mountainpark) in northern Hesse, Germany. ''Hercules'' is a copper statue depicting the ancient Greek demigod Heracles (Gr. Ηρακλής, German Herkules). The statue is located at the top of a pyramid, which stands on top of the octagon; the statue and the other parts of the monument were constructed at different times. Today "Hercules" refers to the whole monument, including the Octagon and Pyramid. The monument is the highest point in the Wilhelmshöhe Bergpark. The monument is located in Bad Wilhelmshöhe, on the Eastern ridge of the Habichtswald. It was built in an artificial dell of the Karlsberg ( above sea level) on the western-most and highest location () of the line of sight Schloss Wilhelmshöhe – Hercules. The Hercules monument and the surrounding Wilhelmshöhe Bergpark were inscribed as a World Heritage Site in 2013, owing to their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the '' Regierungsbezirk'' Schwaben with an impressive Altstadt (historical city centre). Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is the third-largest city in Bavaria (after Munich and Nuremberg) with a population of 300,000 inhabitants, with 885,000 in its metropolitan area. After Neuss, Trier, Cologne and Xanten, Augsburg is one of Germany's oldest cities, founded in 15 BC by the Romans as Augusta Vindelicorum, named after the Roman emperor Augustus. It was a Free Imperial City from 1276 to 1803 and the home of the patrician Fugger and Welser families that dominated European banking in the 16th century. According to Behringer, in the sixteenth century, it became "the dominant centre o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice, Landgrave Of Hesse-Kassel
Maurice of Hesse-Kassel (german: Moritz; 25 May 1572 – 15 March 1632), also called Maurice the Learned or Moritz, was the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel) in the Holy Roman Empire from 1592 to 1627. Life Maurice was born in Kassel as the son of William IV, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, and of his wife Sabine of Württemberg. Although Maurice had been raised in the Lutheran faith, he converted to Calvinism in 1605. On the principle '' Cuius regio eius religio'', Maurice's subjects were also required to convert to Calvinism. Maurice's conversion was controversial since the Peace of Augsburg had only settled religious matters betweens Roman Catholics and Lutherans and had not considered Calvinists. Maurice tried to introduce Calvinism to the lands which he had inherited from the extinct Hesse-Marburg branch of his family. Such a change of faith was contrary to the inheritance rules, and resulted in an ongoing conflict with the Hesse-Darmstadt branch. It also brought him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdschloss
A ''Jagdschloss'' is a hunting lodge in German-speaking countries. It is a '' schloss'' set in a wildlife park or a hunting area (such as a forest, field or by a lake) that served primarily as accommodation for a ruler or aristocrat and his entourage while hunting in the area. Characteristics A ''Jagdschloss'' was often the venue for a banquet accompanying a hunt, and sometimes it also hosted festivals and other events. The term ''Jagdschloss'' is often equated to the '' Lustschloss'' or ''maison de plaisance'', particularly as the hunt was also a recreational activity. However, a ''Lustschloss'' and ''Jagdschloss'' differ in function as well as architecture. The layout and furnishing of a ''Lustschloss'' is unconstrained, while that of a ''Jagdschloss'' is always related to hunting: the walls may be adorned with antlers and other trophies, with scenes of hunting, and also by a deliberate use of wood or other natural materials. A ''Jagdschloss'' could also be very lavishly fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip I, Landgrave Of Hesse
Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse (13 November 1504 – 31 March 1567), nicknamed (in English: "the Magnanimous"), was a German nobleman and champion of the Protestant Reformation, notable for being one of the most important of the early Protestant rulers in Germany. Biography Early life and embracing of Protestantism Philip was the son of Landgrave William II of Hesse and his second wife Anna of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. His father died when Philip was five years old, and in 1514 his mother, after a series of struggles with the Estates of Hesse, succeeded in becoming regent on his behalf. The struggles over authority continued, however. To put an end to them, Philip was declared of age in 1518, his actual assumption of power beginning the following year. The power of the Estates had been broken by his mother, but he owed her little else. His education had been very imperfect, and his moral and religious training had been neglected. Despite all this, he developed rapidly as a state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the '' Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X until January 1521. The Diet of Worms of May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Mainz on the left bank, and Wiesbaden, the capital of the neighbouring state Hesse, on the right bank. Mainz is an independent city with a population of 218,578 (as of 2019) and forms part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region. Mainz was founded by the Romans in the 1st century BC as a military fortress on the northernmost frontier of the empire and provincial capital of Germania Superior. Mainz became an important city in the 8th century AD as part of the Holy Roman Empire, capital of the Electorate of Mainz and seat of the Archbishop-Elector of Mainz, the Primate of Germany. Mainz is famous as the birthplace of Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of a movable-type printing press, who in the early 1450s manufactured his first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canons Regular
Canons regular are priests who live in community under a rule ( and canon in greek) and are generally organised into religious orders, differing from both secular canons and other forms of religious life, such as clerics regular, designated by a partly similar terminology. Preliminary distinctions All canons regular are to be distinguished from secular canons who belong to a resident group of priests but who do not take public vows and are not governed in whatever elements of life they lead in common by a historical Rule. One obvious place where such groups of priests are required is at a cathedral, where there were many Masses to celebrate and the Divine Office to be prayed together in community. Other groups were established at other churches which at some period in their history had been considered major churches, and (often thanks to particular benefactions) also in smaller centres. As a norm, canons regular live together in communities that take public vows. Their ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Landscape Garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a style of " landscape" garden which emerged in England in the early 18th century, and spread across Europe, replacing the more formal, symmetrical French formal garden which had emerged in the 17th century as the principal gardening style of Europe. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. Created and pioneered by William Kent and others, the “informal” garden style originated as a revolt against the architectural garden and drew inspiration from paintings of landscapes by Salvator Rosa, Claude Lorrain, and Nicolas Poussin.Bris, Michel Le. 1981. ''Romantics and Romanticism.'' Skira/Rizzoli International Publications, Inc. New York 1981. 215 pp. age 17Tomam, Rolf, editor. 2000. ''Neoclassicism and Romanticism: Architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
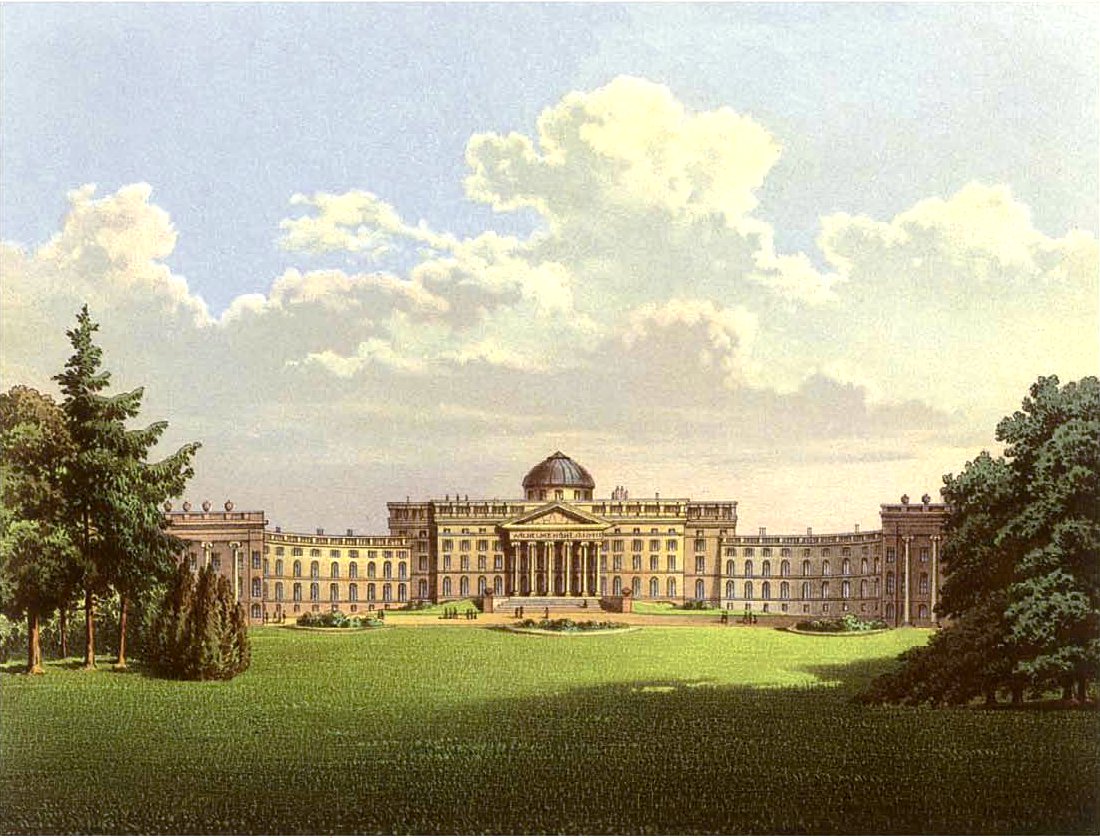
Schloss Wilhelmshöhe
Schloss Wilhelmshöhe is a Neoclassical palace located in , a part of Kassel, Germany. It was built for Landgrave Wilhelm (William) IX of Hesse in the late 18th century. Emperor Wilhelm II made extensive use of it as a summer residence and personal retreat. Today, the palace houses the art gallery Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, part of ''Museumslandschaft Hessen Kassel''. Since 2013, ''Schloss Wilhelmshöhe'' has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site '' Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe'' because of its contribution to Baroque architecture and the outstanding water features that surround the palace. History Beginning in the 12th century the site was used as a monastery. Under Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse 1504-1567 it was secularised and used as a castle. This castle was replaced by a new one from 1606 to 1610 by Landgrave Moritz. The current Neoclassical ''Schloss Wilhelmshöhe'' was designed by architects Simon Louis du Ry and from 1786 to 1798 for Landgrave William IX of Hess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Feature
In landscape architecture and garden design, a water feature is one or more items from a range of fountains, jeux d'eau, pools, ponds, rills, artificial waterfalls, and streams. Before the 18th century they were usually powered by gravity, though the famous Hanging Gardens of Babylon are described by Strabo as supplied by an Archimedean screw and other examples were supplied with water using hydraulic rams. Ancient water features were powered using gravitational forces, human power or animals to pump in the water. Since the 18th century, the majority of water features have been powered by pumps. In the past, the power source was sometimes a steam engine, but in modern features it is almost always powered by electricity. There is an increasing range of innovative designs as the market becomes more established and people become more aware of alternate installation methods, such as solar power. The advantages of using solar power include environmental benefits, no electrical line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


.jpg)