|
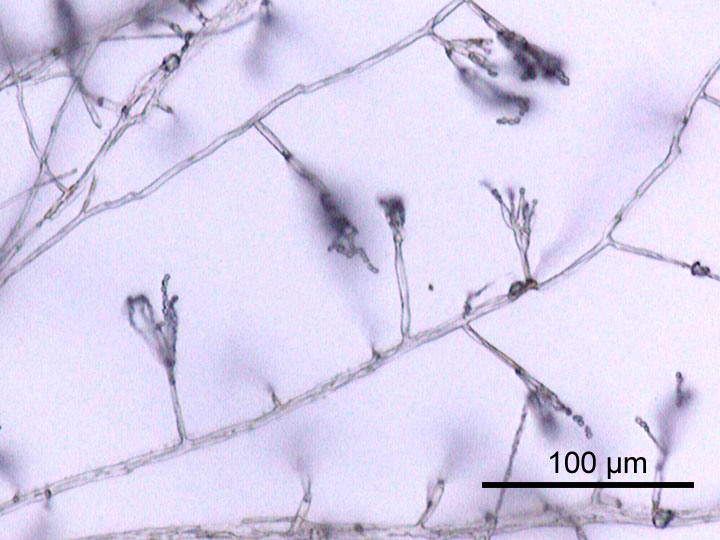
Byssoloma Aptrootii
''Byssoloma'' is a genus of foliicolous lichen, leaf-dwelling lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae. Taxonomy The genus was circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribed by the Italian botanist Vittore Benedetto Antonio Trevisan de Saint-Léon in 1853. Description Species in genus ''Byssoloma'' form crustose lichen, crustose, effuse (spreading) lichens that lack a (outer protective layer). Their , or photosynthesis, photosynthetic partner, is of the type, a form of green algae. The apothecia (fruiting bodies), are (directly attached to the thallus without a stalk) and approximately circular in shape. They lack a (a rim formed by the lichen thallus) and possess a , which is a layer of loosely arranged hyphae that can appear hairy or web-like (-) in some species. The hymenium, the spore-bearing tissue, reacts with iodine to turn blue (I+ blue). The , consisting of paraphyses (filamentous support structures), is unbranched or slightly branched and not or only slightly thickened at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (: cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are o ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byssoloma Subdiscordans 99142347
''Byssoloma'' is a genus of leaf-dwelling lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae. Taxonomy The genus was circumscribed by the Italian botanist Vittore Benedetto Antonio Trevisan de Saint-Léon in 1853. Description Species in genus ''Byssoloma'' form crustose, effuse (spreading) lichens that lack a (outer protective layer). Their , or photosynthetic partner, is of the type, a form of green algae. The apothecia (fruiting bodies), are (directly attached to the thallus without a stalk) and approximately circular in shape. They lack a (a rim formed by the lichen thallus) and possess a , which is a layer of loosely arranged hyphae that can appear hairy or web-like (-) in some species. The hymenium, the spore-bearing tissue, reacts with iodine to turn blue (I+ blue). The , consisting of paraphyses (filamentous support structures), is unbranched or slightly branched and not or only slightly thickened at the tips. The , a layer beneath the hymenium, is dark red-brown and may turn pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Product
Lichen products, also known as lichen substances, are organic compounds produced by a lichen. Specifically, they are secondary metabolites. Lichen products are represented in several different chemical classes, including terpenoids, orcinol derivatives, chromones, xanthones, depsides, and depsidones. Over 800 lichen products of known chemical structure have been reported in the scientific literature, and most of these compounds are exclusively found in lichens. Examples of lichen products include usnic acid (a dibenzofuran), atranorin (a depside), lichexanthone (a xanthone), salazinic acid (a depsidone), and isolichenan, an α-glucan. Many lichen products have biological activity, and research into these effects is ongoing. Biosynthesis Most lichen products are biochemically synthesized via the acetyl-polymalonyl pathway (also known as polyketide pathway), while only a few originate from the mevalonate and shikimate biosynthetic pathways. Occurrence Lichen products accumu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Metabolite
Secondary metabolites, also called ''specialised metabolites'', ''secondary products'', or ''natural products'', are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, archaea, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the normal cell growth, growth, Biological development, development, or reproduction of the organism. Instead, they generally mediate ecological biological interaction, interactions, which may produce a Natural selection, selective advantage for the organism by increasing its survivability or fecundity. Specific secondary metabolites are often restricted to a narrow set of species within a phylogenetic group. Secondary metabolites often play an important role in plant defense against herbivory and other interspecies defenses. Humans use secondary metabolites as medicines, flavourings, pigments, and recreational drugs. The term secondary metabolite was first coined by Albrecht Kossel, the 1910 Nobel Prize laureate for medicine and physio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argopsin
Argopsin, also known as 1-chloropannarin, is a secondary metabolite produced by many lichen species, such as '' Biatora cuprea'' and '' Micarea lignaria''. Argopsin (also known as 1'-chloropannarin) is a chlorinated depsidone compound first isolated from the lichen '' Argopsis friesiana'' by Siegfried Huneck and Elke Mackenzie in 1975. It was independently discovered by both Huneck and Mackenzie's team and by Bodo and Molho in the same year. The structure was confirmed through multiple analytical methods including mass spectrometry, which showed characteristic isotope peaks at mass-to-charge ratios (m/z) of 396, 398, and 400 in a 9:6:1 ratio, indicating the presence of two chlorine atoms. Its UV spectrum matched that of pannarin, and infrared spectroscopy revealed characteristic aldehyde (1725 cm⁻¹) and hydroxyl (3500 cm⁻¹) bands. The researchers synthesized argopsin by chlorinating pannarin in acetic acid, which produced a compound identical to the naturall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
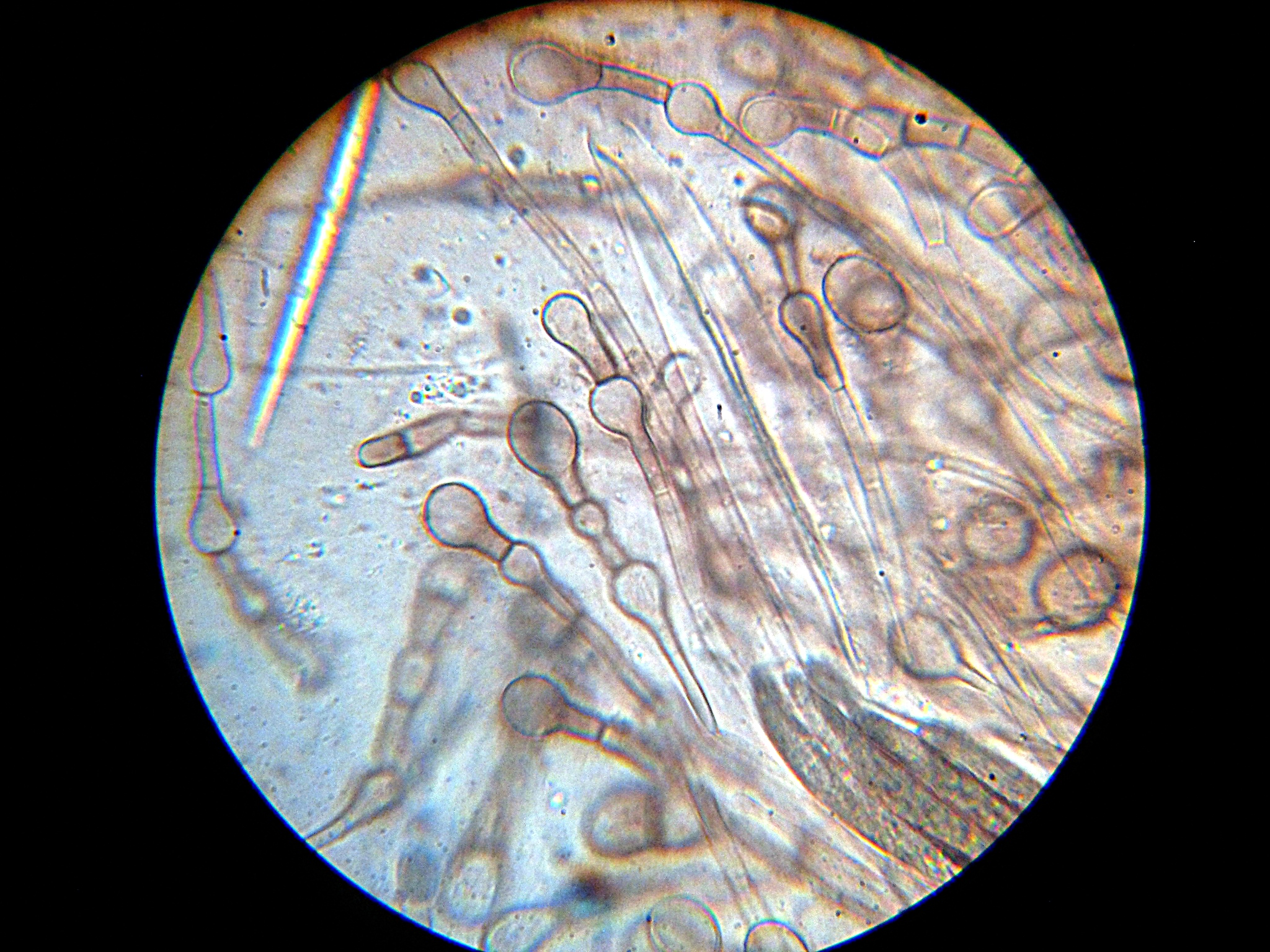
Conidia
A conidium ( ; : conidia), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (: chlamydoconidia), is an asexual, non- motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, ('). They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis. They are produced exogenously. The two new haploid cells are genetically identical to the haploid parent, and can develop into new organisms if conditions are favorable, and serve in biological dispersal. Asexual reproduction in ascomycetes (the phylum Ascomycota) is by the formation of conidia, which are borne on specialized stalks called conidiophores. The morphology of these specialized conidiophores is often distinctive between species and, before the development of molecular techniques at the end of the 20th century, was widely used for identification of (''e.g.'' '' Metarhizium'') species. The terms microconidia and macroconidia are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conidiophore
A conidium ( ; : conidia), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (: chlamydoconidia), is an Asexual reproduction, asexual, non-motility, motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, ('). They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis. They are produced exogenously. The two new haploid cells are genetically identical to the haploid parent, and can develop into new organisms if conditions are favorable, and serve in biological dispersal. Asexual reproduction in ascomycetes (the phylum Ascomycota) is by the formation of conidia, which are borne on specialized stalks called conidiophores. The Morphology (biology), morphology of these specialized conidiophores is often distinctive between species and, before the development of molecular techniques at the end of the 20th century, was widely used for identification of (''e.g.'' ''Metarhizium#Species, Metarh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 μm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnidia
A pycnidium (plural pycnidia) is an asexual fruiting body produced by mitosporic fungi, for instance in the order Sphaeropsidales ( Deuteromycota, Coelomycetes) or order Pleosporales (Ascomycota, Dothideomycetes). It is often spherical or inversely pearshaped ( obpyriform) and its internal cavity is lined with conidiophore A conidium ( ; : conidia), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (: chlamydoconidia), is an Asexual reproduction, asexual, non-motility, motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word f ...s. When ripe, an opening generally appears at the top, through which the pycnidiospores escape. References {{reflist Further reading *Kulik, Martin M. "Symptomless infection, persistence, and production of pycnidia in host and non-host plants by Phomopsis batatae, Phomopsis phaseoli, and Phomopsis sojae, and the taxonomic implications." Mycologia(1984): 274–291. *Calpouzos, L., and D. B. Lapis. "Effects of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum
In biology, a septum (Latin language, Latin for ''something that encloses''; septa) is a wall, dividing a Body cavity, cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate. Examples Human anatomy * Interatrial septum, the wall of tissue that is a sectional part of the left and right atria of the heart * Interventricular septum, the wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart * Lingual septum, a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that separates the halves of the tongue *Nasal septum: the cartilage wall separating the nostrils of the nose * Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli from each other in the lungs * Orbital septum, a palpebral ligament in the upper and lower eyelids * Septum pellucidum or septum lucidum, a thin structure separating two fluid pockets in the brain * Uterine septum, a malformation of the uterus * Septum of the penis, Penile septum, a fibrous w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |